- C#-异常处理(1)
- 异常处理 (1)
- C++异常处理
- F#-异常处理(1)
- F#异常处理
- C++中的异常处理
- C++中的异常处理(1)
- C#-异常处理
- C++异常处理
- C#异常处理(1)
- C#异常处理
- F#异常处理(1)
- C++中的异常处理
- F#-异常处理
- C#中的异常处理(1)
- C++异常处理(1)
- C#中的异常处理
- 处理异常 (1)
- Python | 异常处理
- Python异常处理(1)
- Python异常处理
- 硒异常处理python(1)
- Python 3-异常处理(1)
- Python异常处理
- Python异常处理
- Python 3-异常处理
- JavaScript中的异常处理(1)
- JavaScript中的异常处理
- 如何处理异常 (1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-18 09:58:45 🧑 作者: Mango
异常是程序执行期间遇到的任何错误情况或意外行为。可能由于多种原因引发异常,其中一些原因如下-
-
您的代码或您调用的代码(例如共享库)中的错误,
-
操作系统资源不可用,
-
公共语言运行时遇到的意外条件(例如无法验证的代码)
句法
异常具有将程序流从一个部分转移到另一个部分的能力。在.NET Framework中,异常处理具有以下四个关键字-
-
try-在此块中,程序标识出引发某些异常的特定条件。
-
catch -catch关键字指示捕获异常。在try块之后是一个或多个catch块,以使用要在程序中处理问题的位置的异常处理程序来捕获异常。
-
最终-最终块用于执行给定的一组语句,无论是否引发异常。例如,如果打开文件,则无论是否引发异常,都必须关闭该文件。
-
throw-问题出现时,程序将引发异常。这是使用throw关键字完成的。
使用这四个关键字的语法如下-
try {
///This will still trigger the exception
}
catch (ExceptionClassName e) {
// error handling code
}
catch (ExceptionClassName e) {
// error handling code
}
catch (ExceptionClassName e) {
// error handling code
}
finally {
// statements to be executed
}
在try块可能会根据程序流的情况引发一个以上异常的情况下,将使用多个catch语句。
层次结构
.NET框架中几乎所有异常类都直接或间接地从Exception类派生。从Exception类派生的最重要的异常类是-
-
ApplicationException类-它支持由程序生成的异常。当开发人员要定义异常时,则应从此类派生类。
-
SystemException类-它是所有预定义的运行时系统异常的基类。以下层次结构显示了运行时提供的标准异常。

下表列出了运行时提供的标准异常以及创建派生类的条件。
| Exception type | Base type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Exception | Object | Base class for all exceptions. |
| SystemException | Exception | Base class for all runtime-generated errors. |
| IndexOutOfRangeException | SystemException | Thrown by the runtime only when an array is indexed improperly. |
| NullReferenceException | SystemException | Thrown by the runtime only when a null object is referenced. |
| AccessViolationException | SystemException | Thrown by the runtime only when invalid memory is accessed. |
| InvalidOperationException | SystemException | Thrown by methods when in an invalid state. |
| ArgumentException | SystemException | Base class for all argument exceptions. |
| ArgumentNullException | ArgumentException | Thrown by methods that do not allow an argument to be null. |
| ArgumentOutOfRangeException | ArgumentException | Thrown by methods that verify that arguments are in a given range. |
| ExternalException | SystemException | Base class for exceptions that occur or are targeted at environments outside the runtime. |
| SEHException | ExternalException | Exception encapsulating Win32 structured exception handling information. |
例
让我们举一个简单的例子来更好地理解这个概念。首先创建一个名为WPFExceptionHandling的新WPF项目。
将一个文本框从工具箱拖到设计窗口。以下XAML代码创建一个文本框,并使用一些属性对其进行初始化。
这是C#中带有异常处理的文件读取。
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows;
namespace WPFExceptionHandling {
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
ReadFile(0);
}
void ReadFile(int index) {
string path = @"D:\Test.txt";
StreamReader file = new StreamReader(path);
char[] buffer = new char[80];
try {
file.ReadBlock(buffer, index, buffer.Length);
string str = new string(buffer);
str.Trim();
textBox.Text = str;
}
catch (Exception e) {
MessageBox.Show("Error reading from "+ path + "\nMessage = "+ e.Message);
}
finally {
if (file != null) {
file.Close();
}
}
}
}
}
当您编译并执行上述代码时,它将产生以下窗口,其中在文本框中显示文本。
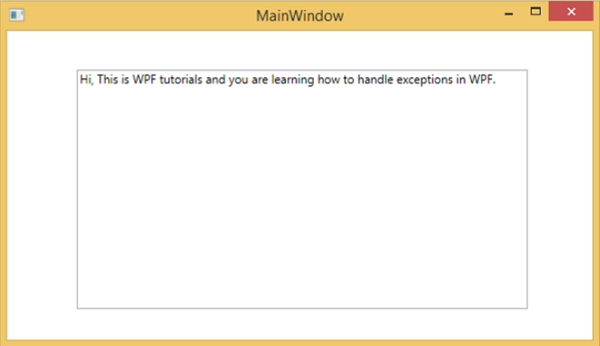
当引发异常或手动将其抛出时(如以下代码所示),它将显示一个带有错误的消息框。
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows;
namespace WPFExceptionHandling {
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
ReadFile(0);
}
void ReadFile(int index) {
string path = @"D:\Test.txt";
StreamReader file = new StreamReader(path);
char[] buffer = new char[80];
try {
file.ReadBlock(buffer, index, buffer.Length);
string str = new string(buffer);
throw new Exception();
str.Trim();
textBox.Text = str;
}
catch (Exception e) {
MessageBox.Show("Error reading from "+ path + "\nMessage = "+ e.Message);
}
finally {
if (file != null) {
file.Close();
}
}
}
}
}
当执行上述代码时引发异常时,它将显示以下消息。
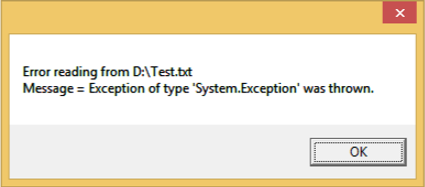
我们建议您执行上述代码并尝试其功能。