Python - 使用 Tkinter 的 MCQ 问答游戏
先决条件: Python GUI – tkinter
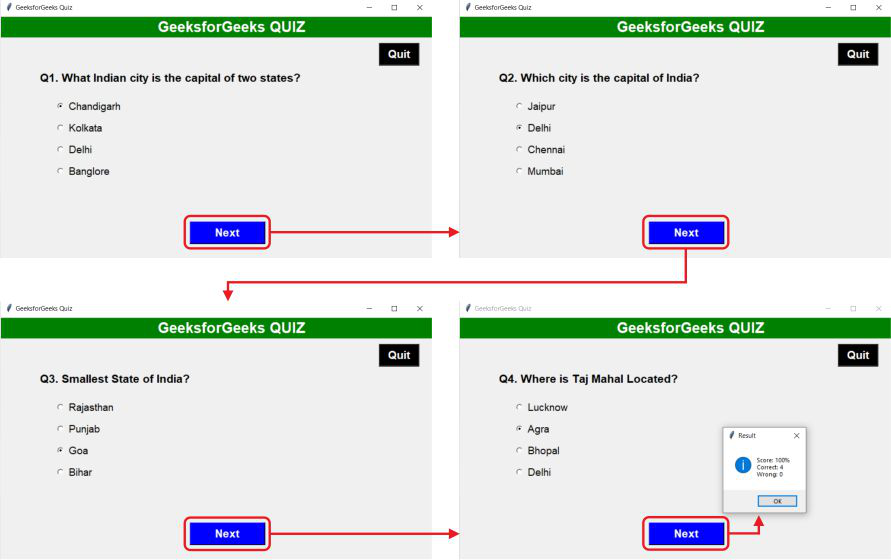
Python提供了一个标准的 GUI 框架 Tkinter,用于开发快速简便的 GUI 应用程序。在这里,我们将使用带有 GUI 的Python开发一个简单的多项选择测验。我们将使用 Tkinter 在Python创建一个多项选择测验。首先,我们将在您喜欢的目录中创建一个名为 Quiz 的库。
概述
需要的步骤
1. 我们将创建 data.json 来存储数据
测验的数据在data.json 中定义,JSON 数据是名称/值对并包含值数组。我们为测验定义了示例数据,如下所示:
{
"question": [
"Q1. What Indian city is the capital of two states?",
"Q2. Which city is the capital of India?",
"Q3. Smallest State of India?",
"Q4. Where is Taj Mahal Located?"
],
"answer": [
1,
2,
3,
2
],
"options": [
["Chandigarh",
"Kolkata",
"Delhi",
"Banglore"
],
["Jaipur",
"Delhi",
"Chennai",
"Mumbai"
],
["Rajasthan",
"Punjab",
"Goa",
"Bihar"
],
["Lucknow",
"Agra",
"Bhopal",
"Delhi"
]
]
}2. 在 quiz.py 中使用 Tkinter 创建 GUI
- 导入模块:tkinter 和 json
- 创建应用程序的主窗口(容器)
- 添加小部件以显示数据
- 为按钮添加功能
- 在测验中使用数据
注意: data.json 和 quiz.py 都将在我们上面定义的同一目录中创建。
现在我们已经创建了用于存储数据的 data.json 文件,我们将创建包含测验程序的quiz.py文件。
Python3
# Python program to create a simple GUI
# Simple Quiz using Tkinter
#import everything from tkinter
from tkinter import *
# and import messagebox as mb from tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox as mb
#import json to use json file for data
import json
#class to define the components of the GUI
class Quiz:
# This is the first method which is called when a
# new object of the class is initialized. This method
# sets the question count to 0. and initialize all the
# other methoods to display the content and make all the
# functionalities available
def __init__(self):
# set question number to 0
self.q_no=0
# assigns ques to the display_question function to update later.
self.display_title()
self.display_question()
# opt_selected holds an integer value which is used for
# selected option in a question.
self.opt_selected=IntVar()
# displaying radio button for the current question and used to
# display options for the current question
self.opts=self.radio_buttons()
# display options for the current question
self.display_options()
# displays the button for next and exit.
self.buttons()
# no of questions
self.data_size=len(question)
# keep a counter of correct answers
self.correct=0
# This method is used to display the result
# It counts the number of correct and wrong answers
# and then display them at the end as a message Box
def display_result(self):
# calculates the wrong count
wrong_count = self.data_size - self.correct
correct = f"Correct: {self.correct}"
wrong = f"Wrong: {wrong_count}"
# calcultaes the percentage of correct answers
score = int(self.correct / self.data_size * 100)
result = f"Score: {score}%"
# Shows a message box to display the result
mb.showinfo("Result", f"{result}\n{correct}\n{wrong}")
# This method checks the Answer after we click on Next.
def check_ans(self, q_no):
# checks for if the selected option is correct
if self.opt_selected.get() == answer[q_no]:
# if the option is correct it return true
return True
# This method is used to check the answer of the
# current question by calling the check_ans and question no.
# if the question is correct it increases the count by 1
# and then increase the question number by 1. If it is last
# question then it calls display result to show the message box.
# otherwise shows next question.
def next_btn(self):
# Check if the answer is correct
if self.check_ans(self.q_no):
# if the answer is correct it increments the correct by 1
self.correct += 1
# Moves to next Question by incrementing the q_no counter
self.q_no += 1
# checks if the q_no size is equal to the data size
if self.q_no==self.data_size:
# if it is correct then it displays the score
self.display_result()
# destroys the GUI
gui.destroy()
else:
# shows the next question
self.display_question()
self.display_options()
# This method shows the two buttons on the screen.
# The first one is the next_button which moves to next question
# It has properties like what text it shows the functionality,
# size, color, and property of text displayed on button. Then it
# mentions where to place the button on the screen. The second
# button is the exit button which is used to close the GUI without
# completing the quiz.
def buttons(self):
# The first button is the Next button to move to the
# next Question
next_button = Button(gui, text="Next",command=self.next_btn,
width=10,bg="blue",fg="white",font=("ariel",16,"bold"))
# palcing the button on the screen
next_button.place(x=350,y=380)
# This is the second button which is used to Quit the GUI
quit_button = Button(gui, text="Quit", command=gui.destroy,
width=5,bg="black", fg="white",font=("ariel",16," bold"))
# placing the Quit button on the screen
quit_button.place(x=700,y=50)
# This method deselect the radio button on the screen
# Then it is used to display the options available for the current
# question which we obtain through the question number and Updates
# each of the options for the current question of the radio button.
def display_options(self):
val=0
# deselecting the options
self.opt_selected.set(0)
# looping over the options to be displayed for the
# text of the radio buttons.
for option in options[self.q_no]:
self.opts[val]['text']=option
val+=1
# This method shows the current Question on the screen
def display_question(self):
# setting the Question properties
q_no = Label(gui, text=question[self.q_no], width=60,
font=( 'ariel' ,16, 'bold' ), anchor= 'w' )
#placing the option on the screen
q_no.place(x=70, y=100)
# This method is used to Display Title
def display_title(self):
# The title to be shown
title = Label(gui, text="GeeksforGeeks QUIZ",
width=50, bg="green",fg="white", font=("ariel", 20, "bold"))
# place of the title
title.place(x=0, y=2)
# This method shows the radio buttons to select the Question
# on the screen at the specified position. It also returns a
# lsit of radio button which are later used to add the options to
# them.
def radio_buttons(self):
# initialize the list with an empty list of options
q_list = []
# position of the first option
y_pos = 150
# adding the options to the list
while len(q_list) < 4:
# setting the radio button properties
radio_btn = Radiobutton(gui,text=" ",variable=self.opt_selected,
value = len(q_list)+1,font = ("ariel",14))
# adding the button to the list
q_list.append(radio_btn)
# placing the button
radio_btn.place(x = 100, y = y_pos)
# incrementing the y-axis position by 40
y_pos += 40
# return the radio buttons
return q_list
# Create a GUI Window
gui = Tk()
# set the size of the GUI Window
gui.geometry("800x450")
# set the title of the Window
gui.title("GeeksforGeeks Quiz")
# get the data from the json file
with open('data.json') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# set the question, options, and answer
question = (data['question'])
options = (data['options'])
answer = (data[ 'answer'])
# create an object of the Quiz Class.
quiz = Quiz()
# Start the GUI
gui.mainloop()
# END OF THE PROGRAM输出: