使用Python的 SQL
在本文中,将讨论 SQLite3 与Python的集成。在这里,我们将讨论使用Python对 SQLite3 数据库进行的所有 CRUD 操作。 CRUD 包含四个主要操作 -

注意:这需要对 SQL 有基本的了解。
在这里,我们将 SQLite 与Python连接起来。 Python有一个名为sqlite3的 SQLite3 本地库。让我们解释一下它是如何工作的。
连接到 SQLite 数据库
- 要使用 SQLite,我们必须导入sqlite3 。
import sqlite3- 然后使用 connect() 方法创建一个连接并传递您要访问的数据库的名称,如果有一个具有该名称的文件,它将打开该文件。否则, Python将创建一个具有给定名称的文件。
sqliteConnection = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')- 在此之后,调用游标对象能够向 SQL 发送命令。
cursor = sqliteConnection.cursor()示例:使用Python连接到 SQLite3 数据库
Python3
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# print statement will execute if there
# are no errors
print("Connected to the database")
# close the connection
connection.close()Python
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# SQL command to create a table in the database
sql_command = """CREATE TABLE emp (
staff_number INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
fname VARCHAR(20),
lname VARCHAR(30),
gender CHAR(1),
joining DATE);"""
# execute the statement
crsr.execute(sql_command)
# close the connection
connection.close()Python3
# Python code to demonstrate table creation and
# insertions with SQL
# importing module
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# SQL command to insert the data in the table
sql_command = """INSERT INTO emp VALUES (23, "Rishabh",\
"Bansal", "M", "2014-03-28");"""
crsr.execute(sql_command)
# another SQL command to insert the data in the table
sql_command = """INSERT INTO emp VALUES (1, "Bill", "Gates",\
"M", "1980-10-28");"""
crsr.execute(sql_command)
# To save the changes in the files. Never skip this.
# If we skip this, nothing will be saved in the database.
connection.commit()
# close the connection
connection.close()Python3
# importing module
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# primary key
pk = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
# Enter 5 students first names
f_name = ['Nikhil', 'Nisha', 'Abhinav', 'Raju', 'Anshul']
# Enter 5 students last names
l_name = ['Aggarwal', 'Rawat', 'Tomar', 'Kumar', 'Aggarwal']
# Enter their gender respectively
gender = ['M', 'F', 'M', 'M', 'F']
# Enter their jpining data respectively
date = ['2019-08-24', '2020-01-01', '2018-05-14', '2015-02-02', '2018-05-14']
for i in range(5):
# This is the q-mark style:
crsr.execute(f'INSERT INTO emp VALUES ({pk[i]}, "{f_name[i]}", "{l_name[i]}", "{gender[i]}", "{date[i]}")')
# To save the changes in the files. Never skip this.
# If we skip this, nothing will be saved in the database.
connection.commit()
# close the connection
connection.close()Python
# importing the module
import sqlite3
# connect withe the myTable database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor object
crsr = connection.cursor()
# execute the command to fetch all the data from the table emp
crsr.execute("SELECT * FROM emp")
# store all the fetched data in the ans variable
ans = crsr.fetchall()
# Since we have already selected all the data entries
# using the "SELECT *" SQL command and stored them in
# the ans variable, all we need to do now is to print
# out the ans variable
for i in ans:
print(i)Python3
# Import module
import sqlite3
# Connecting to sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Updating
cursor.execute('''UPDATE emp SET lname = "Jyoti" WHERE fname="Rishabh";''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()Python3
# Import module
import sqlite3
# Connecting to sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Updating
cursor.execute('''DELETE FROM emp WHERE fname="Rishabh";''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()Python3
# Import module
import sqlite3
# Connecting to sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Updating
cursor.execute('''DROP TABLE Student;''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()输出:
Connected to the database光标对象
在进一步讨论 SQLite3 和Python之前,让我们简要讨论一下游标对象。
- 游标对象用于建立连接以执行 SQL 查询。
- 它充当 SQLite 数据库连接和 SQL 查询之间的中间件。它是在连接到 SQLite 数据库后创建的。
- 游标是一种用于遍历和获取数据库记录的控制结构。
- 所有命令将仅使用游标对象执行。
执行 SQLite3 查询——创建表
连接到数据库并创建游标对象后,让我们看看如何执行查询。
- 要在数据库中执行查询,请创建一个对象并在其中写入带有注释的 SQL 命令。示例:- sql_comm = “SQL 语句”
- 并且执行命令非常容易。调用游标方法execute()并将sql命令的名称作为参数传入其中。将一些命令保存为 sql_comm 并执行它们。执行所有活动后,通过提交这些更改将更改保存在文件中,然后断开连接。
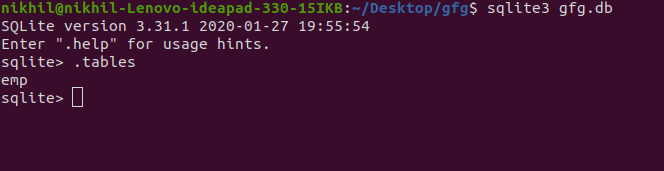
示例:使用Python创建 SQLite3 表
在此示例中,我们将使用Python创建 SQLite3 表。标准 SQL 命令将用于创建表。
Python
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# SQL command to create a table in the database
sql_command = """CREATE TABLE emp (
staff_number INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
fname VARCHAR(20),
lname VARCHAR(30),
gender CHAR(1),
joining DATE);"""
# execute the statement
crsr.execute(sql_command)
# close the connection
connection.close()
输出:
插入表格
要将数据插入表中,我们将再次将 SQL 命令编写为字符串,并将使用 execute() 方法。
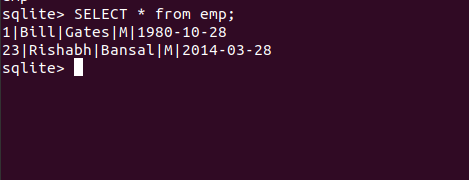
示例 1:使用Python将数据插入 SQLite3 表
Python3
# Python code to demonstrate table creation and
# insertions with SQL
# importing module
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# SQL command to insert the data in the table
sql_command = """INSERT INTO emp VALUES (23, "Rishabh",\
"Bansal", "M", "2014-03-28");"""
crsr.execute(sql_command)
# another SQL command to insert the data in the table
sql_command = """INSERT INTO emp VALUES (1, "Bill", "Gates",\
"M", "1980-10-28");"""
crsr.execute(sql_command)
# To save the changes in the files. Never skip this.
# If we skip this, nothing will be saved in the database.
connection.commit()
# close the connection
connection.close()
输出:
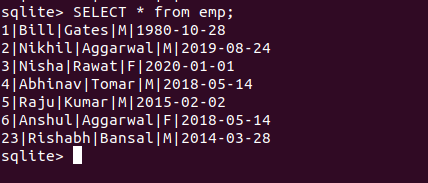
示例 2:插入用户输入的数据
Python3
# importing module
import sqlite3
# connecting to the database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor
crsr = connection.cursor()
# primary key
pk = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
# Enter 5 students first names
f_name = ['Nikhil', 'Nisha', 'Abhinav', 'Raju', 'Anshul']
# Enter 5 students last names
l_name = ['Aggarwal', 'Rawat', 'Tomar', 'Kumar', 'Aggarwal']
# Enter their gender respectively
gender = ['M', 'F', 'M', 'M', 'F']
# Enter their jpining data respectively
date = ['2019-08-24', '2020-01-01', '2018-05-14', '2015-02-02', '2018-05-14']
for i in range(5):
# This is the q-mark style:
crsr.execute(f'INSERT INTO emp VALUES ({pk[i]}, "{f_name[i]}", "{l_name[i]}", "{gender[i]}", "{date[i]}")')
# To save the changes in the files. Never skip this.
# If we skip this, nothing will be saved in the database.
connection.commit()
# close the connection
connection.close()
输出:
获取数据
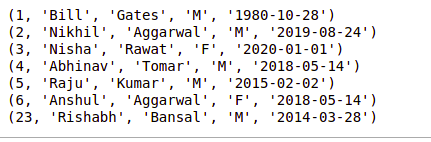
在本节中,我们讨论了如何创建表以及如何在数据库中添加新行。获取数据 from records 就像插入它们一样简单。执行方法使用“Select * from table_name”从表中获取所有数据的SQL命令,所有表数据可以以列表的形式在一个对象中获取。
示例:使用Python从 sqlite3 表中读取数据
Python
# importing the module
import sqlite3
# connect withe the myTable database
connection = sqlite3.connect("gfg.db")
# cursor object
crsr = connection.cursor()
# execute the command to fetch all the data from the table emp
crsr.execute("SELECT * FROM emp")
# store all the fetched data in the ans variable
ans = crsr.fetchall()
# Since we have already selected all the data entries
# using the "SELECT *" SQL command and stored them in
# the ans variable, all we need to do now is to print
# out the ans variable
for i in ans:
print(i)
输出:
注意:需要注意的是,将创建的数据库文件将与Python文件位于同一文件夹中。如果我们希望更改文件的路径,请在打开文件时更改路径。
更新数据
为了更新 SQLite3 表中的数据,我们将使用 UPDATE 语句。我们可以根据我们的要求使用 UPDATE 语句更新单列和多列。
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2,…
WHERE condition; 在上述语法中,SET 语句用于为特定列设置新值,而 WHERE 子句用于选择需要更新列的行。
示例:使用Python更新 SQLite3 表
Python3
# Import module
import sqlite3
# Connecting to sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Updating
cursor.execute('''UPDATE emp SET lname = "Jyoti" WHERE fname="Rishabh";''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
输出:
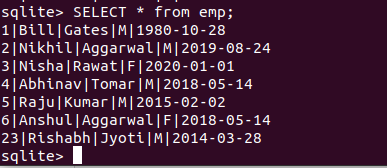
删除数据
要从 SQLite3 表中删除数据,我们可以使用 delete 命令。
DELETE FROM table_name [WHERE Clause]示例:使用Python从 SQLite3 表中删除
Python3
# Import module
import sqlite3
# Connecting to sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Updating
cursor.execute('''DELETE FROM emp WHERE fname="Rishabh";''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
输出:
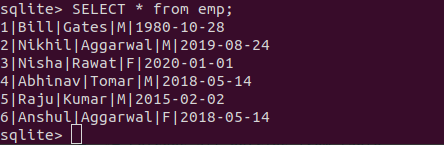
删除表
DROP 用于删除整个数据库或一个表。它删除了表中的两条记录以及表结构。
句法:
DROP TABLE TABLE_NAME;示例:使用Python删除 SQLite3 表
删除前 gfg.db 中的表总数
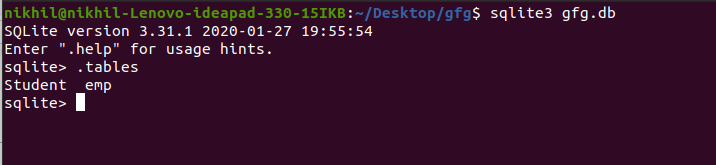
现在让我们删除 Student 表,然后再次检查数据库中的总表。
Python3
# Import module
import sqlite3
# Connecting to sqlite
conn = sqlite3.connect('gfg.db')
# Creating a cursor object using
# the cursor() method
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Updating
cursor.execute('''DROP TABLE Student;''')
# Commit your changes in the database
conn.commit()
# Closing the connection
conn.close()
输出:
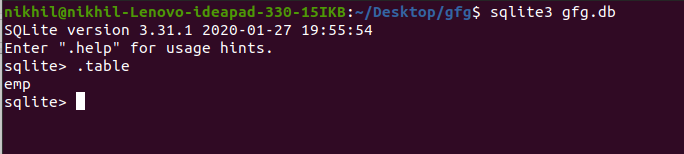
注意:要了解更多关于使用Python的 SQLit3 的信息,请参阅我们的Python SQLite3 教程。