使用 Keras 和 Tensorflow 构建辅助 GAN
先决条件:生成对抗网络
本文将演示如何使用 Keras 和 TensorFlow 库构建辅助生成对抗网络。使用的数据集是预加载到 Keras 中的MNIST Image 数据集。
第 1 步:设置环境
Step 1 : Open Anaconda prompt in Administrator mode.
Step 2 : Create a virtual environment using the command : conda create --name acgan python=3.7
Step 3 : Then, activate the environment using the command : conda activate acgan
Step 4 : Install the following libraries -
4.1 - Tensorflow --> pip install tensorflow==2.1
4.2 - Keras --> pip install keras==2.3.1 第 2 步:导入所需的库
Python3
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply
from keras.layers.convolutional import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as npPython3
# Defining the Input shape
image_shape = (28, 28, 1)
classes = 10
latent_dim = 100
# Defining the optimizer and the losses
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
losses = ['binary_crossentropy','sparse_categorical_crossentropy']Python3
def build_generator():
model = Sequential()
# Building the input layer
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.82))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3,3), padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.82))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3,3), padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.82))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(Conv2D(1, (3,3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
# Generating the output image
noise = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
z = Flatten()(Embedding(classes, latent_dim)(label))
model_input = multiply([noise, z])
image = model(model_input)
return Model([noise, label], image)Python3
def build_discriminator():
model = Sequential()
# Building the input layer
model.add(Conv2D(16, (3,3), strides=2, input_shape=image_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, (3,3), strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3,3), strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3,3), strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
image = Input(shape=image_shape)
# Extract features from images
features = model(image)
# Building the output layer
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(features)
label = Dense(classes, activation="softmax")(features)
return Model(image, [validity, label])Python3
def display_images():
r = 10
c = 10
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c,latent_dim))
new_labels = np.array([num for _ in range(r) for num in range(c)])
gen_images = generator.predict([noise, new_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_images = 0.5 * gen_images + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
count = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_images[count,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
count += 1
plt.show()
plt.close()Python3
def train_acgan(epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X, y), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Configure inputs
X = X.astype(np.float32)
X = (X - 127.5) / 127.5
X = np.expand_dims(X, axis=3)
y = y.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Select a random batch of images
index = np.random.randint(0, X.shape[0], batch_size)
images = X[index]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, latent_dim))
# The labels of the digits that the generator tries to create an
# image representation of
new_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, (batch_size, 1))
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_images = generator.predict([noise, new_labels])
image_labels = y[index]
# Training the discriminator
disc_loss_real = discriminator.train_on_batch(
images, [valid, image_labels])
disc_loss_fake = discriminator.train_on_batch(
gen_images, [fake, new_labels])
disc_loss = 0.5 * np.add(disc_loss_real, disc_loss_fake)
# Training the generator
gen_loss = combined.train_on_batch(
[noise, new_labels], [valid, new_labels])
# Print the accuracies
print ("%d [acc.: %.2f%%, op_acc: %.2f%%]" % (
epoch, 100 * disc_loss[3], 100 * disc_loss[4]))
# display at every defined epoch interval
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
display_images()Python3
# Build and compile the discriminator
discriminator = build_discriminator()
discriminator.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
generator = build_generator()
# Defining the input for the generator
#and generating the images
noise = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
image = generator([noise, label])
# Disable the Discriminator
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes in the generated image
# as input and determines validity
# and the label of that image
valid, target_label = discriminator(image)
# The combined model (both generator and discriminator)
# Training the generator to fool the discriminator
combined = Model([noise, label], [valid, target_label])
combined.compile(loss=losses, optimizer=optimizer)
train_acgan(epochs=14000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=2000)第 3 步:定义要在后续流程中使用的参数
蟒蛇3
# Defining the Input shape
image_shape = (28, 28, 1)
classes = 10
latent_dim = 100
# Defining the optimizer and the losses
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
losses = ['binary_crossentropy','sparse_categorical_crossentropy']
第 4 步:定义一个效用函数来构建生成器
蟒蛇3
def build_generator():
model = Sequential()
# Building the input layer
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.82))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3,3), padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.82))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3,3), padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.82))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(Conv2D(1, (3,3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
# Generating the output image
noise = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
z = Flatten()(Embedding(classes, latent_dim)(label))
model_input = multiply([noise, z])
image = model(model_input)
return Model([noise, label], image)
第 5 步:定义一个效用函数来构建鉴别器
蟒蛇3
def build_discriminator():
model = Sequential()
# Building the input layer
model.add(Conv2D(16, (3,3), strides=2, input_shape=image_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, (3,3), strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3,3), strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, (3,3), strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
image = Input(shape=image_shape)
# Extract features from images
features = model(image)
# Building the output layer
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(features)
label = Dense(classes, activation="softmax")(features)
return Model(image, [validity, label])
第 6 步:定义一个效用函数来显示生成的图像
蟒蛇3
def display_images():
r = 10
c = 10
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c,latent_dim))
new_labels = np.array([num for _ in range(r) for num in range(c)])
gen_images = generator.predict([noise, new_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_images = 0.5 * gen_images + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
count = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_images[count,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
count += 1
plt.show()
plt.close()
第 7 步:构建和训练 AC-GAN
蟒蛇3
def train_acgan(epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X, y), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Configure inputs
X = X.astype(np.float32)
X = (X - 127.5) / 127.5
X = np.expand_dims(X, axis=3)
y = y.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Select a random batch of images
index = np.random.randint(0, X.shape[0], batch_size)
images = X[index]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, latent_dim))
# The labels of the digits that the generator tries to create an
# image representation of
new_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, (batch_size, 1))
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_images = generator.predict([noise, new_labels])
image_labels = y[index]
# Training the discriminator
disc_loss_real = discriminator.train_on_batch(
images, [valid, image_labels])
disc_loss_fake = discriminator.train_on_batch(
gen_images, [fake, new_labels])
disc_loss = 0.5 * np.add(disc_loss_real, disc_loss_fake)
# Training the generator
gen_loss = combined.train_on_batch(
[noise, new_labels], [valid, new_labels])
# Print the accuracies
print ("%d [acc.: %.2f%%, op_acc: %.2f%%]" % (
epoch, 100 * disc_loss[3], 100 * disc_loss[4]))
# display at every defined epoch interval
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
display_images()
第 8 步:构建生成对抗网络
蟒蛇3
# Build and compile the discriminator
discriminator = build_discriminator()
discriminator.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
generator = build_generator()
# Defining the input for the generator
#and generating the images
noise = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
image = generator([noise, label])
# Disable the Discriminator
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes in the generated image
# as input and determines validity
# and the label of that image
valid, target_label = discriminator(image)
# The combined model (both generator and discriminator)
# Training the generator to fool the discriminator
combined = Model([noise, label], [valid, target_label])
combined.compile(loss=losses, optimizer=optimizer)
train_acgan(epochs=14000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=2000)
输出(每 2000 个纪元间隔):
时代 0

时代2000

时代4000

时代6000

纪元8000
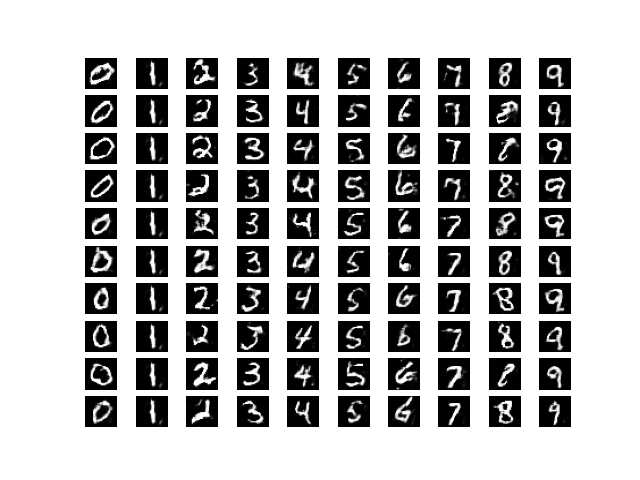
纪元10000
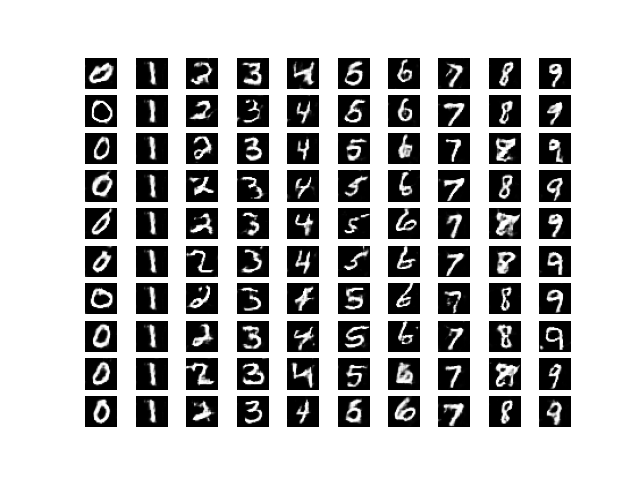
纪元12000

纪元14000
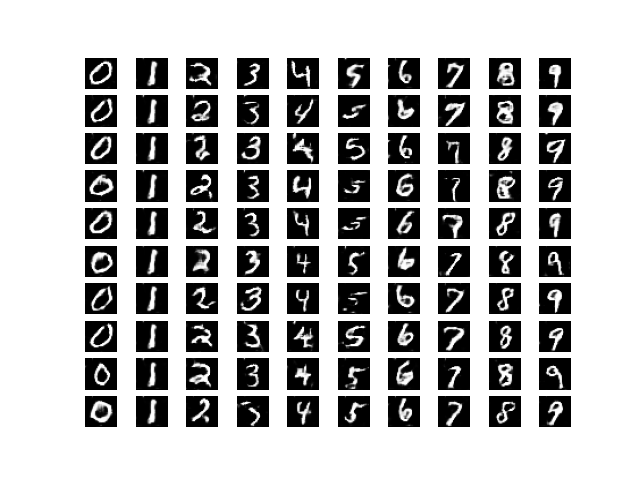
最后结果
通过视觉观察生成图像的进展,可以得出结论,网络正在以可接受的水平工作。可以通过训练网络更多时间或调整网络参数来提高图像质量。如有任何疑问/疑问,请在下方评论。