基于可增长数组的堆栈
我们都知道堆栈也称为后进先出(LIFO)结构。 Stack主要有两个主要操作,即push和pop,其中push在顶部插入一个元素,pop从堆栈顶部移除一个元素。
现在,每当考虑堆栈的实现时,它的大小都是预先确定的或固定的。即使它是动态分配的,一旦它被分配,它的大小仍然不能改变。因此出现了一种称为“堆栈已满”的情况。
但是,如果堆栈可以随着更多元素的插入或将来插入更多元素而增长怎么办。请记住,我们谈论的是基于数组的堆栈。可增长堆栈是分配更多内存的概念,这样“堆栈已满”的情况就不会轻易出现。
可以通过分配比先前堆栈内存更大的新内存并将元素从旧堆栈复制到新堆栈来实现基于数组的可增长堆栈。然后最后将新堆栈的名称更改为旧堆栈的名称
可增长堆栈有两种策略:
1. Tight Strategy : 向旧栈中添加一个常量 (N+c)
2.增长策略:旧堆栈大小翻倍(2N)
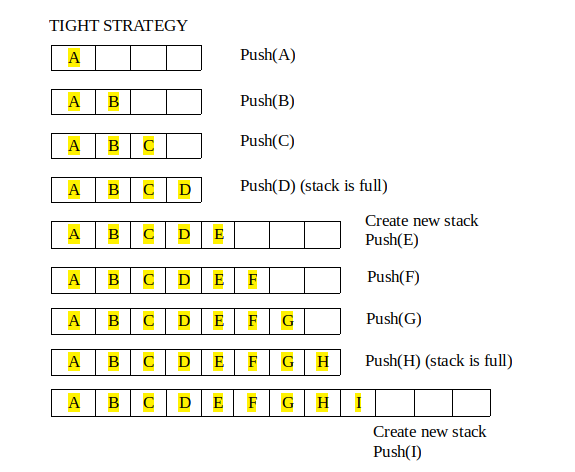
可增长堆栈上有两个操作:
1. 常规推送操作:在栈顶添加一个元素
2. 特殊推送操作:创建一个大小大于旧堆栈的新堆栈(根据上述策略之一)并从旧堆栈中复制所有元素,然后将新元素推送到新堆栈。
C++
// CPP Program to implement growable array based stack
// using tight strategy
#include
using namespace std;
// constant amount at which stack is increased
#define BOUND 4
// top of the stack
int top = -1;
// length of stack
int length = 0;
// function to create new stack
int* create_new(int* a)
{
// allocate memory for new stack
int* new_a = new int[length + BOUND];
// copying the content of old stack
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
new_a[i] = a[i];
// re-sizing the length
length += BOUND;
return new_a;
}
// function to push new element
int* push(int* a, int element)
{
// if stack is full, create new one
if (top == length - 1)
a = create_new(a);
// insert element at top of the stack
a[++top] = element;
return a;
}
// function to pop an element
void pop(int* a)
{
top--;
}
// function to display
void display(int* a)
{
// if top is -1, that means stack is empty
if (top == -1)
cout << "Stack is Empty" << endl;
else {
cout << "Stack: ";
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// creating initial stack
int *a = create_new(a);
// pushing element to top of stack
a = push(a, 1);
a = push(a, 2);
a = push(a, 3);
a = push(a, 4);
display(a);
// pushing more element when stack is full
a = push(a, 5);
a = push(a, 6);
display(a);
a = push(a, 7);
a = push(a, 8);
display(a);
// pushing more element so that stack can grow
a = push(a, 9);
display(a);
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to implement growable array based stack
// using tight strategy
class GFG
{
// constant amount at which stack is increased
static final int BOUND = 4;
// top of the stack
static int top = -1;
// length of stack
static int length = 0;
// function to create new stack
static int[] create_new(int[] a)
{
// allocate memory for new stack
int[] new_a = new int[length + BOUND];
// copying the content of old stack
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
new_a[i] = a[i];
// re-sizing the length
length += BOUND;
return new_a;
}
// function to push new element
static int[] push(int[] a, int element)
{
// if stack is full, create new one
if (top == length - 1)
a = create_new(a);
// insert element at top of the stack
a[++top] = element;
return a;
}
// function to pop an element
static void pop(int[] a)
{
top--;
}
// function to display
static void display(int[] a)
{
// if top is -1, that means stack is empty
if (top == -1)
System.out.println("Stack is Empty");
else
{
System.out.print("Stack: ");
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++)
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// creating initial stack
int []a = create_new(new int[length + BOUND]);
// pushing element to top of stack
a = push(a, 1);
a = push(a, 2);
a = push(a, 3);
a = push(a, 4);
display(a);
// pushing more element when stack is full
a = push(a, 5);
a = push(a, 6);
display(a);
a = push(a, 7);
a = push(a, 8);
display(a);
// pushing more element so that stack can grow
a = push(a, 9);
display(a);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghPython3
# Python3 Program to implement growable array based stack
# using tight strategy
# constant amount at which stack is increased
BOUND = 4
# top of the stack
top = -1;
a = []
# length of stack
length = 0;
# function to create new stack
def create_new():
global length;
# allocate memory for new stack
new_a = [0 for i in range(length + BOUND)];
# copying the content of old stack
for i in range(length):
new_a[i] = a[i];
# re-sizing the length
length += BOUND;
return new_a
# function to push new element
def push( element):
global top, a
# if stack is full, create new one
if (top == length - 1):
a = create_new();
top +=1
# insert element at top of the stack
a[top] = element;
return a;
# function to pop an element
def pop():
global top
top -= 1;
# function to display
def display():
global top
# if top is -1, that means stack is empty
if (top == -1):
print("Stack is Empty")
else:
print("Stack: ", end = '')
for i in range(top + 1):
print(a[i], end = ' ')
print()
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# creating initial stack
a = create_new();
# pushing element to top of stack
push(1);
push(2);
push(3);
push(4);
display();
# pushing more element when stack is full
push(5);
push(6);
display();
push(7);
push(8);
display();
# pushing more element so that stack can grow
push( 9);
display();
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56.C#
// C# Program to implement growable array based stack
// using tight strategy
using System;
class GFG
{
// constant amount at which stack is increased
static int BOUND = 4;
// top of the stack
static int top = -1;
// length of stack
static int length = 0;
// function to create new stack
static int[] create_new(int[] a)
{
// allocate memory for new stack
int[] new_a = new int[length + BOUND];
// copying the content of old stack
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
new_a[i] = a[i];
// re-sizing the length
length += BOUND;
return new_a;
}
// function to push new element
static int[] push(int[] a, int element)
{
// if stack is full, create new one
if (top == length - 1)
a = create_new(a);
// insert element at top of the stack
a[++top] = element;
return a;
}
// function to pop an element
static void pop(int[] a)
{
top--;
}
// function to display
static void display(int[] a)
{
// if top is -1, that means stack is empty
if (top == -1)
Console.WriteLine("Stack is Empty");
else
{
Console.Write("Stack: ");
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++)
Console.Write(a[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// creating initial stack
int []a = create_new(new int[length + BOUND]);
// pushing element to top of stack
a = push(a, 1);
a = push(a, 2);
a = push(a, 3);
a = push(a, 4);
display(a);
// pushing more element when stack is full
a = push(a, 5);
a = push(a, 6);
display(a);
a = push(a, 7);
a = push(a, 8);
display(a);
// pushing more element so that stack can grow
a = push(a, 9);
display(a);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
.
输出:
Stack: 1 2 3 4
Stack: 1 2 3 4 5 6
Stack: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Stack: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9