Java中的类类型转换
类型转换是将一种原始数据类型的值评估为另一种类型。在Java中,有两种类型的转换,即向上转换和向下转换,如下所示:
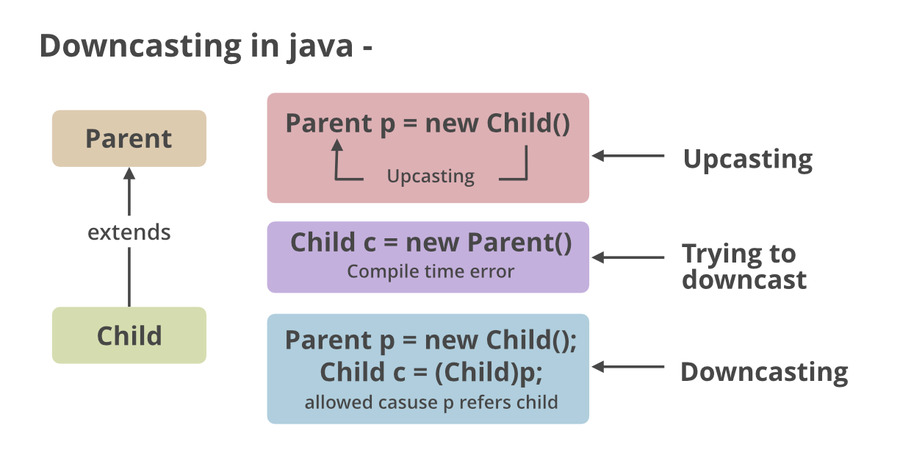
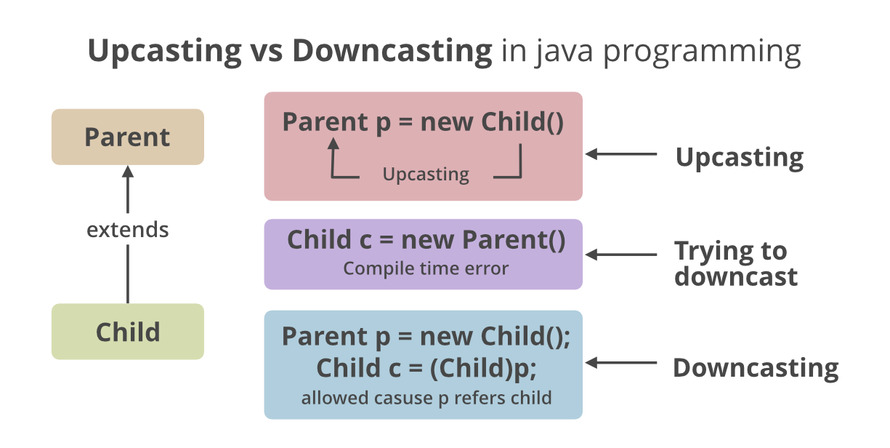
- 向上转换是在继承树的向上方向上将子类型转换为超类型。这是一个自动过程,在子类对象由超类引用变量引用的情况下,无需为此付出任何努力。人们可以将其与动态多态性联系起来。
- 隐式转换是指由编译器在没有转换语法的情况下完成的类类型转换。
- 显式转换是指程序员使用转换语法完成的类类型转换。
- 向下转换是指子类类型引用父类的对象时的过程称为向下转换。如果直接执行,编译器会报错,因为在运行时抛出 ClassCastException。只有使用 instanceof运算符才能实现 已经向上转换的对象,该对象只能向下转换。
为了执行类类型转换,我们必须遵循以下两条规则:
- 类必须是“IS-A-关系”
- 一个对象必须具有它要转换的类的属性。
执行:
(A)向上转型
示例 1
Java
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Parent class
class Parent
{
// Function
void show()
{
// Print message for this class
System.out.println("Parent show method is called");
}
}
// Class 2
// Child class
class Child extends Parent
{
// Overriding existing method of Parent class
@Override
// Same Function which will override
// existing Parent class function
void show()
{
// Print message for this class
System.out.println("Child show method is called");
}
}
// Class3
// Main class
class GFG
{
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a Parent class object
// but referencing it to a Child class
Parent obj = new Child();
// Calling the show() method to execute
obj.show();
}
}Java
// Java Program to illustrate Downcasting
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Parent class
class Vehicles {
}
// Class 2
// Child class
class Car extends Vehicles {
static void method(Vehicles v)
{
//
if (v instanceof Car) {
// Downcasting
Car c = (Car)v;
// Display message
System.out.println("Downcasting performed");
}
}
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of Vehicle class
// and referring it to Car class
Vehicles v = new Car();
Car.method(v);
}
}Java
// Java Program showing ClassCastException
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Parent class/ Member class
class Member {
// Member variable of this class
String name;
long phone;
// Member function of this class
void chat()
{
// Print message of Member/ Child class
System.out.println(
name + " : chatting in whatsapp group");
}
}
// Class 2
// Child class/ Admin class
class Admin extends Member {
// Member function of this class
void addUser()
{
// Print message of Admin/ Parent class
System.out.println(
name
+ " : adding a new user in whatsapp group");
}
}
// Class3 - Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object Ad
Member mem = new Admin();
// Upcasting access only general property of
// superclass
// Custom entry for Member class
mem.name = "Sneha";
mem.phone = 9876543210l;
// Calling function
mem.chat();
Admin ad = (Admin)mem;
// Downcast to access specific property of subclass
ad.addUser();
}
}输出
Child show method is called输出说明:这里调用了父类对象,但引用了子类对象。因此,人们可以将其与动态多态性或函数覆盖联系起来。
(B)向下转型
示例 2
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Downcasting
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Parent class
class Vehicles {
}
// Class 2
// Child class
class Car extends Vehicles {
static void method(Vehicles v)
{
//
if (v instanceof Car) {
// Downcasting
Car c = (Car)v;
// Display message
System.out.println("Downcasting performed");
}
}
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of Vehicle class
// and referring it to Car class
Vehicles v = new Car();
Car.method(v);
}
}
输出
Downcasting performedNOTE : Without perform upcast if we try to downcast , ClassCastException will be thrown.
- It is a runtime exception or unchecked exception.
- It is class, present in java.lang package.
- It can be avoided by using a operator known as ‘instanceof’.
示例 3
Java
// Java Program showing ClassCastException
// Importing input output classes
import java.io.*;
// Class 1
// Parent class/ Member class
class Member {
// Member variable of this class
String name;
long phone;
// Member function of this class
void chat()
{
// Print message of Member/ Child class
System.out.println(
name + " : chatting in whatsapp group");
}
}
// Class 2
// Child class/ Admin class
class Admin extends Member {
// Member function of this class
void addUser()
{
// Print message of Admin/ Parent class
System.out.println(
name
+ " : adding a new user in whatsapp group");
}
}
// Class3 - Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object Ad
Member mem = new Admin();
// Upcasting access only general property of
// superclass
// Custom entry for Member class
mem.name = "Sneha";
mem.phone = 9876543210l;
// Calling function
mem.chat();
Admin ad = (Admin)mem;
// Downcast to access specific property of subclass
ad.addUser();
}
}
输出
Sneha : chatting in whatsapp group
Sneha : adding a new user in whatsapp group