胺的命名
胺是有机化学中在碱性氮原子上具有孤对的分子和官能团。胺是正式的氨衍生物,其中一个或多个氢原子被烷基或芳基取代(这些可分别称为烷基胺和芳基胺;两种类型的取代基都连接到一个氮原子上的胺可称为烷基芳基胺)。氨基酸、生物胺、三甲胺、苯胺都是重要的胺;可以在类别:胺中找到完整的胺列表。一氯胺和其他无机氨衍生物称为胺(NClH 2 )。氨基是指取代基-NH 2 。
胺的结构
Amines, like ammonia, have a trivalent nitrogen atom with an unshared pair of electrons. As a result, amines’ nitrogen orbitals are sp3 hybridised, and their geometry is pyramidal.
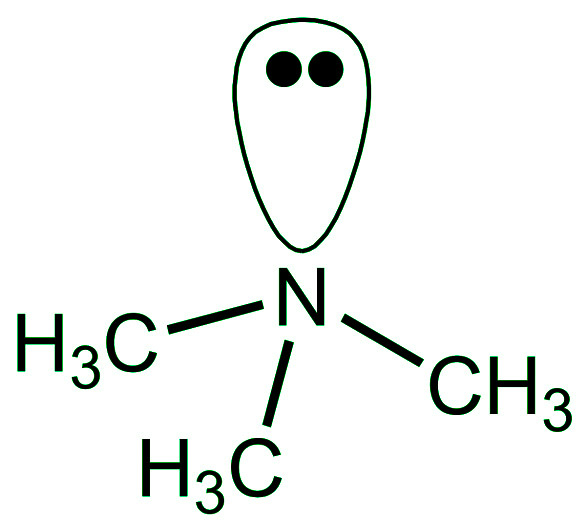
根据胺的组成,氮的三个 sp 3杂化轨道中的每一个都与氢或碳的轨道重叠。所有胺在氮的第四轨道上都有一对非共享电子。由于存在一对未共享的电子,C-N-E 的角度(其中 E 是 C 或 H)小于 109.5 ∘ ;例如,在三甲胺的情况下为 108 ∘ ,如图 1 所示。
胺的分类
胺是衍生自氨 (NH 3 ) 的化合物。来自氨的氢基团被替换以产生这些衍生物。烷基或芳基负责取代氨中的氢原子。胺在其自然状态下表现得像碱。这是因为氮原子本身在其轨道上有 2 个价电子。该化学品还具有与其相连的烷基、芳基和氢原子。结果,胺基用作碱和电子供体。
母体氨中被胺中的烷基或芳基取代的氢原子数可用于对其进行分类。就分类而言,胺与烷基卤化物或醇不同。其根本原因是在胺中,氮原子形成三个中性单键并与之形成孤对。其他基团最多可以代替氨中的三个氢原子。然而,可以删除单独的一对,并通过随后的卤化物处理添加一个新的组。
- 伯胺、仲胺、叔胺和季胺是四种胺。 1°、2°、3°、4° 胺分别是伯胺、仲胺、叔胺和季胺。
- 1° 胺是伯氨基酸的另一个名称。伯胺是通过取代氨中的一个氢原子制成的。氨基是伯胺的另一个名称。因为它含有两个氢原子和一个烷基,所以这种胺是极碱性的。此外,氮有两个价电子,使分子非常碱性。
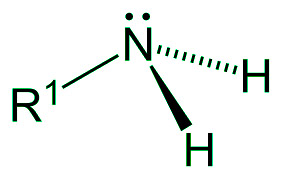
伯胺
- 2°胺也称为仲胺。仲胺是通过取代氨分子中的两个氢原子制成的。烷基或芳基用于取代化合物的两个氢原子。
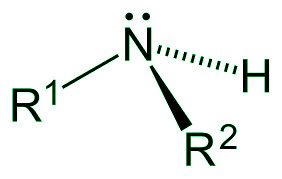
仲胺
- 3°胺是叔胺的别称。氨中所有三个氢原子的取代产生这些胺。烷基或芳基可用于取代氢原子。因为分子中没有氢原子,所以它的沸点比其他胺衍生物低。这是由于它们无法相互形成氢键。

叔胺
- 4°胺是季胺的另一个名称。季胺是与卤化物形成键的季铵化合物。
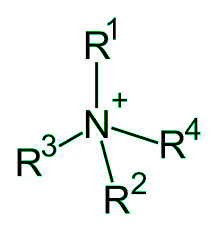
季胺
胺的命名
胺也称为烷基胺。按字母顺序,确定与 N 原子相连的烷基,然后是胺。在 IUPAC 命名系统中,它们被称为 Alkanamine。选择与 N 原子相连的碳原子链最长的母体化合物,后缀胺取代母体烃名称中的最后一个字母“e”。
按字母顺序,取代基称为前缀。混合胺中的烷基名称按字母顺序列出。当两个或三个相同的烷基连接到氮原子时,前缀 di- 或 tri- 被添加到烷基的名称中。以下是一些知名胺的 IUPAC 名称(粗体字母)和常用名称(括号中)。
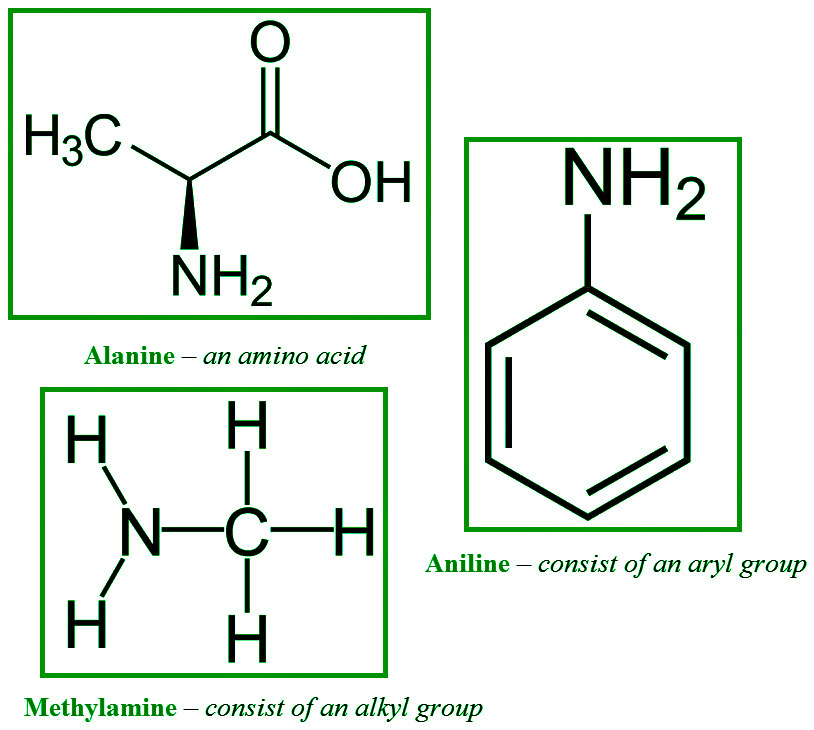
- 伯胺:当氨中的三个氢原子之一被烷基或芳族基团取代时,会形成伯胺。甲胺和大多数氨基酸是重要的基本烷基胺,而苯胺是一种伯芳香胺。
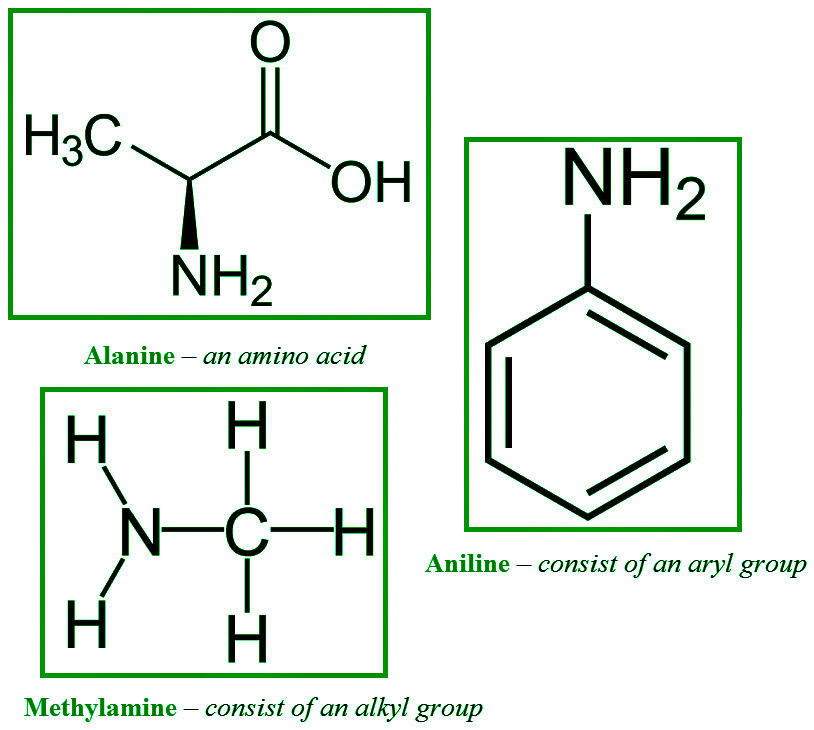
大多数仲胺和叔胺的名称是相似的。如果有机组不同,我们单独表示它们,如果它们在通用语言中相同,则使用前缀 di- 或 tri-。位置 N 在系统命名法中用于识别与氮原子键合的取代基。
- 仲胺:仲胺是具有两个有机取代基的胺,可以是烷基、芳基或两者兼有。它们通过氢原子与氮相连。仲胺比伯胺和叔胺碱性更强。接受质子后产生的化学物质的稳定性用于解释胺的碱性(将氮原子上的孤对电子提供给质子)。给电子基团是烷基。由于烷基的给电子能力,具有两个烷基的仲胺中氮原子上的正电荷降低。因此,仲胺比其他胺更具碱性。
例如二甲胺就是一个众所周知的例子。另一方面,二苯胺是一种芳香胺。

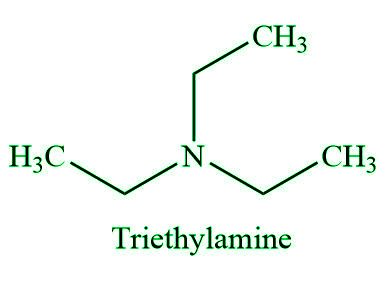
- 叔胺:氨分子中的所有氢都被叔胺中的烃基取代。同样,您更有可能遇到所有三个烃基均为烷基且所有三个相同的简单烃基。该名称类似于仲胺。
例如,两个例子是三甲胺(具有明显的鱼腥味)和 EDTA。
- 芳胺: NH 2基团直接与芳胺中的苯环相连。芳香胺在通用命名系统中称为芳胺,通过在芳基名称上加后缀胺来命名。它们也被称为苯胺的衍生物,苯胺是最基本的芳香胺。
例如,最简单的芳香胺是苯胺,其他胺在 IUPAC 体系中被指定为苯胺的衍生物。胺的全名总是写成一个单词。下面列出了一些芳香胺及其常用名称和 IUPAC 名称。

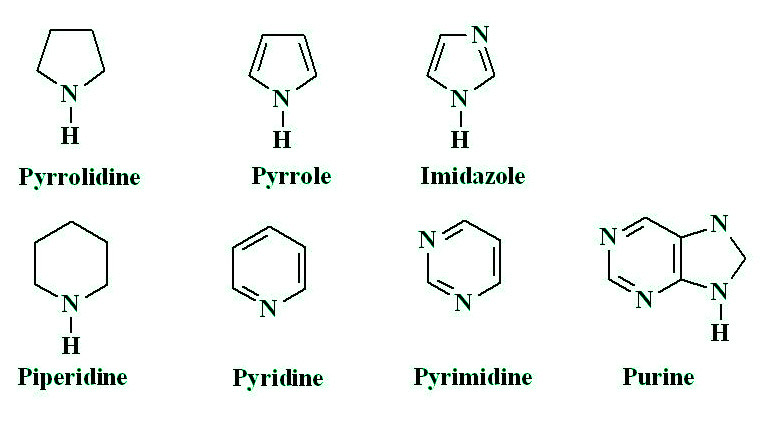
- 杂环胺:杂环胺 (HCA) 是在烹制牛肉、猪、家禽和鱼等肌肉肉时产生的致癌和致突变化合物。当氨基酸和肌酸在高温烹调下结合时,会产生 HCA,并且当肉类过度煮熟或变黑时,它们会形成更多数量的 HCA。由于烹饪肌肉肉,已鉴定出 17 种不同的 HCA,它们可能对人类构成癌症风险。
当 HCA 被细胞色素 P450 1A2 介导的氨基氧化激活,随后乙酰化或硫酸化产生直接作用的反应性诱变剂攻击 DNA 中的关键位点时,它们具有很高的致癌潜力。这些 HCA 中的一些已被证明会导致大鼠的乳腺、结肠和胰腺癌。避免高温烹饪、添加高抗氧化剂的食物或添加大豆蛋白都有助于减少食物中的 HCA。尽管如此,没有确凿的证据表明烹饪程度会影响结直肠癌的风险。
示例问题
问题1:描述胺的结构。
回答:
The nitrogen atom of amines is trivalent and bears an unshared pair of electrons in its structure. As a result, amines’ nitrogen orbitals are sp3 hybridised, and their geometry is pyramidal. Each of the three hybridised orbitals of nitrogen overlaps with orbitals of hydrogen or carbon, depending on the amine composition. In the fourth orbital of nitrogen, all amines have an unshared pair of electrons. Due to the presence of an unshared pair of electrons, the angle C–N–E (where E is C or H) is less than 109.5∘ ; for example, in the case of trimethylamine, it is 108∘ .
问题2:描述胺的分类?
回答:
Amines are divided into several categories. Amines are ammonia-based organic compounds with alkyl or aryl groups replacing one or more hydrogen atoms. Depending on whether alkyl groups replace one, two, or all three hydrogen atoms in ammonia, they are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary (R). Amines are ammonia derivatives that are made by substituting alkyl and/or aryl groups for one, two, or all three hydrogen atoms.
问题3:胺的命名是怎么做的?
回答:
The amines can be named in a variety of ways. Amines are also known as alkylamines. In alphabetical order, the alkyl groups linked to the N-atom are identified, followed by amine. In the IUPAC nomenclature system, they are referred to as Alkanamine. The parent compound with the longest carbon atom chain attached to the N-atom is chosen, and the suffix amine substitutes the last letter “e” in the parent hydrocarbon’s name. Prefixes are the names given to the substituents in alphabetical sequence.
问题4:什么是伯胺?给出一些常见胺的IUPAC名称和通用名称。
回答:
Primary amines are formed when one of the three hydrogen atoms in ammonia is replaced with an alkyl or aromatic group. Methylamine and most amino acids are important fundamental alkylamines, while aniline is a primary aromatic amine.
问题5:胺的碱度顺序是什么?
回答:
Amine has the ability to contribute a pair of electrons to form a base due to the presence of lone pair electrons on the nitrogen atom. The basicity of amines is determined by the following criteria: structural, electronic, and solvent considerations.
In the gaseous state the order of basicity of amine, when R = Me, 3°>2°>1°
In the aqueous solution the order of basicity of amine, when R = Me, 2°>1°>3°
In the aqueous solution the order of basicity of amine, when R = Et, 2°>3°>1°
问题 6:胺是如何制备的?
回答:
Some of the important methods of preparation of amines are:
- Alkylation of Ammonia
- Alkylation of Azide Ion and Reduction
- Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis
- Reduction of Nitro Compounds
- Reduction of Nitriles, Isonitriles, and Oximes
- Reductive Amination of Carbonyl Compounds
- From Amides
- Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation