用Java实现 Patricia Trie
Patricia Trie 或前缀树或基数树是一种有序的结构化树,它通常应用它存储的数据。节点在树中的位置定义了与该节点相关联的键,这与二叉搜索树相比,尝试不同,在二叉搜索树中,节点存储仅对应于该节点的键。
每个节点都有一个前缀是字符串,而另一个是空字符串。
Patricia trie 的一般操作是-
- 插入
- 搜索
- 删除

方法:
- 首先,我们简单地创建一个 PatriciaTrieNode 类,在其中声明该类的所有变量。
- 现在我们声明另一个 PatriciaTest,在那里我们构建 PatriciaTest 构造函数
- 我们声明像makeEmpty()或isEmpty()这样的函数来检查节点的状态。
- 我们将声明函数位,这将帮助我们将元素存储在节点中。
- 我们将首先检查它的长度是否不等于 max Bits。
- 然后我们编写代码从左边得到key k的第i位
- 现在我们将编写一个布尔搜索函数,它有助于查找元素是否在节点中。
- 布尔搜索会取一个数字,这将有助于我们搜索根节点'
- PatriciaTrieNode 搜索节点将搜索给定的数据元素是否存在
- 如果存在,则返回 yes 否则 no。
- PatriciaTrieNode 搜索是一个搜索元素的函数。
- 它将有两个元素 current 和 next Node。
- 下一个节点将保留在元素 t 的左子节点,而当前节点是 t。
- 在while循环的帮助下,我们将检查下一个节点是否大于当前节点
- 如果满足,我们将检查当前节点是否等于下一个“节点”。
- 返回下一个节点。
- 现在我们将创建一个函数insert PatriciaTrieNode
- 在这里,我们将声明 current、parent、'LastNode'、'NewNode'。
- 我们将相应地设置数据、左子和右子等参数。
- 如果我们已经输入了相同的密钥,我们也会检查条件
- 如果我们还没有输入它,我们会将密钥存储在不同的变量中
- 这里我们将它设置为数据、右孩子、左孩子等等
- 如果父级匹配左子级,则为 NewNode 或右子级成为 NewNode
- 现在我们将声明主类
- 我们会声明扫描仪
- 我们还将为 PatriciaTest 创建一个对象
- 我们将声明一个字符
- 现在我们将声明 switch 关键字
- 可以使用字符访问此 switch 关键字。
- 我们可以选择插入、搜索、清空或检查是否为空
- 我们可以根据满足while的给定输入继续循环。
执行:
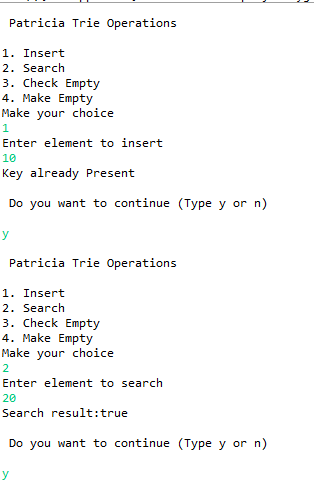
情况1
Patricia Trie
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
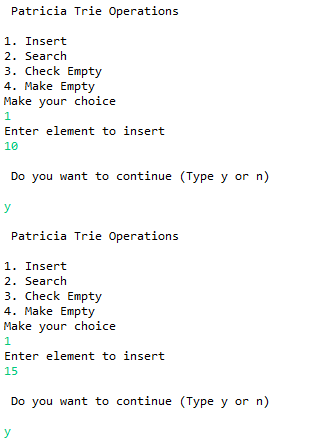
1
Enter element to insert
10
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
1
Enter element to insert
20
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
1
Enter element to insert
30
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
1
Enter element to insert
10
Key already Present
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
2
Enter element to search
20
Search result : true
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
4
Patricia Trie Cleared
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
n案例二
Patricia Trie
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
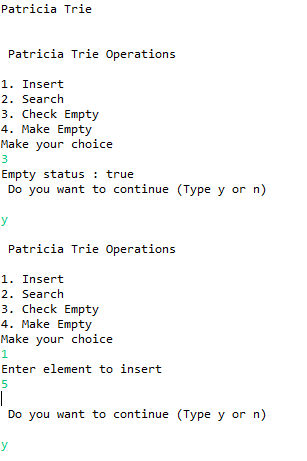
3
Empty status : true
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
1
Enter element to insert
5
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
1
Enter element to insert
10
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
1
Enter element to insert
15
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
y
Patricia Trie Operations
1. Insert
2. Search
3. Check Empty
4. Make Empty
Make your choice
2
Enter element to search
10
Search result : true
Do you want to continue (Type y or n)
n例子
Java
// Java Program to implement Patrica trie
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Importing Scanner class to display menu
// or simply to takke input from user
import java.util.Scanner;
// Class 1
// class PatriciaTrieNode is created
// to obtained its elements
class PatriciaTrieNode {
// Member variables of this class
// Declaring elements, number and data.
int number;
int data;
// Two nodes are considered into action
// node1 -> left child and
// node2 -> right child
PatriciaTrieNode leftChild, rightChild;
}
class PraticiaTest {
// Member variable of this class
// Declaring two elements
// Maxbits can help us to store elements in the Trie
// The root helps us to fix a global value.
private PatriciaTrieNode root;
private static final int MaxBits = 10;
// Method 1
// PatriciaTrie where initially
// the root equals NULL
public PraticiaTest() { root = null; }
// Method 2 - isEmpty()
// Method used to check if the function is empty as
// it returns true or false basing on the condition
public boolean isEmpty() { return root == null; }
// Method 3 - makeEmpty()
// Method used to help in emptying the root
// of the Patricia Node
public void makeEmpty() { root = null; }
// Method 4 - bit()
// Declaring the function bit which performs a search
// operation in finding the bit which should be matched
// as input
private boolean bit(int k, int i)
{
// Step 1 : Binary input is first converted to
// string as in strings its easy to match its
// corporate values
String binary = Integer.toString(k, 2);
// Step2: Condition check while input length
// is not equal to the length of the maxbits
while (binary.length() != MaxBits)
// Step 3: Keep adding the binary value
// until it gets the last number
binary = "0" + binary;
// Step 4: If the binary matches the desired value
// needed, true will be returned
if (binary.charAt(i - 1) == '1')
return true;
// else we return false
return false;
}
// Method 5 - search()
public boolean search(int k)
{
// Taking int num , as the half value of
// the of entered elements
int num = (int)(Math.log(k) / Math.log(2));
// Condition check whether number
// is greater than maxBits
if (num > MaxBits) {
// Display message
// Print number has exceeded the limit
System.out.println("Exceeded the limit");
// And return false
return false;
}
// Now when an element is created for the class
// named as 'searchNode'
// This searches Node will go to the next
// search function
PatriciaTrieNode searchNode = search(root, k);
// Now we will search the data element whether
// k is present in our node or not.
// If it is present print true
// else print false
if (searchNode.data == k)
return true;
else
return false;
}
// By now, search operation of
// PatriciaTrieNode class is declared
private PatriciaTrieNode search(PatriciaTrieNode t,
int k)
{
// Now these are the currentNode and nextNode
PatriciaTrieNode currentNode, nextNode;
// Step 1 : Now if the elemenents present in the t
// mode
// are NULL,then NULL will be returned
if (t == null) {
return null;
}
// Step 2: Now, considering the next node value to
// be the left child of the present variable t
nextNode = t.leftChild;
// Step 3: Next we keep the current node value
// to be "t"
currentNode = t;
// Condition check
// Step 4: If the next node bitnumber is greater
// than the current numbers bitcode
while (nextNode.number > currentNode.number) {
// Step 5: Making the current Node as the next
// node
// It is more like checking each
// as the next node becomes the current node
// Each time desired output won't be obtained
currentNode = nextNode;
// Step 6: Putting this nextNode in the bitwise
// operator This method helps us to find whether
// it is LeftChild or Right Child
nextNode = (bit(k, nextNode.number))
? nextNode.rightChild
: nextNode.leftChild;
}
// Step 7: Now we return the next Node..
return nextNode;
}
// Method 6 - insert()
// Inserting the value element inside PatriciaTrieNode
public void insert(int element)
{
// Num is the variable where the value entered by
// the user will be stored. This value will be
// helpful to calculate the serahc index as well
int num
= (int)(Math.log(element) / Math.log(2)) + 1;
// Now taking num greater than maxBits, it can be
// said
// that the PatriciaTrieNode is full
if (num > MaxBits) {
// This will print the statement that we are
// full
// Display message
System.out.println(
"We are full, The number is too large");
return;
}
// Now the root value becomes the value
// where the element gets inserted
root = insert(root, element);
}
// Now defining a function insert of the class
// PraticiaTrieNode
private PatriciaTrieNode insert(PatriciaTrieNode t,
int element)
{
// Here the praticiaNode will have current , parent
// It will also have lastNode and newNode
PatriciaTrieNode current = null, parent, lastNode,
newNode;
int i;
// Here t equals null
// Condition check
// If it equals null simply declare
// the following attributes
if (t == null) {
t = new PatriciaTrieNode();
// Number is initialized to be 0
t.number = 0;
// Data of the t node should be
// the element number
t.data = element;
// where as the child will be t and
t.leftChild = t;
// Right child of the t will be made empty
// or be equal to null
t.rightChild = null;
// Return the data t
return t;
}
// Now declaring the lastNode to be search
lastNode = search(t, element);
// If we declare the last node to be
// a part of the search function.
// Now we can compare it with the data
// already present in the PatriciaTrieNode
// If we have the key already Present
if (element == lastNode.data) {
// Print the display message
System.out.println("Key already Present");
// Return t
return t;
}
// Iterating variable variable from
// first element to last element
for (i = 1;
bit(element, i) == bit(lastNode.data, i); i++)
// Keep current to the left Child
current = t.leftChild;
// Parent is equal to t
parent = t;
// Condition check
// Current number is greater than parent number
// And if current number is less than i
while (current.number > parent.number
&& current.number < i) {
// If parent is current
parent = current;
// Now we will see whether the new node
// is more flexible to the rightChild
// or is it ore available to the left child
// using scope resolution operator
current = (bit(element, current.number))
? current.rightChild
: current.leftChild;
}
// Now we are taking this as newnode
newNode = new PatriciaTrieNode();
// If we take newnode of number as i
newNode.number = i;
// Now taking data as element
newNode.data = element;
// Now taking the leftchild as depending onn the
// condition
// we fix it either to be current or newNode
newNode.leftChild
= bit(element, i) ? current : newNode;
// Now again taking the condition we fix
// The right child either to be newNode or
// curentNode
newNode.rightChild
= bit(element, i) ? newNode : current;
// If we take current and parent as left child are
// same We fix them to be newNode
if (current == parent.leftChild) {
parent.leftChild = newNode;
}
else {
// else we take the right child to be the
// newNode
parent.rightChild = newNode;
}
// we return the value to t
return t;
}
}
// Main Class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Scanner class to take input choices from user
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Declare the object of the PracticiaTest class
PraticiaTest pt = new PraticiaTest();
// Display message
System.out.println("Patricia Trie\n");
// Declaring a variable 'ch' of character with help
// of this character we will be able to make choiced
char ch;
// Do-while is used for switching operations
// using switch case
// Do loop includes execution in the body
// which will execute once atleast as
// condition is checked at last
do {
// Display Messages
// Heading would be patricia Trie Operations
System.out.println(
"\n Patricia Trie Operations\n");
// Menu
// These are the following options
// that we would keep in a Patricia Trie
// (1) Inserting the element
System.out.println("1. Insert");
// (2) earching the element
System.out.println("2. Search");
// (3) Checking for The Trie to be empty
System.out.println("3. Check Empty");
// (4) Making it empty
System.out.println("4. Make Empty");
// Display message
// Reading the choice of the user
System.out.println("Make your choice");
// Switch variable
int choice = sc.nextInt();
// Switch case keyboard enables to decide the
// choice
switch (choice) {
// Case 1 : Insertion
// We would simply call the insert function
// And set the data
case 1:
System.out.println(
"Enter element to insert");
pt.insert(sc.nextInt());
break;
// Case 2: Enter the element to search
case 2:
// If we would find the data we would give
// necessary output If not we would return
// false Print and display
System.out.println(
"Enter element to search");
System.out.println(
"Search result:"
+ pt.search(sc.nextInt()));
break;
// Case: 3
case 3:
// This is to check if the Trie is empty
// Print and display
System.out.print("Empty status : "
+ pt.isEmpty());
break;
// Case 4 : Empty the patricia Trie
case 4:
// Print and display
System.out.println("Patricie Trie Cleared");
// Calling makeEmpty() to empty the Trie
pt.makeEmpty();
break;
// Default case for invalid entry
default:
// Print and display
System.out.println("Wrong entry\n");
break;
}
// Now if we wish to continue
// Then we would press y and continue
// If not we would simply exit from the blocks
System.out.println(
"\n Do you want to continue (Type y or n)\n");
ch = sc.next().charAt(0);
}
// Condition in do-while loop
while (ch == 'Y' || ch == 'y');
}
}输出:
情况1

案例二