- Java-数字类(1)
- Java-数字类(1)
- 猜数字java(1)
- java中数字的幂(1)
- Java-数字类
- Java 数字字段 (1)
- java 数字中的数字 - Java 代码示例
- java 是数字 - Java (1)
- 猜数字java代码示例
- java代码示例中数字的幂
- java 是数字 - Java 代码示例
- 数字列表java(1)
- 是数字 c# (1)
- C++中的数字
- C++中的数字(1)
- 数字(1)
- 第 n 个数字在 {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 中(1)
- 第n个数字,其数字为{0,1,2,3,4,5}(1)
- 数字
- c++中的强数字(1)
- 第n个数字,其数字为{0,1,2,3,4,5}
- 数字 (1)
- 玩数字
- 玩数字(1)
- 第 n 个数字在 {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 中
- Java 数字字段 - 任何代码示例
- java 从字符串中获取数字 - Java (1)
- 添加数字java(1)
- java 从字符串中删除非数字 - Java (1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-12-21 01:36:06 🧑 作者: Mango
通常,在使用Numbers时,我们使用原始数据类型,例如byte,int,long,double等。
例
int i = 5000;
float gpa = 13.65f;
double mask = 125;
但是,在开发过程中,我们遇到了需要使用对象而不是原始数据类型的情况。为了实现这一点,Java提供了包装器类。
所有包装器类(Integer,Long,Byte,Double,Float,Short)都是抽象类Number的子类。
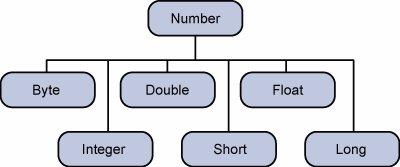
包装类的对象包含或包装其各自的原始数据类型。将原始数据类型转换为对象称为boxing ,编译器会注意这一点。因此,在使用包装器类时,您只需要将原始数据类型的值传递给Wrapper类的构造函数。
Wrapper对象将转换回原始数据类型,此过程称为拆箱。 Number类是java.lang包的一部分。
以下是装箱和拆箱的示例-
例
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Integer x = 5; // boxes int to an Integer object
x = x + 10; // unboxes the Integer to a int
System.out.println(x);
}
}
这将产生以下结果-
输出
15
为x分配整数值时,编译器将整数装箱,因为x是整数对象。以后,将x取消装箱,以便可以将它们添加为整数。
编号方法
以下是Number类的所有子类实现的实例方法的列表-
| Sr.No. | Method & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | xxxValue()
Converts the value of this Number object to the xxx data type and returns it. |
| 2 | compareTo()
Compares this Number object to the argument. |
| 3 | equals()
Determines whether this number object is equal to the argument. |
| 4 | valueOf()
Returns an Integer object holding the value of the specified primitive. |
| 5 | toString()
Returns a String object representing the value of a specified int or Integer. |
| 6 | parseInt()
This method is used to get the primitive data type of a certain String. |
| 7 | abs()
Returns the absolute value of the argument. |
| 8 | ceil()
Returns the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to the argument. Returned as a double. |
| 9 | floor()
Returns the largest integer that is less than or equal to the argument. Returned as a double. |
| 10 | rint()
Returns the integer that is closest in value to the argument. Returned as a double. |
| 11 | round()
Returns the closest long or int, as indicated by the method’s return type to the argument. |
| 12 | min()
Returns the smaller of the two arguments. |
| 13 | max()
Returns the larger of the two arguments. |
| 14 | exp()
Returns the base of the natural logarithms, e, to the power of the argument. |
| 15 | log()
Returns the natural logarithm of the argument. |
| 16 | pow()
Returns the value of the first argument raised to the power of the second argument. |
| 17 | sqrt()
Returns the square root of the argument. |
| 18 | sin()
Returns the sine of the specified double value. |
| 19 | cos()
Returns the cosine of the specified double value. |
| 20 | tan()
Returns the tangent of the specified double value. |
| 21 | asin()
Returns the arcsine of the specified double value. |
| 22 | acos()
Returns the arccosine of the specified double value. |
| 23 | atan()
Returns the arctangent of the specified double value. |
| 24 | atan2()
Converts rectangular coordinates (x, y) to polar coordinate (r, theta) and returns theta. |
| 25 | toDegrees()
Converts the argument to degrees. |
| 26 | toRadians()
Converts the argument to radians. |
| 27 | random()
Returns a random number. |
接下来是什么?
在下一节中,我们将介绍Java中的字符类。您将学习如何在Java中使用对象字符和原始数据类型char。