📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-07 03:48:38 🧑 作者: Mango
分布式跟踪简介
分布式跟踪
分布式跟踪是一种监视和分析应用程序的技术,尤其是使用微服务体系结构构建的应用程序。也称为分布式请求跟踪。开发人员使用分布式跟踪来调试和优化代码。
分布式跟踪提供了一个地方,在这里我们可以看到“特定请求正在发生什么?”这很重要,因为微服务中涉及多种组件。
如果我们要解决问题或调试问题,则需要一个中央服务器。因此,术语“分布式跟踪”应运而生。
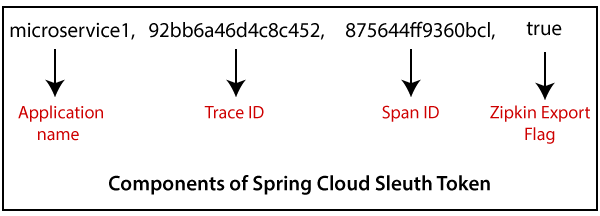
在本节中,我们将结合使用Spring Cloud Sleuth和Zipkin 。 Spring Cloud Sleuth为我们提出的每个请求分配一个唯一的ID。我们可以基于所有组件的唯一ID来跟踪所有请求。
春云侦探
Spring Cloud Sleuth是一个Spring Cloud库,通过在适当的HTTP请求标头上添加跟踪和跨度ID ,可以跟踪后续微服务的进度。 Sleuth库基于MDC (映射诊断上下文)概念,我们可以在其中轻松提取值,放入上下文并在日志中显示它们。
齐普金
Zipkin是一个基于Java的开源分布式跟踪系统。它具有管理控制台,该管理控制台提供了用于发送,接收,存储和可视化后续服务的跟踪详细信息的机制。
借助Zipkin服务器,我们可以将所有组件的所有日志放入MQ (RabbitMQ)中。我们将日志发送到合并日志的Zipkin服务器。完成此操作后,我们可以监视不同的请求。我们还可以查找特定请求的情况?
使用Spring Cloud Sleuth实现分布式跟踪
在这一步中,我们将为所有微服务添加Spring Cloud Sleuth。它为所有请求添加唯一的ID。它用于生成跟踪ID ,跨度ID并将其附加到日志,以便工具(Zipkin)可以使用这些ID。
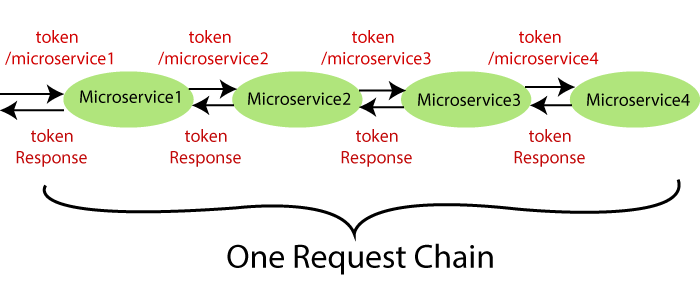
Spring Cloud Sleuth令牌具有以下组件:
- 应用程序名称:在属性文件中定义的应用程序的名称。
- 跟踪ID:侦探添加跟踪ID。对于给定的请求,在所有服务中它都保持不变。
- 跨度ID:侦探还添加了跨度ID。它在一个工作单元中保持不变,但对于给定请求的不同服务而言却不同。
- Zipkin导出标志:表示布尔值。可以是true或
下图显示了Spring Cloud Sleuth令牌。
让我们在项目中实现Spring Cloud Sleuth。
步骤1:选择项目netflix-zuul-api-gateway-server 。
步骤2:打开pom.xml并添加Sleuth依赖项。
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
现在,我们需要跟踪所有请求。如果要跟踪所有请求,则需要创建ALWAYS_SAMPLE 。我们可以使用Bean创建一个Sampler。
取样器
分布式跟踪可能具有非常大量的数据,因此采样在分布式跟踪中很重要。 Spring Cloud Sleuth提供了Sampler策略。在Sampler的帮助下,我们可以实现提供对算法的控制的采样算法。默认情况下,如果跨度(相关性:是单个操作)已经处于活动状态,我们将获得一个连续执行跟踪的过程。
但是新创建的跨度始终标记为nonexportable 。如果所有应用程序都在Sampler上运行,则可以在日志中看到跟踪(由跨度组成的端到端延迟图),而不是在任何远程位置。默认情况下,Spring Cloud Sleuth将所有范围设置为nonexportable 。
当我们将跨度数据导出到Zipkin或Spring Cloud Stream时,Spring Cloud Sleuth提供了AlwaysSampler类,该类将所有内容导出到Zipkin。它还提供了一个PercentageBasedSampler类,该类对跨度的固定部分进行采样。
请记住:如果您使用的是Spring 2.0.0或更高版本,请使用以下Sampler。我们使用相同的方法是因为我们使用的是Spring 2.2.1版本。
@Bean
public Sampler defaultSampler()
{
return Sampler.ALWAYS_SAMPLE;
}
步骤3:打开NetflixZuulApiGatewayServerApplication.java文件并定义一个Bean 。
NetflixZuulApiGatewayServerApplication.java
package com.javatpoint.microservices.netflixzuulapigatewayserver;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.EnableZuulProxy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import brave.sampler.Sampler;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableZuulProxy
public class NetflixZuulApiGatewayServerApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(NetflixZuulApiGatewayServerApplication.class, args);
}
//creating a bean
@Bean
//creating a sampler called
public Sampler defaultSampler()
{
return Sampler.ALWAYS_SAMPLE;
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们已将Spring Cloud Sleuth添加到Zuul API Gateway服务器。
现在,我们还必须在currency-exchange-service和currency-conversion-service中定义Bean。
步骤4:打开currency-exchange-service的pom.xml并添加Sleuth依赖项。
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
步骤5:打开CurrencyExchangeServiceApplication.java文件并定义一个Bean 。
CurrencyExchangeServiceApplication.java
package com.javatpoint.microservices.currencyexchangeservice;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import brave.sampler.Sampler;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class CurrencyExchangeServiceApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(CurrencyExchangeServiceApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
//creating a sampler called always sampler
public Sampler defaultSampler()
{
return Sampler.ALWAYS_SAMPLE;
}
}
步骤6:类似地,打开currency-conversion-service的pom.xml并添加Sleuth依赖项。
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-sleuth
步骤7:打开CurrencyConversionServiceApplication.java文件并定义一个Bean 。
CurrencyConversionServiceApplication.java
package com.javatpoint.microservices.currencyconversionservice;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import brave.sampler.Sampler;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients("com.javatpoint.microservices.currencyconversionservice")
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class CurrencyConversionServiceApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(CurrencyConversionServiceApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
//creating a sampler called always sampler
public Sampler defaultSampler()
{
return Sampler.ALWAYS_SAMPLE;
}
}
现在,我们有三个连接到Spring Cloud Sleuth的应用程序。
步骤8:按以下顺序启动应用程序:
netflix-eureka命名服务器
- 打开浏览器并调用URL http:// localhost:8761 。它返回Eureka界面,如下所示。
货币交换服务(端口8000)
货币兑换服务
netflix-zuul-api-网关服务器
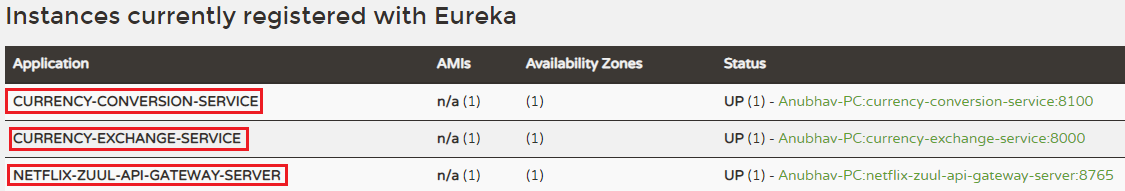
切记:启动每个服务后,刷新Eureka服务器。
它显示了当前在Eureka服务器上注册的所有实例。
步骤9:打开CurrencyExchangeController.java文件,并在其中添加一个记录器。
CurrencyExchangeController.java
package com.javatpoint.microservices.currencyexchangeservice;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class CurrencyExchangeController
{
private Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Autowired
private ExchangeValueRepository repository;
@GetMapping("/currency-exchange/from/{from}/to/{to}") //where {from} and {to} are path variable
public ExchangeValue retrieveExchangeValue(@PathVariable String from, @PathVariable String to) //from map to USD and to map to INR
{
ExchangeValue exchangeValue = repository.findByFromAndTo(from, to);
//setting the port
exchangeValue.setPort(Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("local.server.port")));
logger.info("{}", exchangeValue);
return exchangeValue;
}
}
同样,我们将记录器添加到CurrencyConversionContoller中。
步骤10:打开CurrencyConversionContoller 。 java文件,并在其中添加记录器。
CurrencyConversionContoller 。爪哇
package com.javatpoint.microservices.currencyconversionservice;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class CurrencyConversionController
{
private Logger logger=LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Autowired
private CurrencyExchangeServiceProxy proxy;
@GetMapping("/currency-converter/from/{from}/to/{to}/quantity/{quantity}") //where {from} and {to} represents the column
//returns a bean back
public CurrencyConversionBean convertCurrency(@PathVariable String from, @PathVariable String to, @PathVariable BigDecimal quantity)
{
//setting variables to currency exchange service
Map uriVariables=new HashMap<>();
uriVariables.put("from", from);
uriVariables.put("to", to);
//calling the currency exchange service
ResponseEntity responseEntity=new RestTemplate().getForEntity("http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange/from/{from}/to/{to}", CurrencyConversionBean.class, uriVariables);
CurrencyConversionBean response=responseEntity.getBody();
//creating a new response bean and getting the response back and taking it into Bean
return new CurrencyConversionBean(response.getId(), from, to, response.getConversionMultiple(), quantity, quantity.multiply(response.getConversionMultiple()), response.getPort());
}
//mapping for currency-converter-feign service
@GetMapping("/currency-converter-feign/from/{from}/to/{to}/quantity/{quantity}") //where {from} and {to} represents the column
//returns a bean
public CurrencyConversionBean convertCurrencyFeign(@PathVariable String from, @PathVariable String to, @PathVariable BigDecimal quantity)
{
CurrencyConversionBean response=proxy.retrieveExchangeValue(from, to);
logger.info("{}", response);
//creating a new response bean
//getting the response back and taking it into Bean
return new CurrencyConversionBean(response.getId(), from, to, response.getConversionMultiple(), quantity, quantity.multiply(response.getConversionMultiple()), response.getPort());
}
}
步骤12:执行请求http:// localhost:8100 / currency-converter-feign / from / EUR / to / INR / quantity / 100 。它返回以下响应,如下所示。
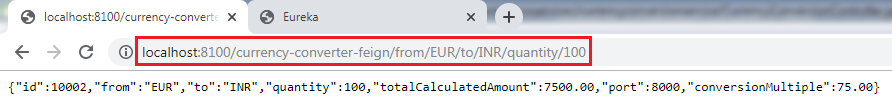
让我们在控制台中查看currency-conversion-service的日志。 currency-conversion-service显示以下日志:

我们还可以看到currency-exchange-service的日志。 currency-exchange-service显示以下日志:

同样,我们可以看到netflix-zuul-api-gateway-server的日志。

让我们仔细看一下以上三种不同服务的日志。我们发现所有这三个服务具有相同的跟踪ID(533f8d3966d8f4e7) 。
Spring Cloud Sleuth将跟踪ID分配给请求。我们可以使用此ID跨多个组件跟踪请求。但是存在一个问题,该日志分布在多个位置。我们使用Zipkin消除此问题。借助Zipkin,我们可以将日志集中在一处。
使用Zipkin进行分布式跟踪
我们已经在currency-conversion-service,currency-exchange-service和netflix-zuul-api-gateway-server中安装了Spring Cloud Sleuth依赖项。我们已经看到为每个请求分配了唯一的ID。我们使用这些ID在这些多个服务的日志中跟踪请求。
但是,我们在跟踪方面面临挑战。如果要跟踪请求,则必须检查单个应用程序的日志。解决此问题的方法称为集中式日志。
我们需要集中所有微服务的所有日志。我们可以搜索Spring Cloud Sleuth分配的ID。在集中的地方,我们将能够搜索并找出特定请求的情况。
有以下用于集中记录的解决方案:
- ELK堆栈(弹性搜索)
- 基巴纳
- 齐普金
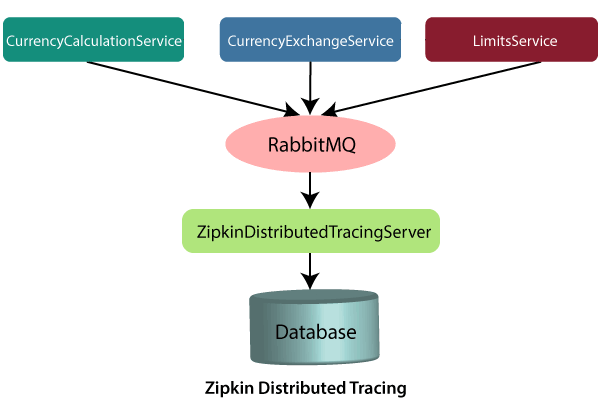
在此分布式跟踪中,我们将使用Zipkin分布式跟踪服务器。它为我们提供了所有微服务的统一视图。我们从单个微服务获取所有日志消息。 Zipkin服务器收集日志消息。所有微服务都将日志消息放在称为RabbitMQ的队列中,而Zipkin从RabbitMQ中选择这些日志消息。 Zipkin跟踪服务器与数据库连接。
在我们的例子中,我们使用内存数据库。我们将从数据库中提取日志消息。在下一步中,我们将安装RabbitMQ。