📌 相关文章
- OpenCV |保存图像
- OpenCV |保存图像(1)
- OpenCV |保存图像
- Python|用于读取和保存图像的 OpenCV 程序
- Python|用于读取和保存图像的 OpenCV 程序(1)
- 如何保存图像 opencv - Python (1)
- 如何保存图像 opencv - Python 代码示例
- 使用Python在 OpenCV 中读取图像
- 使用Python在 OpenCV 中读取图像(1)
- 使用C ++在OpenCV中读取和显示图像
- 使用C ++在OpenCV中读取和显示图像(1)
- 使用C++在OpenCV中读取和显示图像
- 使用C++在OpenCV中读取和显示图像(1)
- python opencv检查图像读取 - Python(1)
- opencv 保存图像 rgb - Python (1)
- python opencv检查图像读取 - Python代码示例
- 在 C# 中保存图像(1)
- opencv 保存图像 rgb - Python 代码示例
- OpenCV-以灰度读取图像
- 在 C# 代码示例中保存图像
- 在Python中读取图像
- 读取图像 python (1)
- OpenCV-将图像读取为BGR(1)
- OpenCV-将图像读取为BGR
- 使用 OpenCV 保存视频
- 使用 OpenCV 保存视频(1)
- 读取图像 python 代码示例
- OpenCV-存储图像
- OpenCV-存储图像(1)
📜 OpenCV读取和保存图像
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-07 06:31:08 🧑 作者: Mango
OpenCV读取并保存图像
OpenCV读取图像
OpenCV允许我们对图像执行多种操作,但是这样做必须读取图像文件作为输入,然后我们才能对其执行各种操作。 OpenCV提供以下用于读取和写入图像的功能。
OpenCV读函数
imread()函数从指定的文件加载图像并返回它。语法为:
cv2.imread(filename[,flag])
参数:
filename:要加载的文件名
flag:该标志指定加载图像的颜色类型:
- CV_LOAD_IMAGE_ANYDEPTH-如果我们将其设置为标志,则当输入具有相应的深度时,它将返回16位/ 32位图像,否则将其转换为8位。
- CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR-如果我们将其设置为标志,它将始终将转换后的图像恢复为原色。
- C V_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE-如果我们将其设置为标志,它将始终将图像转换为灰度。
如果由于不支持的文件格式,缺少的文件,不支持的格式或无效的格式而无法读取图像,则imread()函数将返回一个矩阵。当前,支持以下文件格式。
窗口位图-* .bmp,*。dib
JPEG文件-* .jpeg,*。jpg,*。jpe
便携式网络图形-* .png
便携式图像格式-* .pbm,*。pgm,*。ppm
TIFF文件-* .tiff,*。tif
注意:彩色图像,解码图像将具有按BGR顺序存储的通道。
让我们考虑以下示例:
#importing the opencv module
import cv2
# using imread('path') and 0 denotes read as grayscale image
img = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\DEVANSH SHARMA\cat.jpeg',1)
#This is using for display the image
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(3) # This is necessary to be required so that the image doesn't close immediately.
#It will run continuously until the key press.
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输出:它将显示以下图像。
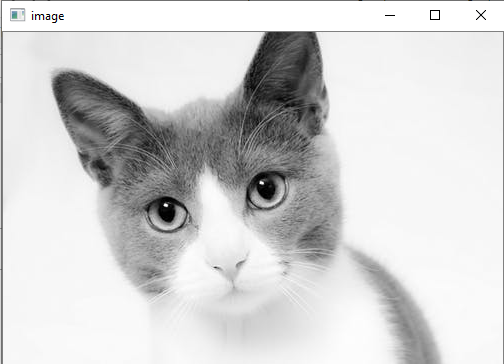
OpenCV保存图像
OpenCV imwrite()函数用于将图像保存到指定文件。文件扩展名定义图像格式。语法如下:
cv2.imwrite(filename, img[,params])
参数:
filename-要加载的文件名
image-要保存的图像。
params-当前支持以下参数:
- 对于JPEG,质量可以从0到100。默认值为95。
- 对于PNG,质量可以是0到9的压缩级别。默认值为1。
- 对于PPM,PGM或PBM,它可以是二进制格式标志0或1。默认值为1。
让我们考虑以下示例:
import cv2
# read image as grey scale
img = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\DEVANSH SHARMA\cat.jpeg', 1)
# save image
status = cv2.imwrite(r'C:\Users\DEVANSH SHARMA\cat.jpeg', 0, img)
print("Image written to file-system : ", status)
输出:
Image written to file-system : True
如果imwrite()函数返回True,则表示文件已成功写入指定的文件中。