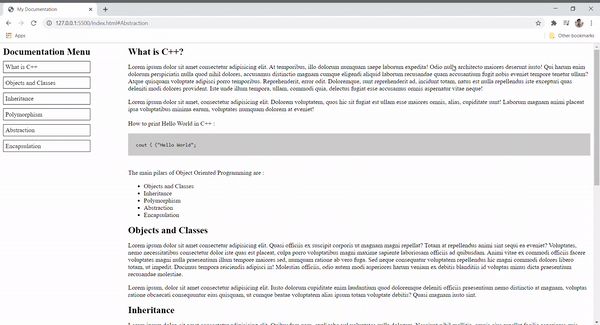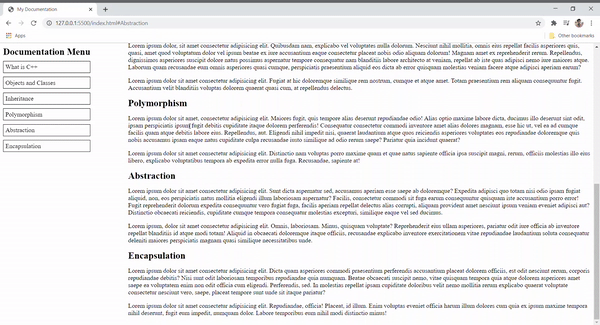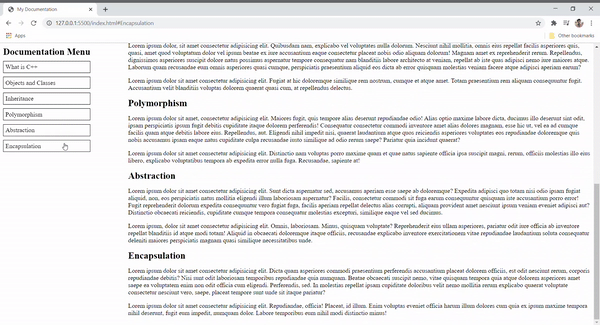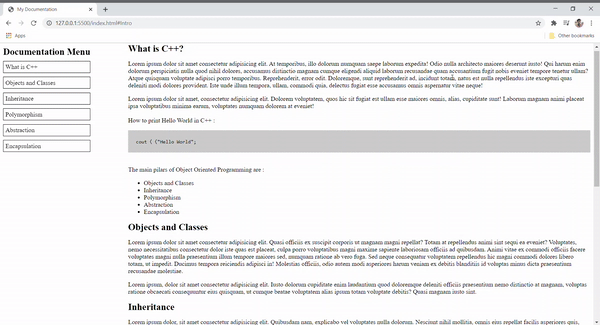
简介 –技术文档是解释相应产品功能的任何文档。在这个项目中,我们将使用 HTML 和 CSS 创建 C++ 的技术文档。该网页有一个菜单部分,可帮助导航到网页的不同部分。
方法 –我们将整个网页分为两个部分。左侧有一个名为“文档菜单”的菜单,其中包含导航栏中列出的所有主题。它包含锚标签,这些标签链接到所有部分的 ID(如继承、多态等)。在右侧,我们对每个主题都有描述。这背后的想法是,一旦用户单击左侧部分中的主题之一,相应的主题详细信息将加载右侧的内容。在 CSS 文件中,我们只是美化文本,如对齐、填充边距等。
执行 –
HTML Code
What is C++?
C++ is a general purpose programming
language and widely used now a days '
for competitive programming. It has
imperative, object-oriented and generic
programming features. C++ runs on lots of
platform like Windows, Linux, Unix, Mac etc.
C++ is an efficient
and powerful language and finds wide use
in various GUI platforms, 3D graphics and
real-time simulations. Because of the
inclusion of rich function libraries,
working in C++ becomes simpler and
convenient than C. Being object-oriented
programming like Java, C++ provides
the support of inheritance, polymorphism,
encapsulation, etc. Unlike C, C++ allows
exception handling and function overloading.
he “Hello World” program is the first
step towards learning any programming
language and also one of the simplest
programs you will learn. All you have
to do is display the message “Hello World”
on the screen.
Let us now look at the program :
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout〈〈"Hello World";
return 0;
}
C++ is an Object Oriented Programming Language.
The main pillars of Object Oriented
Programming are :
- Objects and Classes
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
Objects and Classes
Object-oriented programming – As the name
suggests uses objects in programming.
Object-oriented programming aims to
implement real-world entities like
inheritance, hiding, polymorphism,
etc in programming. The main
aim of OOP is to bind together the data
and the functions that operate on them
so that no other part of the code can
access this data except that function.
Object : An Object is an identifiable
entity with some characteristics and behavior.
An Object is an instance of a Class. When a
class is defined, no memory is allocated but
when it is instantiated (i.e. an
object is created) memory is allocated.
Class : The building block of C++ that
leads to Object-Oriented programming is a Class.
It is a user-defined data type, which holds its
own data members and member functions, which can
be accessed & used by creating an instance
of that class. A class is like a blueprint for
an object. For Example: Consider the Class
of Cars. There may be many cars with different
names and brand but all of them will share
some common properties like all of them will
have 4 wheels, Speed Limit, Mileage range etc.
So here, Car is the class and wheels,
speed limits, mileage are their properties.
Inheritance
The capability of a class to derive
properties and characteristics from
another class is called Inheritance.
Inheritance is one of the most important
feature of Object Oriented Programming.
Sub Class: The class that inherits
properties from another class
is called Sub class or Derived Class.
Super Class: The class whose properties
are inherited by sub class is called Base
Class or Super class. Using inheritance, we
have to write the functions only one time
instead of three times as we
have inherited rest of the three classes
from base class(Vehicle).
Mode of Inheritance :
Public Mode : If we derive a sub
class from a public base class. Then the
public member of the base class will
become public in the derived class and
protected members of the base class
will become protected in derived class.
Protected Mode : If we derive a
sub class from a Protected base class.
Then both public member and protected
members of the base class will become
protected in derived class.
Private Mode : If we derive a
sub class from a Private base class.
Then both public member and protected
members of the base class will become
Private in derived class.
Types of Inheritance in C++ :
Single Inheritance : In single
inheritance, a class is allowed to inherit
from only one class. i.e. one sub class
is inherited by one base class only.
Multiple Inheritance : Multiple
Inheritance is a feature of C++ where a
class can inherit from more than one
classes. i.e one sub class is inherited
from more than one base classes.
Multilevel Inheritance : In this
type of inheritance, a derived class is
created from another derived class.
Hieratical Inheritance : In this
type of inheritance, more than one sub
class is inherited from a single base
class i.e. more than one derived class
is created from a single base class.
Hybrid (Virtual) Inheritance :
Hybrid Inheritance is implemented by
combining more than one type of
inheritance.
For example: Combining Hierarchical
inheritance and Multiple Inheritance.
Polymorphism
The word polymorphism means having many
forms. In simple words, we can define
polymorphism as the ability of a message
to be displayed in more than one form.
A real-life example of polymorphism, a
person at the same time can have
different characteristics.
Like a man at the same time is a father,
a husband, an employee. So the same
person posses different behavior in
different situations. This is called
polymorphism. Polymorphism is considered
as one of the important features of Object
Oriented Programming.
In C++ polymorphism is mainly
divided into two types:
1. Compile time Polymorphism
2. Runtime Polymorphism
Compile time polymorphism: This type of
polymorphism is achieved by function
overloading or operator overloading.
Runtime polymorphism: This type
of polymorphism is achieved by
Function Overriding.
Abstraction
Data abstraction is one of the most
essential and important feature of object
oriented programming in C++. Abstraction
means displaying only essential information
and hiding the details. Data abstraction
refers to providing only essential information
about the data to the outside world,
hiding the background details or implementation.
Consider a real life example of a man driving
a car. The man only knows that pressing the
accelerators will increase the speed of car
or applying brakes will stop the car but he
does not know about how on pressing accelerator
the speed is actually increasing, he does
not know about the inner mechanism of the car
or the implementation of accelerator, brakes
etc in the car. This is what abstraction is.
Abstraction using Classes: We can
implement Abstraction in C++ using classes.
Class helps us to group data members and member
functions using available access specifiers. A
Class can decide which data member will be
visible to outside
world and which is not.
Abstraction in Header files: One
more type of abstraction in C++ can be
header files. For example, consider the
pow() method present in math.h header file.
Whenever we need to calculate power of a
number, we simply call the
function pow() present in the math.h header
file and pass the numbers as arguments
without knowing the underlying algorithm
according to which the function is actually
calculating power of numbers.
Advantages of Data Abstraction:
1. Helps the user to avoid writing
the low level code.
2. Avoids code
duplication and increases reusability.
3. Can change internal implementation of
class independently without
affecting the user.
4. Helps to
increase security of an application or program
as only important details are
provided to the user.
Encapsulation
In normal terms Encapsulation is defined
as wrapping up of data and information
under a single unit. In Object Oriented
Programming, Encapsulation is defined as
binding together the data and the functions
that manipulates them. Consider
a real life example
of encapsulation, in a company there are
different sections like the accounts section,
finance section, sales section etc. The finance
section handles all the financial transactions
and keep records of all the data related to
finance.
Similarly the sales section handles all the
sales related activities and keep records of
all the sales. Now there may arise a situation
when for some reason an official from finance
section needs all the data about sales in a
particular
month. In this case, he is not allowed to
directly access the data of sales section.
He will first have to contact some other
officer in the sales section and then
request him to
give the particular data. This is what
encapsulation is. Here the data of
sales section and the
employees that can manipulate them are
wrapped under a single name “sales section”.
Encapsulation also lead to data abstraction
or hiding. As using encapsulation also hides
the data. In the above example the data of
any of the section like sales, finance or
accounts is hidden from any other section.
In C++ encapsulation
can be implemented using Class
and access modifiers.
CSS Code
div.main-body {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: minmax(300px , auto)1fr;
grid-template-areas: "navbar mainContent";
grid-gap: 20px;
}
nav#navbar {
grid-area: navbar;
position: fixed;
}
nav#navbar a {
display: block;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px 0;
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
}
main#main-doc {
grid-area: mainContent;
}
header {
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
code {
background-color: #CCC;
display: block;
padding: 20px;
}CSS 代码
div.main-body {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: minmax(300px , auto)1fr;
grid-template-areas: "navbar mainContent";
grid-gap: 20px;
}
nav#navbar {
grid-area: navbar;
position: fixed;
}
nav#navbar a {
display: block;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px 0;
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
}
main#main-doc {
grid-area: mainContent;
}
header {
font-size: 1.5rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
code {
background-color: #CCC;
display: block;
padding: 20px;
}
输出: