Java中的类型转换与示例
Java提供了各种数据类型,就像任何其他动态语言一样,如 boolean、char、int、unsigned int、signed int、float、double、long 等,总共提供 7 种类型,其中每种数据类型在存储在内存中时获取不同的空间。当您将一种数据类型的值分配给另一种数据类型时,这两种类型可能彼此不兼容。如果数据类型兼容,则Java将自动执行称为自动类型转换的转换,如果不兼容,则需要显式转换或转换它们。例如,将 int 值分配给 long 变量。Datatype Bits Acquired In Memory boolean 1 byte 8 (1 byte) char 16 (2 bytes) short 16(2 bytes) int 32 (4 bytes) long 64 (8 bytes) float 32 (4 bytes) double 64 (8 bytes)
加宽或自动类型转换
当自动转换两种数据类型时,会发生扩大转换。这发生在:
- 这两种数据类型是兼容的。
- 当我们将较小数据类型的值分配给较大数据类型时。
例如,在Java中,数值数据类型相互兼容,但不支持从数值类型到 char 或 boolean 的自动转换。此外,char 和 boolean 彼此不兼容。

例子:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Automatic Type Conversion
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i = 100;
// Automatic type conversion
// Integer to long type
long l = i;
// Automatic type conversion
// long to float type
float f = l;
// Print and display commands
System.out.println("Int value " + i);
System.out.println("Long value " + l);
System.out.println("Float value " + f);
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate Incompatible data Type
// for Explicit Type Conversion
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] argv)
{
// Declaring character variable
char ch = 'c';
// Declaringinteger variable
int num = 88;
// Trying to insert integer to character
ch = num;
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Explicit Type Conversion
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Double datatype
double d = 100.04;
// Explicit type casting by forcefully getting
// data from long datatype to integer type
long l = (long)d;
// Explicit type casting
int i = (int)l;
// Print statements
System.out.println("Double value " + d);
// While printing we will see that
// fractional part lost
System.out.println("Long value " + l);
// While printing we will see that
// fractional part lost
System.out.println("Int value " + i);
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Conversion of
// Integer and Double to Byte
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring byte variable
byte b;
// Declaring and initializing integer and double
int i = 257;
double d = 323.142;
// Display message
System.out.println("Conversion of int to byte.");
// i % 256
b = (byte)i;
// Print commands
System.out.println("i = " + i + " b = " + b);
System.out.println(
"\nConversion of double to byte.");
// d % 256
b = (byte)d;
// Print commands
System.out.println("d = " + d + " b= " + b);
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Type promotion in Expressions
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initializing primitive types
byte b = 42;
char c = 'a';
short s = 1024;
int i = 50000;
float f = 5.67f;
double d = .1234;
// The Expression
double result = (f * b) + (i / c) - (d * s);
// Printing the result obtained after
// all the promotions are done
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}Java
// Java program to Illustrate Type Casting
// in Integer to Byte
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring byte array
byte b = 50;
// Type casting int to byte
b = (byte)(b * 2);
// Display value in byte
System.out.println(b);
}
}Int value 100
Long value 100
Float value 100.0缩小或显式转换
如果我们想将较大数据类型的值分配给较小的数据类型,我们会执行显式类型转换或缩小。
- 这对于无法进行自动转换的不兼容数据类型很有用。
- 在这里,目标类型指定要将指定值转换为的所需类型。

char 和 number 不兼容。让我们看看我们何时尝试将一种转换为另一种。
Java
// Java program to illustrate Incompatible data Type
// for Explicit Type Conversion
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] argv)
{
// Declaring character variable
char ch = 'c';
// Declaringinteger variable
int num = 88;
// Trying to insert integer to character
ch = num;
}
}
输出:将产生错误
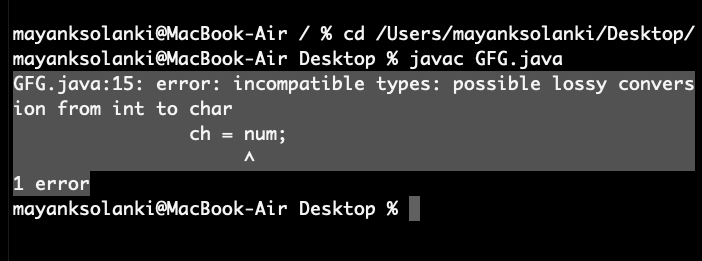
生成此错误是因为整数变量需要 4 个字节,而字符数据类型需要 2 个字节。我们正在尝试将数据从 4 个字节绘制成 2 个字节,这是不可能的。
如何进行显式转换?
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Explicit Type Conversion
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Double datatype
double d = 100.04;
// Explicit type casting by forcefully getting
// data from long datatype to integer type
long l = (long)d;
// Explicit type casting
int i = (int)l;
// Print statements
System.out.println("Double value " + d);
// While printing we will see that
// fractional part lost
System.out.println("Long value " + l);
// While printing we will see that
// fractional part lost
System.out.println("Int value " + i);
}
}
Double value 100.04
Long value 100
Int value 100Note: While assigning value to byte type the fractional part is lost and is reduced to modulo 256(range of byte).
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Conversion of
// Integer and Double to Byte
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring byte variable
byte b;
// Declaring and initializing integer and double
int i = 257;
double d = 323.142;
// Display message
System.out.println("Conversion of int to byte.");
// i % 256
b = (byte)i;
// Print commands
System.out.println("i = " + i + " b = " + b);
System.out.println(
"\nConversion of double to byte.");
// d % 256
b = (byte)d;
// Print commands
System.out.println("d = " + d + " b= " + b);
}
}
Conversion of int to byte.
i = 257 b = 1
Conversion of double to byte.
d = 323.142 b= 67表达式中的类型提升
在计算表达式时,中间值可能会超出操作数的范围,因此表达式值将被提升。类型提升的一些条件是:
- 在评估表达式时, Java自动将每个字节、短或字符操作数提升为 int。
- 如果一个操作数是 long、float 或 double,则整个表达式将分别提升为 long、float 或 double。
例子:
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Type promotion in Expressions
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring and initializing primitive types
byte b = 42;
char c = 'a';
short s = 1024;
int i = 50000;
float f = 5.67f;
double d = .1234;
// The Expression
double result = (f * b) + (i / c) - (d * s);
// Printing the result obtained after
// all the promotions are done
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}
result = 626.7784146484375表达式中的显式类型转换
在计算表达式时,结果会自动更新为操作数的更大数据类型。但是,如果我们将该结果存储在任何较小的数据类型中,它会产生一个编译时错误,因此我们需要对结果进行类型转换。
例子:
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Type Casting
// in Integer to Byte
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring byte array
byte b = 50;
// Type casting int to byte
b = (byte)(b * 2);
// Display value in byte
System.out.println(b);
}
}
100Note: In case of single operands the result gets converted to int and then it is typecast accordingly, as in the above example.