📌 相关文章
- TensorFlow-单层感知器(1)
- TensorFlow中的单层感知器(1)
- TensorFlow中的隐藏层感知器
- TensorFlow中的多层感知器(1)
- TensorFlow中的多层感知器
- R 编程中的单层神经网络(1)
- R 编程中的单层神经网络
- Tensorflow 中的多层感知器学习(1)
- TensorFlow-多层感知器学习(1)
- TensorFlow-多层感知器学习
- Tensorflow 中的多层感知器学习
- PyTorch感知器(1)
- PyTorch感知器
- 非逻辑门感知器算法的实现(1)
- 非逻辑门感知器算法的实现
- TensorFlow 2.0
- TensorFlow 2.0(1)
- TensorFlow 2.0(1)
- TensorFlow 2.0
- 具有3位二进制输入的逻辑门的感知器算法(1)
- 具有3位二进制输入的逻辑门的感知器算法
- 2位二进制输入或逻辑门感知器算法的实现(1)
- 2位二进制输入与逻辑门感知器算法的实现(1)
- 2位二进制输入或逻辑门感知器算法的实现
- 2位二进制输入与逻辑门感知器算法的实现
- 带有 Keras 的多层感知器 带有 Keras 的多层感知器 (1)
- tensorflow - Python (1)
- 带有 Keras 的多层感知器 带有 Keras 的多层感知器 - 无论代码示例
- PyTorch感知器模型|模型设置(1)
📜 TensorFlow-单层感知器
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-10 06:03:31 🧑 作者: Mango
对于理解单层感知器,重要的是理解人工神经网络(ANN)。人工神经网络是一种信息处理系统,其机制受到生物神经电路功能的启发。人工神经网络拥有许多相互连接的处理单元。以下是人工神经网络的示意图-
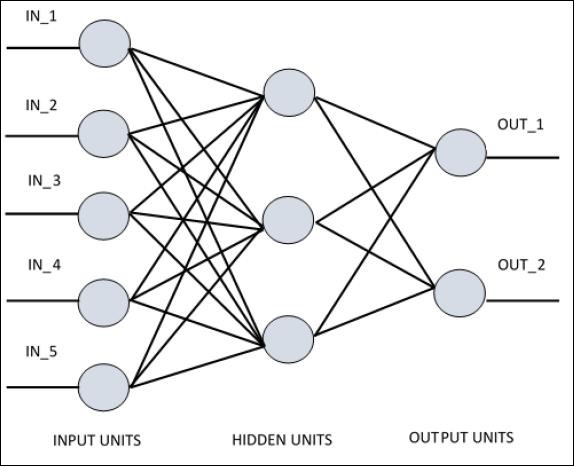
该图显示隐藏的单元与外部层通信。输入和输出单元仅通过网络的隐藏层进行通信。
与节点的连接模式,输入和输出之间的层总数和节点级别以及每层神经元的数量定义了神经网络的体系结构。
有两种类型的体系结构。这些类型专注于人工神经网络的功能,如下所示-
- 单层感知器
- 多层感知器
单层感知器
单层感知器是创建的第一个提出的神经模型。神经元局部记忆的内容由权重向量组成。单层感知器的计算是在输入向量的总和的计算上进行的,每个输入向量的值乘以权重向量的相应元素。输出中显示的值将是激活函数的输入。
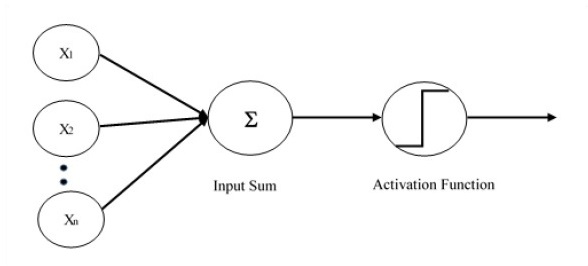
让我们专注于使用TensorFlow解决图像分类问题的单层感知器的实现。展示单层感知器的最佳示例是通过“逻辑回归”的表示。
现在,让我们考虑以下训练逻辑回归的基本步骤-
-
权重在训练开始时用随机值初始化。
-
对于训练集的每个元素,将使用期望输出与实际输出之间的差来计算误差。计算出的误差用于调整权重。
-
重复该过程,直到对整个训练集进行的错误不少于指定的阈值为止,直到达到最大迭代次数为止。
下面提到用于评估逻辑回归的完整代码-
# Import MINST data
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot = True)
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.01
training_epochs = 25
batch_size = 100
display_step = 1
# tf Graph Input
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784]) # mnist data image of shape 28*28 = 784
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10]) # 0-9 digits recognition => 10 classes
# Create model
# Set model weights
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
# Construct model
activation = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b) # Softmax
# Minimize error using cross entropy
cross_entropy = y*tf.log(activation)
cost = tf.reduce_mean\ (-tf.reduce_sum\ (cross_entropy,reduction_indices = 1))
optimizer = tf.train.\ GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
#Plot settings
avg_set = []
epoch_set = []
# Initializing the variables init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0.
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
# Loop over all batches
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = \ mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# Fit training using batch data sess.run(optimizer, \ feed_dict = {
x: batch_xs, y: batch_ys})
# Compute average loss avg_cost += sess.run(cost, \ feed_dict = {
x: batch_xs, \ y: batch_ys})/total_batch
# Display logs per epoch step
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print ("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", "{:.9f}".format(avg_cost))
avg_set.append(avg_cost) epoch_set.append(epoch+1)
print ("Training phase finished")
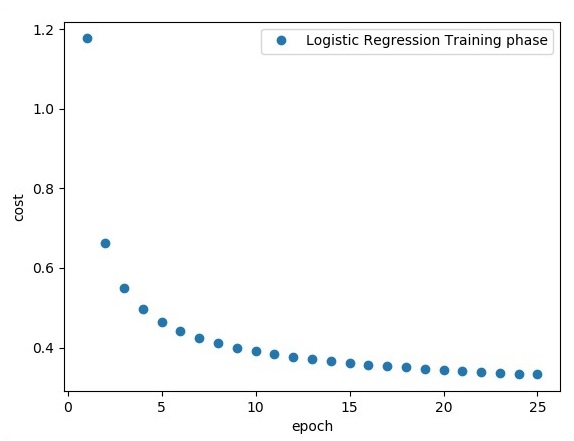
plt.plot(epoch_set,avg_set, 'o', label = 'Logistic Regression Training phase')
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# Test model
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(activation, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
# Calculate accuracy
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) print
("Model accuracy:", accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels}))
输出
上面的代码生成以下输出-
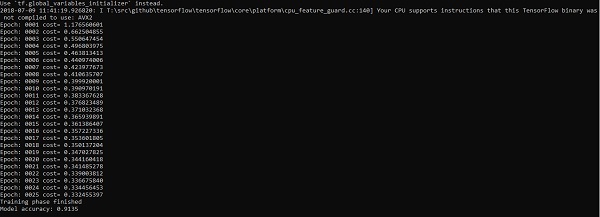
逻辑回归被认为是一种预测分析。 Logistic回归用于描述数据并解释一个因变量和一个或多个名义或自变量之间的关系。