R – 图表和图形
R 语言主要用于统计和数据分析目的,以在软件中以图形方式表示数据。为了以图形方式表示这些数据,R 中使用了图表和图形。
R – 图表
R中存在数百种图表和图形。例如,条形图、箱线图、马赛克图、点图、coplot、直方图、饼图、散点图等。
R 的类型 – 图表
- 条形图或条形图
- 饼图或饼图
- 直方图
- 散点图
- 箱形图
条形图或条形图
R中的条形图或条形图用于将数据向量中的值表示为条形的高度。传递给函数的数据向量在图形的 y 轴上表示。通过使用table()函数而不是数据向量,条形图可以表现得像直方图。
Syntax: barplot(data, xlab, ylab)
where:
- data is the data vector to be represented on y-axis
- xlab is the label given to x-axis
- ylab is the label given to y-axis
注意:要了解barplot()函数中的更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("barplot")例子:
R
# defining vector
x <- c(7, 15, 23, 12, 44, 56, 32)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "barplot.png")
# plotting vector
barplot(x, xlab = "GeeksforGeeks Audience",
ylab = "Count", col = "white",
col.axis = "darkgreen",
col.lab = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()R
# defining vector x with number of articles
x <- c(210, 450, 250, 100, 50, 90)
# defining labels for each value in x
names(x) <- c("Algo", "DS", "Java", "C", "C++", "Python")
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "piechart.png")
# creating pie chart
pie(x, labels = names(x), col = "white",
main = "Articles on GeeksforGeeks", radius = -1,
col.main = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()R
# importing library plotrix for pie3D()
library(plotrix)
# defining vector x with number of articles
x <- c(210, 450, 250, 100, 50, 90)
# defining labels for each value in x
names(x) <- c("Algo", "DS", "Java", "C", "C++", "Python")
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "piechart3d.png")
# creating pie chart
pie3D(x, labels = names(x), col = "white",
main = "Articles on GeeksforGeeks",
labelcol = "darkgreen", col.main = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()R
# defining vector
x <- c(21, 23, 56, 90, 20, 7, 94, 12,
57, 76, 69, 45, 34, 32, 49, 55, 57)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "hist.png")
# hist(x, main = "Histogram of Vector x",
xlab = "Values",
col.lab = "darkgreen",
col.main = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()R
# taking input from dataset Orange already
# present in R
orange <- Orange[, c('age', 'circumference')]
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "plot.png")
# plotting
plot(x = orange$age, y = orange$circumference, xlab = "Age",
ylab = "Circumference", main = "Age VS Circumference",
col.lab = "darkgreen", col.main = "darkgreen",
col.axis = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()R
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "plotmatrix.png")
# plotting scatterplot matrix
# using dataset Orange
pairs(~age + circumference, data = Orange,
col.axis = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()R
# defining vector with ages of employees
x <- c(42, 21, 22, 24, 25, 30, 29, 22,
23, 23, 24, 28, 32, 45, 39, 40)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "boxplot.png")
# plotting
boxplot(x, xlab = "Box Plot", ylab = "Age",
col.axis = "darkgreen", col.lab = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()输出:

饼图或饼图
饼图是一个圆形图表,根据提供的数据的比例分为不同的部分。饼图的总值为 100,而各个部分表示整个饼图的比例。这是以图形形式表示统计数据的另一种方法,而pie()函数用于执行相同的操作。
Syntax: pie(x, labels, col, main, radius)
where,
- x is data vector
- labels shows names given to slices
- col fills the color in the slices as given parameter
- main shows title name of the pie chart
- radius indicates radius of the pie chart. It can be between -1 to +1
注意:要了解pie()函数中的更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("pie")例子:
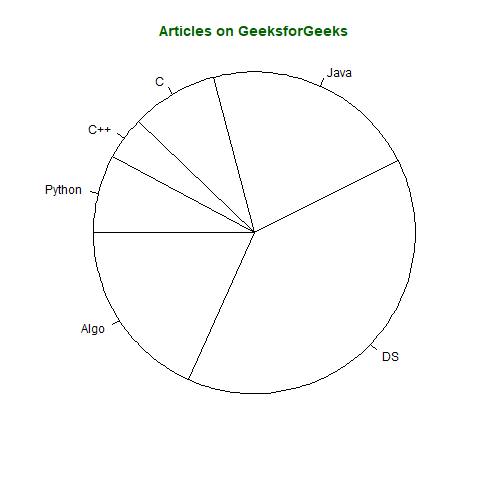
假设,向量 x 表示 GeeksforGeeks 门户网站上以类别名称 (x) 显示的文章数量
R
# defining vector x with number of articles
x <- c(210, 450, 250, 100, 50, 90)
# defining labels for each value in x
names(x) <- c("Algo", "DS", "Java", "C", "C++", "Python")
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "piechart.png")
# creating pie chart
pie(x, labels = names(x), col = "white",
main = "Articles on GeeksforGeeks", radius = -1,
col.main = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:
也可以使用以下语法在 R 中创建 3D 饼图,但需要plotrix库。
Syntax: pie3D(x, labels, radius, main)
注意:要了解 pie3D()函数中的更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("pie3D")例子:
R
# importing library plotrix for pie3D()
library(plotrix)
# defining vector x with number of articles
x <- c(210, 450, 250, 100, 50, 90)
# defining labels for each value in x
names(x) <- c("Algo", "DS", "Java", "C", "C++", "Python")
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "piechart3d.png")
# creating pie chart
pie3D(x, labels = names(x), col = "white",
main = "Articles on GeeksforGeeks",
labelcol = "darkgreen", col.main = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:

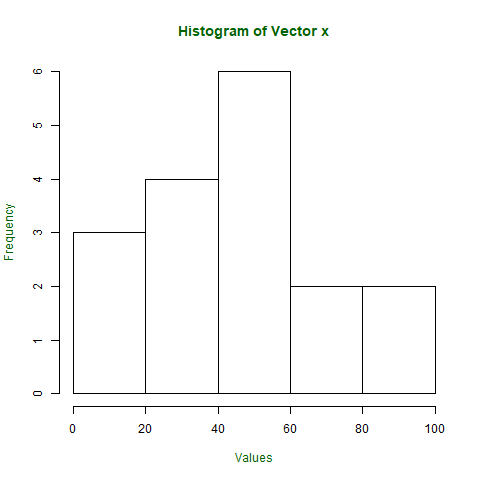
直方图
直方图是一种图形表示,用于创建带有表示向量中分组数据频率的条形图。直方图与条形图相同,但它们之间的唯一区别是直方图表示分组数据的频率,而不是数据本身。
Syntax: hist(x, col, border, main, xlab, ylab)
where:
- x is data vector
- col specifies the color of the bars to be filled
- border specifies the color of border of bars
- main specifies the title name of histogram
- xlab specifies the x-axis label
- ylab specifies the y-axis label
注意:要了解hist()函数中的更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("hist")例子:
R
# defining vector
x <- c(21, 23, 56, 90, 20, 7, 94, 12,
57, 76, 69, 45, 34, 32, 49, 55, 57)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "hist.png")
# hist(x, main = "Histogram of Vector x",
xlab = "Values",
col.lab = "darkgreen",
col.main = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:
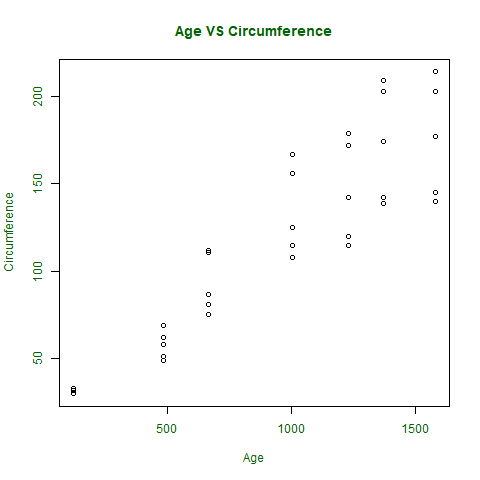
散点图
散点图是另一种类型的图形表示,用于绘制点以显示两个数据向量之间的关系。其中一个数据向量在 x 轴上表示,另一个在 y 轴上表示。
Syntax: plot(x, y, type, xlab, ylab, main)
Where,
- x is the data vector represented on x-axis
- y is the data vector represented on y-axis
- type specifies the type of plot to be drawn. For example, “l” for lines, “p” for points, “s” for stair steps, etc.
- xlab specifies the label for x-axis
- ylab specifies the label for y-axis
- main specifies the title name of the graph
注意:要了解plot()函数中的更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("plot")例子:
R
# taking input from dataset Orange already
# present in R
orange <- Orange[, c('age', 'circumference')]
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "plot.png")
# plotting
plot(x = orange$age, y = orange$circumference, xlab = "Age",
ylab = "Circumference", main = "Age VS Circumference",
col.lab = "darkgreen", col.main = "darkgreen",
col.axis = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:
如果必须绘制散点图以显示 2 个或多个向量之间的关系或绘制向量之间的散点图矩阵,则使用pairs()函数来满足标准。
Syntax: pairs(~formula, data)
where,
- ~formula is the mathematical formula such as ~a+b+c
- data is the dataset form where data is taken in formula
注意:要了解 pair()函数中更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("pairs")例子 :
R
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "plotmatrix.png")
# plotting scatterplot matrix
# using dataset Orange
pairs(~age + circumference, data = Orange,
col.axis = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:

箱形图
箱线图显示了数据在数据向量中的分布情况。它在图中表示五个值,即最小值、第一个四分位数、第二个四分位数(中位数)、第三个四分位数、数据向量的最大值。
Syntax: boxplot(x, xlab, ylab, notch)
where,
- x specifies the data vector
- xlab specifies the label for x-axis
- ylab specifies the label for y-axis
- notch, if TRUE then creates notch on both the sides of the box
注意:要了解boxplot()函数中的更多可选参数,请在 R 控制台中使用以下命令:
help("boxplot")例子:
R
# defining vector with ages of employees
x <- c(42, 21, 22, 24, 25, 30, 29, 22,
23, 23, 24, 28, 32, 45, 39, 40)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file = "boxplot.png")
# plotting
boxplot(x, xlab = "Box Plot", ylab = "Age",
col.axis = "darkgreen", col.lab = "darkgreen")
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:
