与顺序无关的二进制搜索
与顺序无关的二分搜索是二分搜索算法的修改版本。在这个修改后的二进制搜索中,还有一个条件检查。这个算法背后的直觉是如果没有给出排序数组的顺序会怎样。所以这里检查第一个元素的值是大于还是小于最后一个元素。
- 如果第一个元素小于最后一个元素- 那么如果搜索键值X小于区间的中间,则结束指针将更改为中间 -1 否则开始将更改为中间 + 1。
- 如果第一个元素大于最后一个元素,那么如果搜索键值X小于间隔的中间,则开始指针将移动到中间元素的下一个元素,否则结束指针将移动到中间元素之前元素。
最后,如果搜索键值与中间元素匹配,则找到提供给搜索的元素。
与顺序无关的二进制搜索的实现:
让我们借助一个示例来看看 Order-Agnostic Binary Search 的实现。
给定一个大小为N的数组arr[ ]和一个元素X ,并且该数组按任意顺序(升序或降序)排序,任务是查找元素x是否存在于数组中。如果是,则打印其索引,否则打印-1。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {40, 10, 5, 2, 1}, N=5, X=10
Output: 1
Explanation:
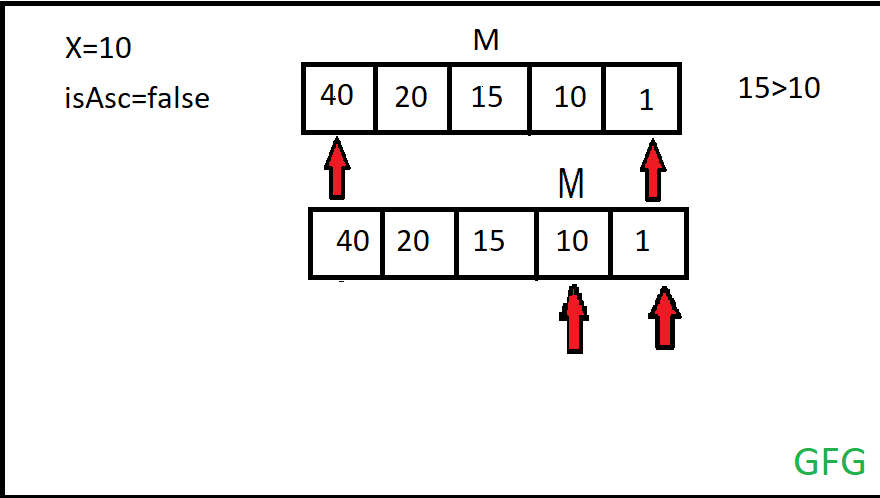
The array is sorted in descending order and the element is present at index 1.
Input: arr[] = {1}, N=1, X=10
Output: -1
方法:蛮力的想法是线性遍历数组并检查元素是否存在于数组中。如果数组的排序顺序已知 - 升序/降序,则对该算法的优化将是使用二进制搜索。可以使用二进制搜索的变体,即与顺序无关的二进制搜索,如下所述:
请按照以下步骤使用 Order-Agnostic Binary Search 解决问题:
- 如果arr[start]小于arr[end]则将布尔变量isAsc初始化为true ,否则将其设置为false。
- 遍历一个while循环,直到start小于等于end并执行以下步骤:
- 将变量middle初始化为start和end 的平均值。
- 如果arr[middle]等于X,则返回middle的值作为答案,
- 如果数组按升序排列,则执行以下步骤:
- 如果arr[middle]小于X,则将start的值设置为middle+1 ,否则将end的值设置为middle-1。
- 否则,如果arr[middle]小于X,则将end的值设置为middle-1 ,否则将start的值设置为middle+1。
- 执行上述步骤后,返回值-1作为未找到元素的答案。
Order-Agnostic Binary Search 的迭代实现。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// An iterative binary search function.
int binarySearch(int arr[], int start, int end, int x)
{
// Checking the sorted order of the given array
bool isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
while (start <= end) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
// Ascending order
if (isAsc == true) {
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] < x)
start = middle + 1;
// If x smaller, ignore right half
else
end = middle - 1;
}
// Descending order
else {
// If x smaller, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] > x)
start = middle + 1;
// If x greater, ignore right half
else
end = middle - 1;
}
}
// Element is not present
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// An iterative binary search function.
static int binarySearch(int arr[], int start, int end, int x)
{
// Checking the sorted order of the given array
boolean isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
while (start <= end) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
// Ascending order
if (isAsc == true) {
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] < x)
start = middle + 1;
// If x smaller, ignore right half
else
end = middle - 1;
}
// Descending order
else {
// If x smaller, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] > x)
start = middle + 1;
// If x greater, ignore right half
else
end = middle - 1;
}
}
// Element is not present
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62.Python
# Python program for the above approach
# An iterative binary search function.
def binarySearch(arr, start, end, x):
# Checking the sorted order of the given array
isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end]
while (start <= end):
middle = start + (end - start) // 2
# Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[middle] == x):
return middle
# Ascending order
if (isAsc == True):
# If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] < x):
start = middle + 1
# If x smaller, ignore right half
else:
end = middle - 1
# Descending order
else:
# If x smaller, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] > x):
start = middle + 1
# If x greater, ignore right half
else:
end = middle - 1
# Element is not present
return -1
# Driver Code
arr = [ 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 ]
x = 10
n = len(arr)
print(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x))
# This code is ciontributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// An iterative binary search function.
static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int start, int end, int x)
{
// Checking the sorted order of the given array
bool isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
while (start <= end) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// Check if x is present at mid
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
// Ascending order
if (isAsc == true) {
// If x greater, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] < x)
start = middle + 1;
// If x smaller, ignore right half
else
end = middle - 1;
}
// Descending order
else {
// If x smaller, ignore left half
if (arr[middle] > x)
start = middle + 1;
// If x greater, ignore right half
else
end = middle - 1;
}
}
// Element is not present
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x));
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.Javascript
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A recursive binary search function.
// It returns location of x in given
// array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int start,
int end, int x)
{
bool isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
if (end >= start) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
if (isAsc == true) {
// If element is smaller than mid,
// then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if (arr[middle] > x)
return binarySearch(
arr, start,
middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1,
end, x);
}
else {
if (arr[middle] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, start,
middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in left subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1,
end, x);
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// A recursive binary search function.
// It returns location of x in given
// array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
static int binarySearch(int arr[], int start, int end, int x) {
boolean isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
if (end >= start) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
if (isAsc == true) {
// If element is smaller than mid,
// then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if (arr[middle] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
} else {
if (arr[middle] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in left subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG {
// A recursive binary search function.
// It returns location of x in given
// array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
static int binarySearch(int []arr, int start, int end, int x) {
bool isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
if (end >= start) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
if (isAsc == true) {
// If element is smaller than mid,
// then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if (arr[middle] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
} else {
if (arr[middle] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in left subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []arr = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x));
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
1时间复杂度: O(log(N))。
辅助空间: O(1)
Order-Agnostic Binary Search 的递归实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A recursive binary search function.
// It returns location of x in given
// array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
int binarySearch(int arr[], int start,
int end, int x)
{
bool isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
if (end >= start) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
if (isAsc == true) {
// If element is smaller than mid,
// then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if (arr[middle] > x)
return binarySearch(
arr, start,
middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1,
end, x);
}
else {
if (arr[middle] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, start,
middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in left subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1,
end, x);
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// A recursive binary search function.
// It returns location of x in given
// array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
static int binarySearch(int arr[], int start, int end, int x) {
boolean isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
if (end >= start) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
if (isAsc == true) {
// If element is smaller than mid,
// then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if (arr[middle] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
} else {
if (arr[middle] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in left subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG {
// A recursive binary search function.
// It returns location of x in given
// array arr[l..r] is present,
// otherwise -1
static int binarySearch(int []arr, int start, int end, int x) {
bool isAsc = arr[start] < arr[end];
if (end >= start) {
int middle = start + (end - start) / 2;
// If the element is present
// at the middle itself
if (arr[middle] == x)
return middle;
if (isAsc == true) {
// If element is smaller than mid,
// then it can only be
// present in left subarray
if (arr[middle] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in right subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
} else {
if (arr[middle] < x)
return binarySearch(arr, start, middle - 1, x);
// Else the element can only be present
// in left subarray
return binarySearch(arr, middle + 1, end, x);
}
}
// Element not found
return -1;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []arr = { 40, 10, 5, 2, 1 };
int x = 10;
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write(binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x));
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
1时间复杂度: O(log(N))。
辅助空间: O(1)