给定一个二叉搜索树,任务是按以下顺序打印 BST 的节点:
- 如果 BST 包含编号为1到N 的级别,则打印顺序为级别1 、级别N 、级别2 、级别N – 1 ,依此类推。
- 顶层顺序 ( 1, 2 , …) 节点从左到右打印,而底层顺序 ( N , N-1 , …) 节点从右到左打印。
例子:
Input:
Output: 27 42 31 19 10 14 35
Explanation:
Level 1 from left to right: 27
Level 3 from right to left: 42 31 19 10
Level 2 from left to right: 14 35
Input: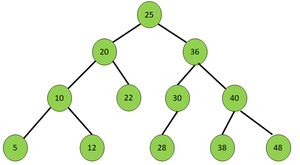
Output: 25 48 38 28 12 5 20 36 40 30 22 10
方法:解决问题的思路是将BST的节点按照级别和节点值的升序和降序存储,并在升序和降序之间交替打印同一级别的所有节点。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个Min Heap和一个Max Heap,分别按照级别和节点值的升序和降序存储节点。
- 对给定的 BST执行层序遍历,将节点存储在各自的优先级队列中。
- 从最小堆和最大堆交替打印每一层的所有节点。
- 如果发现 Min Heap或Max Heap中的任何级别已被打印,则跳到下一个级别。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a BST node
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Utility function to create a new BST node
struct node* newnode(int d)
{
struct node* temp
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = d;
return temp;
}
// Function to print the nodes of a
// BST in Top Level Order and Reversed
// Bottom Level Order alternatively
void printBST(node* root)
{
// Stores the nodes in descending order
// of the level and node values
priority_queue > great;
// Stores the nodes in ascending order
// of the level and node values
priority_queue,
vector >,
greater > >
small;
// Initialize a stack for
// level order traversal
stack > st;
// Push the root of BST
// into the stack
st.push({ root, 1 });
// Perform Level Order Traversal
while (!st.empty()) {
// Extract and pop the node
// from the current level
node* curr = st.top().first;
// Stores level of current node
int level = st.top().second;
st.pop();
// Store in the priority queues
great.push({ level, curr->data });
small.push({ level, curr->data });
// Traverse left subtree
if (curr->left)
st.push({ curr->left, level + 1 });
// Traverse right subtree
if (curr->right)
st.push({ curr->right, level + 1 });
}
// Stores the levels that are printed
unordered_set levelsprinted;
// Print the nodes in the required manner
while (!small.empty() && !great.empty()) {
// Store the top level of traversal
int toplevel = small.top().first;
// If the level is already printed
if (levelsprinted.find(toplevel)
!= levelsprinted.end())
break;
// Otherwise
else
levelsprinted.insert(toplevel);
// Print nodes of same level
while (!small.empty()
&& small.top().first == toplevel) {
cout << small.top().second << " ";
small.pop();
}
// Store the bottom level of traversal
int bottomlevel = great.top().first;
// If the level is already printed
if (levelsprinted.find(bottomlevel)
!= levelsprinted.end()) {
break;
}
else {
levelsprinted.insert(bottomlevel);
}
// Print the nodes of same level
while (!great.empty()
&& great.top().first == bottomlevel) {
cout << great.top().second << " ";
great.pop();
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/*
Given BST
25
/ \
20 36
/ \ / \
10 22 30 40
/ \ / / \
5 12 28 38 48
*/
// Creating the BST
node* root = newnode(25);
root->left = newnode(20);
root->right = newnode(36);
root->left->left = newnode(10);
root->left->right = newnode(22);
root->left->left->left = newnode(5);
root->left->left->right = newnode(12);
root->right->left = newnode(30);
root->right->right = newnode(40);
root->right->left->left = newnode(28);
root->right->right->left = newnode(38);
root->right->right->right = newnode(48);
// Function Call
printBST(root);
return 0;
} 输出:
25 48 38 28 12 5 20 36 40 30 22 10
时间复杂度: O(V log(V)),其中 V 表示给定二叉树中的顶点数
辅助空间: O(V)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。