打印二叉树中所有节点的级别
给定一个二叉树和一个键,编写一个函数来打印给定二叉树中所有键的级别。
例如,考虑下面的树。如果输入键是 3,那么你的函数应该返回 1。如果输入键是 4,那么你的函数应该返回 3。对于键中不存在的键,那么你的函数应该返回 0。
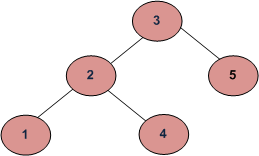
Input:
3
/ \
2 5
/ \
1 4
output:
Level of 1 is 3
Level of 2 is 2
Level of 3 is 1
Level of 4 is 3
Level of 5 is 2我们在下面的帖子中讨论了递归解决方案。
获取二叉树中节点的级别
在这篇文章中,讨论了基于级别顺序遍历的迭代解决方案。我们在遍历时将队列中每个节点的级别与节点一起存储。
C++
// An iterative C++ program to print levels
// of all nodes
#include
using namespace std;
/* A tree node structure */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
void printLevel(struct Node* root)
{
if (!root)
return;
// queue to hold tree node with level
queue > q;
q.push({root, 1}); // let root node be at level 1
pair p;
// Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (!q.empty()) {
p = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << "Level of " << p.first->data
<< " is " << p.second << "\n";
if (p.first->left)
q.push({ p.first->left, p.second + 1 });
if (p.first->right)
q.push({ p.first->right, p.second + 1 });
}
}
/* Utility function to create a new Binary Tree node */
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* temp = new struct Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
/* Driver function to test above functions */
int main()
{
struct Node* root = NULL;
/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */
root = newNode(3);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
printLevel(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print
// levels of all nodes
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Print_Level_Btree {
/* A tree node structure */
static class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
// User defined class Pair to hold
// the node and its level
static class Pair{
Node n;
int i;
Pair(Node n, int i){
this.n = n;
this.i = i;
}
}
// function to print the nodes and
// its corresponding level
static void printLevel(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
// queue to hold tree node with level
Queue q = new LinkedList();
// let root node be at level 1
q.add(new Pair(root, 1));
Pair p;
// Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
p = q.peek();
q.remove();
System.out.println("Level of " + p.n.data +
" is " + p.i);
if (p.n.left != null)
q.add(new Pair(p.n.left, p.i + 1));
if (p.n.right != null)
q.add(new Pair(p.n.right, p.i + 1));
}
}
/* Driver function to test above
functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = null;
/* Constructing tree given in the
above figure */
root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(4);
printLevel(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sumit Ghosh Python3
# Python3 program to print levels
# of all nodes
# Helper function that allocates a new
# node with the given data and None
# left and right pointers.
class newNode:
# Construct to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
def printLevel( root):
if (not root):
return
# queue to hold tree node with level
q = []
# let root node be at level 1
q.append([root, 1])
p = []
# Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (len(q)):
p = q[0]
q.pop(0)
print("Level of", p[0].data, "is", p[1])
if (p[0].left):
q.append([p[0].left, p[1] + 1])
if (p[0].right):
q.append([p[0].right, p[1] + 1 ])
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
Let us create Binary Tree shown
in above example """
root = newNode(3)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(5)
root.left.left = newNode(1)
root.left.right = newNode(4)
printLevel(root)
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Singh(SHUBHAMSINGH10)C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// C# program to print
// levels of all nodes
public class Print_Level_Btree
{
/* A tree node structure */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
// User defined class Pair to hold
// the node and its level
public class Pair
{
public Node n;
public int i;
public Pair(Node n, int i)
{
this.n = n;
this.i = i;
}
}
// function to print the nodes and
// its corresponding level
public static void printLevel(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
// queue to hold tree node with level
LinkedList q = new LinkedList();
// let root node be at level 1
q.AddLast(new Pair(root, 1));
Pair p;
// Do level Order Traversal of tree
while (q.Count > 0)
{
p = q.First.Value;
q.RemoveFirst();
Console.WriteLine("Level of " + p.n.data + " is " + p.i);
if (p.n.left != null)
{
q.AddLast(new Pair(p.n.left, p.i + 1));
}
if (p.n.right != null)
{
q.AddLast(new Pair(p.n.right, p.i + 1));
}
}
}
/* Driver function to test above
functions */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = null;
/* Constructing tree given in the
above figure */
root = new Node(3);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(5);
root.left.left = new Node(1);
root.left.right = new Node(4);
printLevel(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13 Javascript
输出 :
Level of 3 is 1
Level of 2 is 2
Level of 5 is 2
Level of 1 is 3
Level of 4 is 3时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是给定二叉树中的节点数。