📌 相关文章
- 数据分析和数据分析的区别
- 数据分析和数据分析的区别(1)
- 图表中的饼图(1)
- 图表中的饼图
- 大数据分析-数据分析工具(1)
- 大数据分析-数据分析工具
- 数据分析的使用(1)
- 数据分析的使用
- python中的图表(1)
- javascript中的图表(1)
- 什么是数据分析?
- 什么是数据分析?(1)
- 图表 js 删除旧图表 - Javascript (1)
- Excel图表-图表元素(1)
- Excel图表-图表元素
- 图表 js 删除旧图表 - Javascript 代码示例
- Excel图表-创建图表(1)
- Excel图表-创建图表
- python代码示例中的图表
- javascript代码示例中的图表
- 图表 js 清除图表 - Javascript (1)
- Excel图表-图表样式
- Excel图表-图表样式(1)
- 图表 js 清除图表 - Javascript 代码示例
- Excel图表-图表过滤器
- Excel图表-图表过滤器(1)
- 反应图表图表标题 - Javascript (1)
- 大数据分析教程
- 大数据分析教程(1)
📜 大数据分析-图表
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-02 06:42:12 🧑 作者: Mango
分析数据的第一种方法是对数据进行可视化分析。这样做的目的通常是寻找变量与变量的单变量描述之间的关系。我们可以将这些策略划分为-
- 单变量分析
- 多元分析
单变量图形方法
单变量是一个统计术语。实际上,这意味着我们要独立于其余数据来分析变量。允许有效地做到这一点的情节是-
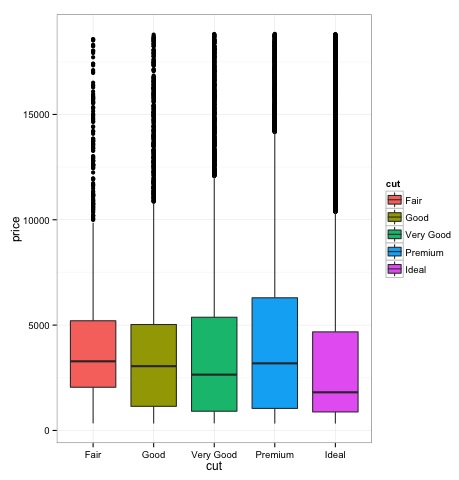
箱线图
箱形图通常用于比较分布。这是一种直观检查分布之间是否存在差异的好方法。我们可以看到不同切割的钻石价格之间是否存在差异。
# We will be using the ggplot2 library for plotting
library(ggplot2)
data("diamonds")
# We will be using the diamonds dataset to analyze distributions of numeric variables
head(diamonds)
# carat cut color clarity depth table price x y z
# 1 0.23 Ideal E SI2 61.5 55 326 3.95 3.98 2.43
# 2 0.21 Premium E SI1 59.8 61 326 3.89 3.84 2.31
# 3 0.23 Good E VS1 56.9 65 327 4.05 4.07 2.31
# 4 0.29 Premium I VS2 62.4 58 334 4.20 4.23 2.63
# 5 0.31 Good J SI2 63.3 58 335 4.34 4.35 2.75
# 6 0.24 Very Good J VVS2 62.8 57 336 3.94 3.96 2.48
### Box-Plots
p = ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = cut, y = price, fill = cut)) +
geom_box-plot() +
theme_bw()
print(p)
我们可以从图中看到,不同类型的切割中钻石价格分布存在差异。
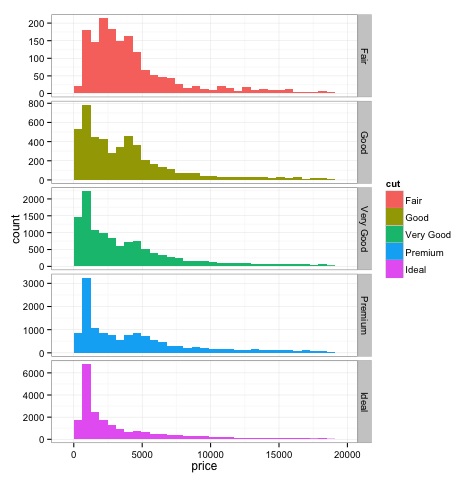
直方图
source('01_box_plots.R')
# We can plot histograms for each level of the cut factor variable using
facet_grid
p = ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = price, fill = cut)) +
geom_histogram() +
facet_grid(cut ~ .) +
theme_bw()
p
# the previous plot doesn’t allow to visuallize correctly the data because of
the differences in scale
# we can turn this off using the scales argument of facet_grid
p = ggplot(diamonds, aes(x = price, fill = cut)) +
geom_histogram() +
facet_grid(cut ~ ., scales = 'free') +
theme_bw()
p
png('02_histogram_diamonds_cut.png')
print(p)
dev.off()
上面的代码输出如下:
多元图形方法
探索性数据分析中的多元图形方法的目的是发现不同变量之间的关系。通常有两种方法可以实现此目的:绘制数值变量的相关矩阵或简单地将原始数据绘制为散点图矩阵。
为了证明这一点,我们将使用钻石数据集。要遵循该代码,请打开脚本bda / part2 / charts / 03_multivariate_analysis.R 。
library(ggplot2)
data(diamonds)
# Correlation matrix plots
keep_vars = c('carat', 'depth', 'price', 'table')
df = diamonds[, keep_vars]
# compute the correlation matrix
M_cor = cor(df)
# carat depth price table
# carat 1.00000000 0.02822431 0.9215913 0.1816175
# depth 0.02822431 1.00000000 -0.0106474 -0.2957785
# price 0.92159130 -0.01064740 1.0000000 0.1271339
# table 0.18161755 -0.29577852 0.1271339 1.0000000
# plots
heat-map(M_cor)
该代码将产生以下输出-
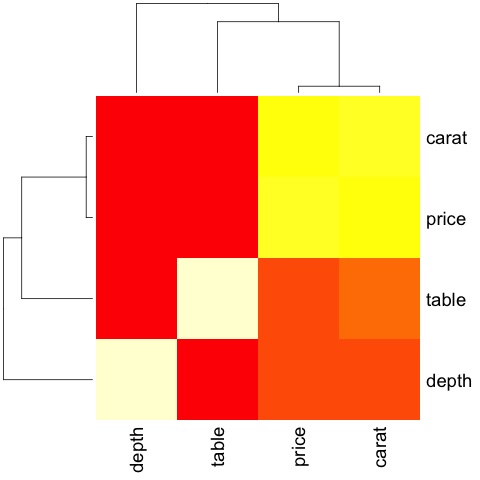
这是一个总结,它告诉我们价格和插入号之间有很强的相关性,而其他变量之间的相关性不大。
当我们有大量变量时,相关矩阵会很有用,在这种情况下,绘制原始数据将不切实际。如上所述,还可以显示原始数据-
library(GGally)
ggpairs(df)
我们可以从图中看出,热图上显示的结果已得到确认,价格和克拉变量之间存在0.922的相关性。
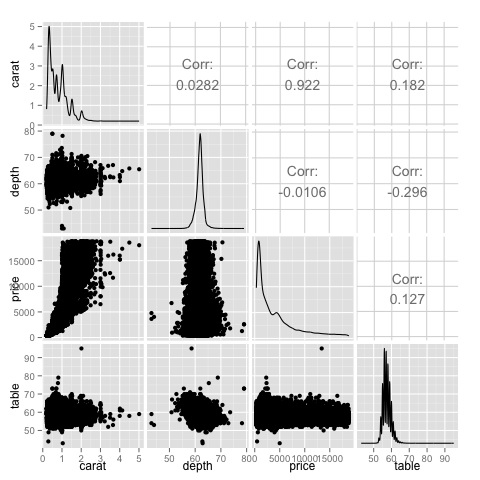
可以在散点图矩阵的(3,1)索引中的价格克拉散点图中可视化此关系。