表达式树的评估
给定一个简单的表达式树,由基本的二元运算符组成,即 + 、 – 、* 和 / 以及一些整数,计算表达式树。
例子:
Input: Root node of the below tree
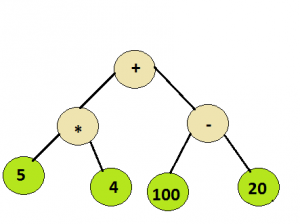
Output:100
Input: Root node of the below tree
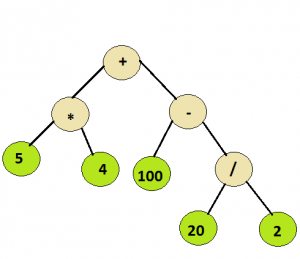
Output: 110
方法:解决此问题的方法基于以下观察:
As all the operators in the tree are binary, hence each node will have either 0 or 2 children. As it can be inferred from the examples above, all the integer values would appear at the leaf nodes, while the interior nodes represent the operators.
Therefore we can do inorder traversal of the binary tree and evaluate the expression as we move ahead.
为了评估语法树,可以遵循递归方法。
Algorithm:
- Let t be the syntax tree
- If t is not null then
- If t.info is operand then
- Return t.info
- Else
- A = solve(t.left)
- B = solve(t.right)
- return A operator B, where operator is the info contained in t
- If t.info is operand then
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to evaluate an expression tree
#include
using namespace std;
// Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree
class node
{
public:
string info;
node *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
node(string x)
{
info = x;
}
};
// Utility function to return the integer value
// of a given string
int toInt(string s)
{
int num = 0;
// Check if the integral value is
// negative or not
// If it is not negative, generate the number
// normally
if(s[0]!='-')
for (int i=0; ileft && !root->right)
return toInt(root->info);
// Evaluate left subtree
int l_val = eval(root->left);
// Evaluate right subtree
int r_val = eval(root->right);
// Check which operator to apply
if (root->info=="+")
return l_val+r_val;
if (root->info=="-")
return l_val-r_val;
if (root->info=="*")
return l_val*r_val;
return l_val/r_val;
}
//driver function to check the above program
int main()
{
// create a syntax tree
node *root = new node("+");
root->left = new node("*");
root->left->left = new node("5");
root->left->right = new node("-4");
root->right = new node("-");
root->right->left = new node("100");
root->right->right = new node("20");
cout << eval(root) << endl;
delete(root);
root = new node("+");
root->left = new node("*");
root->left->left = new node("5");
root->left->right = new node("4");
root->right = new node("-");
root->right->left = new node("100");
root->right->right = new node("/");
root->right->right->left = new node("20");
root->right->right->right = new node("2");
cout << eval(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to evaluate expression tree
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
Node root;
// Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree
public static class Node
{
String data;
Node left, right;
Node(String d)
{
data = d;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
private static int toInt(String s)
{
int num = 0;
// Check if the integral value is
// negative or not
// If it is not negative, generate
// the number normally
if (s.charAt(0) != '-')
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
num = num * 10 + ((int)s.charAt(i) - 48);
// If it is negative, calculate the +ve number
// first ignoring the sign and invert the
// sign at the end
else
{
for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++)
num = num * 10 + ((int)(s.charAt(i)) - 48);
num = num * -1;
}
return num;
}
// This function receives a node of the syntax
// tree and recursively evaluate it
public static int evalTree(Node root)
{
// Empty tree
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Leaf node i.e, an integer
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return toInt(root.data);
// Evaluate left subtree
int leftEval = evalTree(root.left);
// Evaluate right subtree
int rightEval = evalTree(root.right);
// Check which operator to apply
if (root.data.equals("+"))
return leftEval + rightEval;
if (root.data.equals("-"))
return leftEval - rightEval;
if (root.data.equals("*"))
return leftEval * rightEval;
return leftEval / rightEval;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a sample tree
Node root = new Node("+");
root.left = new Node("*");
root.left.left = new Node("5");
root.left.right = new Node("-4");
root.right = new Node("-");
root.right.left = new Node("100");
root.right.right = new Node("20");
System.out.println(evalTree(root));
root = null;
// Creating a sample tree
root = new Node("+");
root.left = new Node("*");
root.left.left = new Node("5");
root.left.right = new Node("4");
root.right = new Node("-");
root.right.left = new Node("100");
root.right.right = new Node("/");
root.right.right.left = new Node("20");
root.right.right.right = new Node("2");
System.out.println(evalTree(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ankit GuptaPython3
# Python program to evaluate expression tree
# Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree
class node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.left = None
self.data = value
self.right = None
# This function receives a node of the syntax tree
# and recursively evaluate it
def evaluateExpressionTree(root):
# empty tree
if root is None:
return 0
# leaf node
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return int(root.data)
# evaluate left tree
left_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.left)
# evaluate right tree
right_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.right)
# check which operation to apply
if root.data == '+':
return left_sum + right_sum
elif root.data == '-':
return left_sum - right_sum
elif root.data == '*':
return left_sum * right_sum
else:
return left_sum // right_sum
# Driver function to test above problem
if __name__ == '__main__':
# creating a sample tree
root = node('+')
root.left = node('*')
root.left.left = node('5')
root.left.right = node('-50')
root.right = node('-')
root.right.left = node('100')
root.right.right = node('20')
print (evaluateExpressionTree(root))
root = None
# creating a sample tree
root = node('+')
root.left = node('*')
root.left.left = node('5')
root.left.right = node('4')
root.right = node('-')
root.right.left = node('100')
root.right.right = node('/')
root.right.right.left = node('20')
root.right.right.right = node('2')
print (evaluateExpressionTree(root))
# This code is contributed by Harshit SidhwaC#
// C# program to evaluate expression tree
using System;
public class GFG
{
// Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree
public class Node {
public
String data;
public
Node left, right;
public Node(String d) {
data = d;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
private static int toInt(String s) {
int num = 0;
// Check if the integral value is
// negative or not
// If it is not negative, generate
// the number normally
if (s[0] != '-')
for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++)
num = num * 10 + ((int) s[i] - 48);
// If it is negative, calculate the +ve number
// first ignoring the sign and invert the
// sign at the end
else {
for (int i = 1; i < s.Length; i++)
num = num * 10 + ((int) (s[i]) - 48);
num = num * -1;
}
return num;
}
// This function receives a node of the syntax
// tree and recursively evaluate it
public static int evalTree(Node root) {
// Empty tree
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Leaf node i.e, an integer
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return toInt(root.data);
// Evaluate left subtree
int leftEval = evalTree(root.left);
// Evaluate right subtree
int rightEval = evalTree(root.right);
// Check which operator to apply
if (root.data.Equals("+"))
return leftEval + rightEval;
if (root.data.Equals("-"))
return leftEval - rightEval;
if (root.data.Equals("*"))
return leftEval * rightEval;
return leftEval / rightEval;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
// Creating a sample tree
Node root = new Node("+");
root.left = new Node("*");
root.left.left = new Node("5");
root.left.right = new Node("-4");
root.right = new Node("-");
root.right.left = new Node("100");
root.right.right = new Node("20");
Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root));
root = null;
// Creating a sample tree
root = new Node("+");
root.left = new Node("*");
root.left.left = new Node("5");
root.left.right = new Node("4");
root.right = new Node("-");
root.right.left = new Node("100");
root.right.right = new Node("/");
root.right.right.left = new Node("20");
root.right.right.right = new Node("2");
Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root));
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616Javascript
输出
60
110时间复杂度: O(n),因为每个节点都被访问一次。