MATLAB 语法
在 MATLAB 环境中编写代码非常简单。我们不需要包含任何库/头文件,我们可以直接在编辑器的命令窗口中开始编写命令。通常,我们在命令行窗口中编写小型且易于执行的程序,而在编辑器中编写具有多行和功能的大型程序。
现在,我们将看到 MATLAB 程序的语法。让我们从非常基本的代码开始,以在命令窗口中显示“Hello World”作为输出:
例子:
Matlab
% A MATLAB program illustrate
% disp function
disp("Hello World")Matlab
% Adding two numbers in the
% MATLAB Command Window
15 + 25Matlab
% MATAB code for multiplying two numbers
% in MATLAB Command Window
20 * 5Matlab
% MATLAB code to assign values
% to two variables and display
% their sum (without the use of
% any semicolon)
a=2
b=3
c=a+bMatlab
% MATLAB code to assign values
% to two variables and display
% their sum (with the use of
% semicolon)
a = 2;
b = 3;
c = a+bMatlab
% MATLAB code to disp function %
% (with the use of semicolon) %
disp('Learning with Geeks for Geeks');这里,disp() 是一个函数,用于显示所需的值作为输出。
输出:
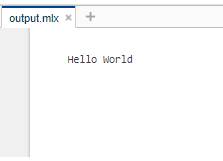
同样,我们可以在命令窗口中执行任何基本操作。让我们来看看其中的一些。
例子 :
MATLAB
% Adding two numbers in the
% MATLAB Command Window
15 + 25
输出 :
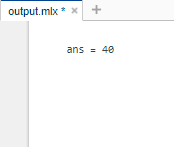
在上面的输出中,' ans'是 MATLAB 中的默认变量,用于存储最近输出的值。此变量仅在生成没有任何特定参数的输出时创建。
例子:
MATLAB
% MATAB code for multiplying two numbers
% in MATLAB Command Window
20 * 5
输出 :
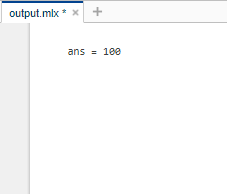
因此,我们可以在 MATLAB 命令窗口中执行各种数学运算。下表总结了可以在 MATLAB 中执行的各种操作及其语法:Sr. No. Operator Operation Sample Input Sample Output 1. + Addition 20 + 30 50 2. – Subtraction 20 – 30 -10 3. * Multiplication 20 × 30 600 4. ^ Exponentiation 2 ^ 3 8 5. \ Left-division operator. 10\5 0.5000 6. / Right-division operator. 10/5 2
在 MATLAB 中声明变量
在 MATLAB 中声明变量相当简单。我们只需要为变量写一个有效的名称,后跟一个等号 ('=')。本文将进一步讨论变量的命名。在 MATLAB 中,我们不需要在声明变量时明确提及变量的类型,
a=7 %declares an integer variable and assigns it the value 7
b=9.81 %declares a float (decimal) variable and assigns it the value 9.81
c = [1,2,3] %declares an array and assigns it the values 1, 2 and 3
d=a = [1,2,3;4,5,6;7,8,9] %declares a 2-D array and assigns it the values 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 and9
在 MATLAB 中命名变量
MATLAB中变量的命名规则如下:
- 变量名必须以字母开头,后面可以跟字母、数字或下划线(不允许使用其他特殊字符)。
- MATLAB 区分大小写,这意味着大写和小写字母被视为不同。 ('GeeksForGeeks' 和 'geeksforgeeks' 被视为单独的变量名称)
- 避免为变量赋予与现有 MATLAB 函数相同的名称。
有效的 MATLAB 变量名称示例
| Valid MATLAB Variable Names |
|---|
| Geeks |
| A_bcd |
| CoDing2001 |
| First_Val |
有效的 MATLAB 变量名称示例
| Variable Name | Cause for Invalidity |
|---|---|
| 7Abc | Variable name should always begin with an alphabet |
| _Geeks | Variable name should always begin with an alphabet |
| end | Variable names should not be the same as already existing MATLAB functions |
| Coding!! | Variable names should not have any special characters except underscore |
MATLAB中分号的使用
与许多编程语言不同,MATLAB 中的每个语句/表达式不一定都以分号结尾。但是,在 MATLAB 中,在语句末尾使用分号来限制语句的结果显示在输出中。
让我们通过几个例子来理解这一点:
例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code to assign values
% to two variables and display
% their sum (without the use of
% any semicolon)
a=2
b=3
c=a+b
输出:
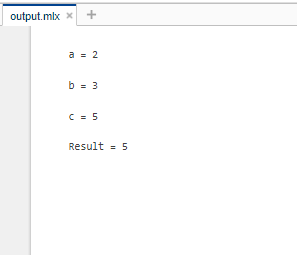
在上面的代码中,虽然我们没有写任何显式的语句来打印存储在变量a、b和c中的值,但是a、b和c的值默认显示为输出。
例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code to assign values
% to two variables and display
% their sum (with the use of
% semicolon)
a = 2;
b = 3;
c = a+b
输出:
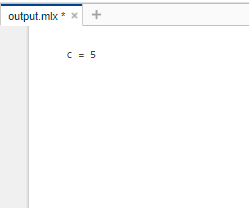
我们可以观察到,这次以分号(a=2; and b=3;)结尾的语句的输出没有显示为输出。因此,可以在 MATLAB 中使用分号来限制语句的结果显示在输出中。
注意:当放在专门用于打印输出的语句末尾时,分号不会限制显示输出。
例子:
MATLAB
% MATLAB code to disp function %
% (with the use of semicolon) %
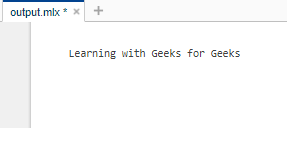
disp('Learning with Geeks for Geeks');
输出:
在 MATLAB 代码中添加注释
向代码添加注释始终被认为是一种很好的做法。注释是在源代码中编写的语句或注释,以使代码更易于人类理解。注释在编译/执行时被简单地忽略。
MATLAB 提供两种类型的注释:
- 单行注释
- 多行注释
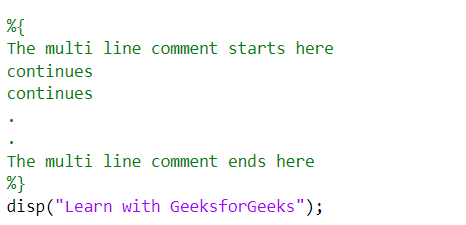
单行注释:它们用“%”(百分号)表示。这意味着注释仅应用于单行,这意味着一行中 '%' 之后的所有内容都是注释,因此不会被执行。

多行注释:它们由 '%{'(百分号和左大括号)和 '%}'(百分号和右大括号)表示。 '%{' 和 '%}' 之间的所有内容都是注释,因此不会执行。
在 MATLAB 中保存工作
要保存 MATLAB 脚本,请转到编辑器选项卡并单击“另存为”,然后为您的脚本提供适当的名称。用 MATLAB 编写的脚本以“.m”扩展名存储。