- python中的二进制搜索(1)
- python 二进制搜索 - Python (1)
- python代码示例中的二进制搜索
- 使二进制搜索树(1)
- 使二进制搜索树
- 使二进制搜索树
- 使二进制搜索树(1)
- 二进制搜索 c++ (1)
- 使二进制搜索树
- 二进制搜索 (1)
- python 二进制搜索 - Python 代码示例
- 二进制搜索 c++ 代码示例
- JavaScript中的二进制搜索
- 二进制搜索 javascript (1)
- JavaScript中的二进制搜索(1)
- 二进制搜索 java (1)
- PHP中的二进制搜索
- PHP中的二进制搜索(1)
- 二进制搜索 javascript 代码示例
- 二进制搜索 - 任何代码示例
- 二进制搜索 java 代码示例
- js 中的二进制搜索 - Javascript (1)
- 线性搜索与二进制搜索
- 线性搜索与二进制搜索(1)
- Scala中的二进制搜索
- Scala中的二进制搜索(1)
- 二进制搜索树|设置1(搜索和插入)
- js 中的二进制搜索 - Javascript 代码示例
- 插值搜索与二进制搜索
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-29 01:11:38 🧑 作者: Mango
Python的二进制搜索
本教程将学习如何使用Python应用二进制搜索算法来查找给定列表中元素的索引位置。
介绍
二进制搜索是一种在列表中查找特定元素的算法。假设我们有一千个元素的列表,并且我们需要获取特定元素的索引位置。使用二进制搜索算法,我们可以很快找到元素的索引位置。
搜索算法很多,但是二进制搜索是其中最受欢迎的算法。
必须对列表中的元素进行排序以应用二进制搜索算法。如果元素未排序,则首先对其进行排序。
让我们了解二进制搜索的概念。
二元搜索的概念
在二元搜索算法中,我们可以使用以下方法找到元素位置。
- 递归方法
- 迭代法
分治法是递归方法。在此方法中,一次又一次调用函数,直到在列表中找到一个元素为止。
一组语句被重复多次,以在迭代方法中找到元素的索引位置。 while循环用于完成此任务。
二进制搜索比线性搜索更有效,因为我们不需要搜索每个列表索引。必须对列表进行排序以实现二进制搜索算法。
让我们逐步执行二进制搜索。
我们有一个排序的元素列表,我们正在寻找索引位置45。
[12、24、32、39、45、50、54]
因此,我们在列表中设置了两个指针。一个指针用于表示较小的值,称为low,第二个指针用于表示较大的值,称为high。
接下来,我们计算数组中中间元素的值。
mid = (low+high)/2
Here, the low is 0 and the high is 7.
mid = (0+7)/2
mid = 3 (Integer)
现在,我们将搜索到的元素与中间索引值进行比较。在这种情况下,32不等于45。因此,我们需要做进一步比较以找到元素。
如果我们搜索的数字等于中位数。然后返回中点,否则移至进一步的比较。
要搜索的数字大于中间数字,我们将n与中间元素右侧的中间元素进行比较,并将low设置为low = mid + 1。
否则,将n与mid左侧的元素的中间元素进行比较,并将high设置为high = mid-1。
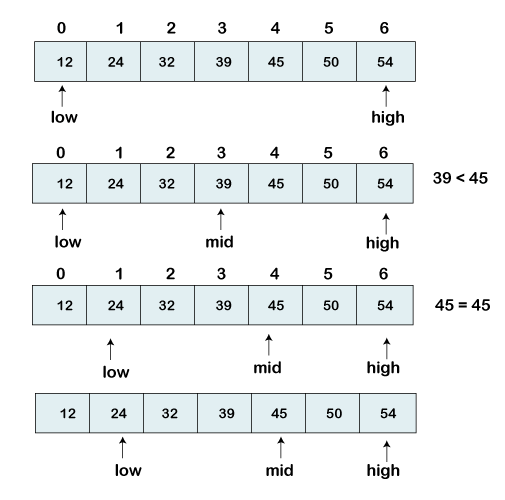
重复直到找到我们要搜索的号码。
在Python实现二进制搜索
首先,我们使用迭代方法实现二进制搜索。我们将重复一组语句并对列表中的每个项目进行迭代。我们将找到中间值,直到搜索完成。
让我们了解以下迭代方法程序。
Python实现
# Iterative Binary Search Function method Python Implementation
# It returns index of n in given list1 if present,
# else returns -1
def binary_search(list1, n):
low = 0
high = len(list1) - 1
mid = 0
while low <= high:
# for get integer result
mid = (high + low) // 2
# Check if n is present at mid
if list1[mid] < n:
low = mid + 1
# If n is greater, compare to the right of mid
elif list1[mid] > n:
high = mid - 1
# If n is smaller, compared to the left of mid
else:
return mid
# element was not present in the list, return -1
return -1
# Initial list1
list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54]
n = 45
# Function call
result = binary_search(list1, n)
if result != -1:
print("Element is present at index", str(result))
else:
print("Element is not present in list1")
输出:
Element is present at index 4
说明:
在以上程序中-
- 我们创建了一个名为binary_search()函数,该函数带有两个参数-要排序的列表和要搜索的数字。
- 我们声明了两个变量来存储列表中的最小值和最大值。将低值分配给初始值0,将高值分配给len(list1) -1,将中值分配为0。
- 接下来,我们声明了while循环,其条件是最低的等于且小于最高的while循环将在未找到数字的情况下进行迭代。
- 在while循环中,我们找到中间值并将索引值与要搜索的数字进行比较。
- 如果中间索引的值小于n ,则将中间值增加1并将其分配给。搜索移到左侧。
- 否则,请减小中值并将其分配给高值。搜索移到右侧。
- 如果n等于中值,则返回mid 。
- 这将一直发生,直到低点等于并且小于高点为止。
- 如果我们到达函数的末尾,则该元素不存在于列表中。我们返回-1到调用函数。
让我们了解二进制搜索的递归方法。
递归二进制搜索
递归方法可用于二进制搜索。在此,我们将定义一个递归函数,该递归函数将不断调用自身直至满足条件。
让我们使用递归函数了解上面的程序。
Python程序
# Python program for recursive binary search.
# Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1
def binary_search(list1, low, high, n):
# Check base case for the recursive function
if low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
# If element is available at the middle itself then return the its index
if list1[mid] == n:
return mid
# If the element is smaller than mid value, then search moves
# left sublist1
elif list1[mid] > n:
return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n)
# Else the search moves to the right sublist1
else:
return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n)
else:
# Element is not available in the list1
return -1
# Test list1ay
list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54]
n = 32
# Function call
res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n)
if res != -1:
print("Element is present at index", str(res))
else:
print("Element is not present in list1")
输出:
Element is present at index 2
说明
上面的程序类似于先前的程序。我们声明了一个递归函数及其基本条件。条件是最小值小于或等于最大值。
- 我们像上一个程序一样计算中间数。
- 我们使用了if语句来进行二进制搜索。
- 如果中间值等于我们要查找的数字,则返回中间值。
- 如果中间值小于该值,则我们正在寻找递归函数binary_search() ,并将中间值增加1并分配给low。
- 如果中间值大于我们正在寻找的值,则再次使用递归函数binary_search()并将中间值减小一并将其分配给low。
在最后一部分,我们编写了主程序。它与先前的程序相同,但唯一的区别是我们在binary_search()函数传递了两个参数。
这是因为我们无法将初始值分配给递归函数的low,high和mid。每次调用递归时,将为这些变量重置值。那会给出错误的结果。
复杂度
在最佳情况下,二分搜索算法的复杂度为O(1)。如果我们要查找的元素在第一次比较中找到,就会发生这种情况。 O(logn)是二分查找中最差且平均的情况。这取决于进行搜索以查找所需元素的次数。
结论
二进制搜索算法是搜索列表中元素的最有效,最快捷的方法。跳过不必要的比较。顾名思义,搜索分为两个部分。它集中在列表的一侧,该列表与我们正在搜索的数字接近。
我们已经讨论了找到给定数字的索引位置的两种方法。