构造一个 DFA 的程序,它接受在所有 'b' 之前具有所有 'a' 的语言
给定一个字符串S ,他的任务是设计一个确定性有限自动机 (DFA)来接受语言L = {a N b M | N≥0,M≥0,N+M≥1} 。 ,即,一种常规语言L ,使得所有“a”都出现在“b”{a,ab,aab,bb…,}的第一次出现之前。如果给定的字符串遵循给定的语言L ,则打印“Accepted” 。否则,打印“不接受” 。
例子
Input: S = “aabbb”
Output: Accepted
Explanation: All the ‘a’ come before ‘b’ s.
Input: S = “ba”
Output: Not Accepted
Explanation: ‘b’ comes before ‘a’.
Input: S = “aaa”
Output: Accepted
Explanation: Note that ‘b’ does not need to occur in S
Input: S = “b”
Output: Accepted
Explanation: Note that ‘a’ does not need to occur in S
处理方法:只有满足以下情况才能接受该问题:
- 所有字符都可以是'a'。
- 所有字符都可以是'b'。
- 所有的“b”都出现在所有的“a”之后。
- 字符串中至少有一个字符。
这可以借助 DFA 的状态转移图更好地可视化
状态转换图:
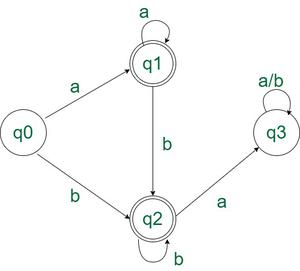
上述DFA的状态转移图
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function for state zero Q0
int startStateQ0(char s) {
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for first state Q1
int firstStateQ1(char s) {
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for second state Q2
int secondStateQ2(char s) {
int state;
if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for third state Q3
int thirdStateQ3(char s) {
int state = 3;
return state;
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
int isAcceptedString(string String) {
int l = String.length();
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
int state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(String[i]);
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(String[i]);
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(String[i]);
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(String[i]);
else
return 0;
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main() {
string String = "ba";
if (isAcceptedString(String))
cout << "ACCEPTED";
else
cout << "NOT ACCEPTED";
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal. Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Function for state zero Q0
static int startStateQ0(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for first state Q1
static int firstStateQ1(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for second state Q2
static int secondStateQ2(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for third state Q3
static int thirdStateQ3(char s)
{
int state = 3;
return state;
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
static int isAcceptedString(String Str)
{
int l = Str.length();
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
int state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(Str.charAt(i));
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(Str.charAt(i));
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(Str.charAt(i));
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(Str.charAt(i));
else
return 0;
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
String Str = "ba";
if (isAcceptedString(Str) != 0)
System.out.println("ACCEPTED");
else
System.out.println("NOT ACCEPTED");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.Python3
# Function for state zero Q0
def startStateQ0(s):
if (s == 'a'):
state = 1
elif (s == 'b'):
state = 2
else:
state = -1
return state
# Function for first state Q1
def firstStateQ1(s):
if (s == 'a'):
state = 1
elif (s == 'b'):
state = 2
else:
state = -1
return state
# Function for second state Q2
def secondStateQ2(s):
if (s == 'b'):
state = 2
elif (s == 'a'):
state = 3
else:
state = -1
return state
# Function for third state Q3
def thirdStateQ3(s):
state = 3
return state
#Function to check
#if the string is accepted or not
def isAcceptedString(String):
l = len(String)
# dfa tells the number associated
# with the present dfa = state
state = 0
for i in range(l):
if (state == 0):
state = startStateQ0(String[i])
elif (state == 1):
state = firstStateQ1(String[i])
elif (state == 2):
state = secondStateQ2(String[i])
elif (state == 3):
state = thirdStateQ3(String[i])
else:
return 0
if(state == 1 or state == 2):
return 1
else:
return 0
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
String = "ba"
if (isAcceptedString(String)):
print("ACCEPTED")
else:
print("NOT ACCEPTED")C#
// C# Program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Function for state zero Q0
static int startStateQ0(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for first state Q1
static int firstStateQ1(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'a')
state = 1;
else if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for second state Q2
static int secondStateQ2(char s)
{
int state;
if (s == 'b')
state = 2;
else if (s == 'a')
state = 3;
else
state = -1;
return state;
}
// Function for third state Q3
static int thirdStateQ3(char s)
{
int state = 3;
return state;
}
// Function to check
// if the string is accepted or not
static int isAcceptedString(string Str)
{
int l = Str.Length;
// dfa tells the number associated
// with the present dfa = state
int state = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (state == 0)
state = startStateQ0(Str[i]);
else if (state == 1)
state = firstStateQ1(Str[i]);
else if (state == 2)
state = secondStateQ2(Str[i]);
else if (state == 3)
state = thirdStateQ3(Str[i]);
else
return 0;
}
if (state == 1 || state == 2)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
public static void Main()
{
string Str = "ba";
if (isAcceptedString(Str) != 0)
Console.Write("ACCEPTED");
else
Console.Write("NOT ACCEPTED");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.Javascript
输出
NOT ACCEPTED时间复杂度: O(N) 其中 N 是字符串的长度
辅助空间: O(1)