- Cassandra-数据模型(1)
- Cassandra数据模型(1)
- 数据模型 - Python 代码示例
- 分层数据模型与网络数据模型之间的区别
- 分层数据模型与网络数据模型之间的区别(1)
- 扩展数据模型
- 扩展数据模型(1)
- 数据模型的构建块
- 数据模型的构建块(1)
- 关系数据模型
- 关系数据模型(1)
- DBMS |数据模型
- DBMS中的数据模型
- DBMS 中的数据模型
- DBMS 中的数据模型(1)
- DBMS-数据模型
- DBMS 中的数据模型
- DBMS |数据模型(1)
- DBMS中的数据模型(1)
- DBMS 中的数据模型(1)
- DBMS-数据模型(1)
- 将数据加载到数据模型中(1)
- 将数据加载到数据模型中
- 多维数据模型(1)
- 多维数据模型
- Neo4j-数据模型
- Neo4j中的数据模型(1)
- Neo4j中的数据模型
- Neo4j-数据模型(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-02 06:12:34 🧑 作者: Mango
Cassandra的数据模型与我们通常在RDBMS中看到的模型大不相同。本章概述了Cassandra如何存储其数据。
簇
Cassandra数据库分布在可以一起运行的多台计算机上。最外层的容器称为群集。对于故障处理,每个节点都包含一个副本,如果发生故障,则由副本负责。 Cassandra以环形格式将节点排列在群集中,并为其分配数据。
键空间
键空间是Cassandra中数据的最外层容器。 Cassandra中Keyspace的基本属性是-
-
复制因子-它是集群中将接收相同数据副本的计算机数。
-
副本放置策略-只是将副本放置在环中的策略。我们有一些策略,例如简单策略(机架感知策略),旧网络拓扑策略(机架感知策略)和网络拓扑策略(数据中心共享策略)。
-
列族-键空间是一个或多个列族列表的容器。列族又是行集合的容器。每行包含有序的列。列族代表数据的结构。每个键空间至少有一个列族,经常有许多列族。
创建Keyspace的语法如下-
CREATE KEYSPACE Keyspace name
WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor' : 3};
下图显示了键空间的示意图。
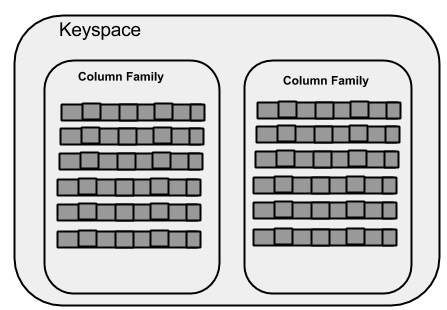
列族
列族是用于行的有序集合的容器。每行又是列的有序集合。下表列出了区分列族和关系数据库表的要点。
| Relational Table | Cassandra column Family |
|---|---|
| A schema in a relational model is fixed. Once we define certain columns for a table, while inserting data, in every row all the columns must be filled at least with a null value. | In Cassandra, although the column families are defined, the columns are not. You can freely add any column to any column family at any time. |
| Relational tables define only columns and the user fills in the table with values. | In Cassandra, a table contains columns, or can be defined as a super column family. |
Cassandra列族具有以下属性-
-
keys_cached-代表每个SSTable保持缓存位置的数量。
-
rows_cached-表示其全部内容将被缓存在内存中的行数。
-
preload_row_cache-它指定是否要预填充行缓存。
注–与不固定列族模式的关系表不同,Cassandra不会强制单个行包含所有列。
下图显示了Cassandra列系列的示例。
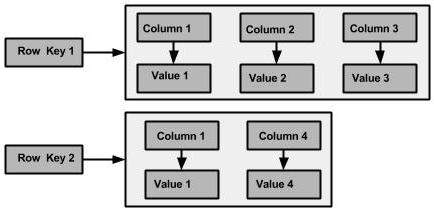
柱
列是Cassandra的基本数据结构,具有三个值,即键或列名,值和时间戳。下面给出的是列的结构。

超柱
超级列是特殊列,因此,它也是一个键值对。但是超级列存储子列的地图。
通常,列族存储在磁盘上的单个文件中。因此,为了优化性能,将可能要查询的列保持在同一列族中很重要,在此超级列可能会有所帮助。以下是超级列的结构。

Cassandra和RDBMS的数据模型
下表列出了区分Cassandra数据模型和RDBMS数据模型的要点。
| RDBMS | Cassandra |
|---|---|
| RDBMS deals with structured data. | Cassandra deals with unstructured data. |
| It has a fixed schema. | Cassandra has a flexible schema. |
| In RDBMS, a table is an array of arrays. (ROW x COLUMN) | In Cassandra, a table is a list of “nested key-value pairs”. (ROW x COLUMN key x COLUMN value) |
| Database is the outermost container that contains data corresponding to an application. | Keyspace is the outermost container that contains data corresponding to an application. |
| Tables are the entities of a database. | Tables or column families are the entity of a keyspace. |
| Row is an individual record in RDBMS. | Row is a unit of replication in Cassandra. |
| Column represents the attributes of a relation. | Column is a unit of storage in Cassandra. |
| RDBMS supports the concepts of foreign keys, joins. | Relationships are represented using collections. |