📌 相关文章
- 如何将 R 中的抖动函数用于散点图?
- 如何将 R 中的抖动函数用于散点图?(1)
- JavaScript 中的去抖动(1)
- JavaScript 中的去抖动
- 在 R 中使用 ggplot2 创建具有多个组的散点图(1)
- 在 R 中使用 ggplot2 创建具有多个组的散点图
- R-散点图(1)
- R-散点图
- Base R 和 ggplot2 中的透明散点图(1)
- Base R 和 ggplot2 中的透明散点图
- 散点图 |创建散点图 - Python (1)
- Python散点图
- Python散点图(1)
- 散点图 |创建散点图 - Python 代码示例
- 如何在 R 中的 ggplot2 中使用抖动数据点制作分组箱线图(1)
- 如何在 R 中的 ggplot2 中使用抖动数据点制作分组箱线图
- 在 R 中使用 ggplot2 散点图综合指南(1)
- 在 R 中使用 ggplot2 散点图综合指南
- 如何将配对点与 R 中 ggplot2 中散点图中的线连接起来?
- 散点图,散点图和气泡图(1)
- 散点图,散点图和气泡图
- ggplot2-使用轴(1)
- ggplot2-使用轴
- 抖动的概念
- 散点图矩阵(1)
- 散点图矩阵
- python中数据框的散点图(1)
- Excel中的散点图(1)
- Excel中的散点图
📜 ggplot2-散点图和抖动图
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-01 06:48:30 🧑 作者: Mango
散点图类似于通常用于绘制的折线图。散点图显示一个变量与另一个变量有多少关联。变量之间的关系称为相关性,通常在统计方法中使用。我们将使用称为“虹膜”的相同数据集,其中每个变量之间都有很多差异。这是一个著名的数据集,它以厘米为单位,对来自3种鸢尾花的50种花朵的萼片长度和宽度以及花瓣的长度和宽度进行测量。该物种称为鸢尾鸢尾,杂色和维吉尼亚。
创建基本散点图
使用“ ggplot2”包创建散点图涉及以下步骤:
为了创建基本的散点图,执行以下命令-
> # Basic Scatter Plot
> ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Petal.Length)) +
+ geom_point()

添加属性
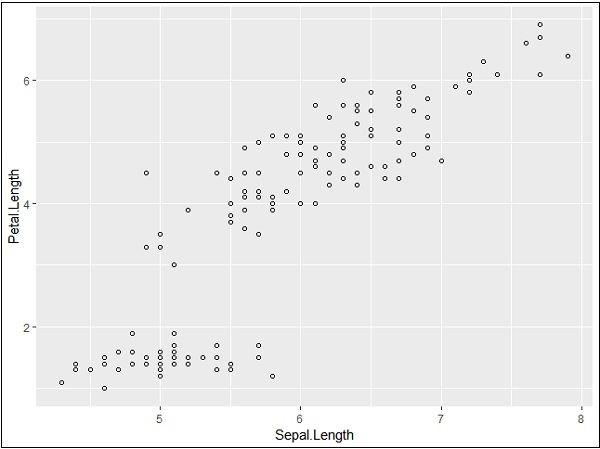
我们可以在geom_point()函数名为shape的属性来更改点的形状。
> # Change the shape of points
> ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Petal.Length)) +
+ geom_point(shape=1)
我们可以将颜色添加到所需散点图中添加的点。
> ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Petal.Length, colour=Species)) +
+ geom_point(shape=1)
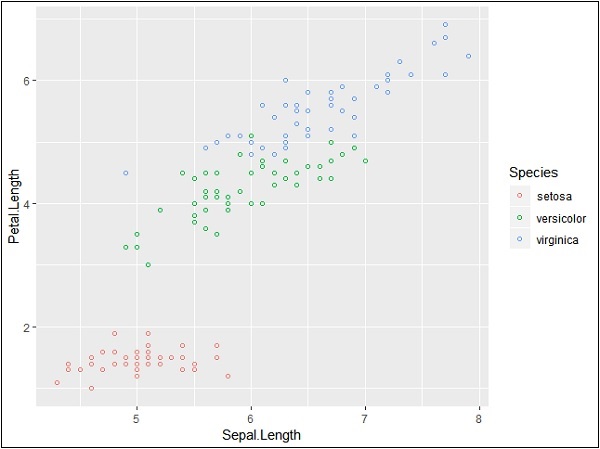
在此示例中,我们根据图例中提到的物种创建了颜色。在所提到的地块中,这三种物种是独特的。
现在,我们将重点放在建立变量之间的关系上。
> ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Petal.Length, colour=Species)) +
+ geom_point(shape=1) +
+ geom_smooth(method=lm)
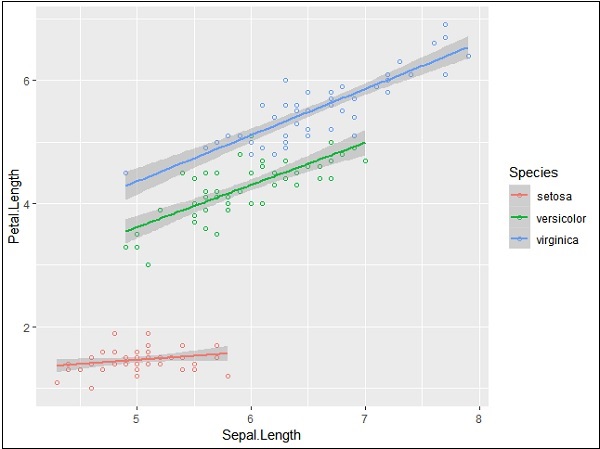
geom_smooth函数有助于重叠模式和创建所需变量的模式。
属性方法“ lm”提到需要开发的回归线。
> # Add a regression line
> ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Petal.Length, colour=Species)) +
+ geom_point(shape=1) +
+ geom_smooth(method=lm)
我们还可以使用下面提到的语法添加没有阴影置信区域的回归线-
># Add a regression line but no shaded confidence region
> ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Petal.Length, colour=Species)) +
+ geom_point(shape=1) +
+ geom_smooth(method=lm, se=FALSE)
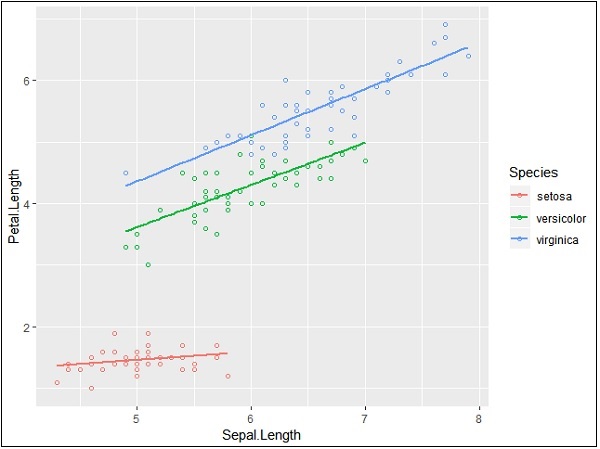
阴影区域表示除置信区域以外的其他内容。
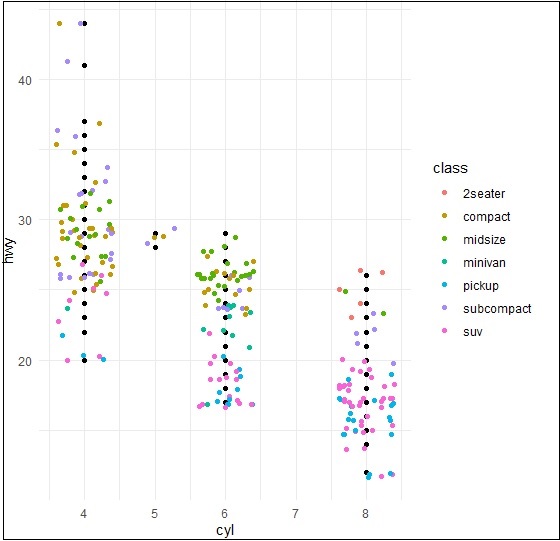
抖动图
抖动图包括特殊效果,可用来描绘散布图。抖动不过是分配给点以将它们分开的随机值,如下所述-
> ggplot(mpg, aes(cyl, hwy)) +
+ geom_point() +
+ geom_jitter(aes(colour = class))