📌 相关文章
- 图形和图形模型(1)
- 图形和图形模型
- Python图形数据
- python中的图形实现(1)
- 图形 - 任何代码示例
- python中的图形数据结构(1)
- python代码示例中的图形实现
- 图形在 - C 编程语言(1)
- 如何在Python绘制图形(1)
- 如何在Python绘制图形
- python代码示例中的图形数据结构
- 3d 图形 python (1)
- 在Python中可视化图形
- 在Python中可视化图形(1)
- Matplotlib-图形类
- Matplotlib-图形类(1)
- 图形在 - C 编程语言代码示例
- 3d 图形 python 代码示例
- 图形简介(1)
- 图形简介
- 在C图形中绘制圆
- 在C图形中绘制圆(1)
- MATLAB-图形
- MATLAB-图形(1)
- 图形表示 (1)
- 图形数据结构
- 图形数据结构(1)
- SVG-图形
- SVG-图形(1)
📜 Python图形
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-07 08:39:31 🧑 作者: Mango
图形是一组对象的图形表示,其中一些对象对通过链接连接。相互连接的对象由称为顶点的点表示,而连接这些顶点的链接称为边。与图形相关的各种术语和功能在此处的教程中进行了详细描述。在本章中,我们将了解如何使用Python程序创建图形并向其中添加各种数据元素。以下是我们在图形上执行的基本操作。
- 显示图顶点
- 显示图形边缘
- 添加一个顶点
- 添加边缘
- 创建图
使用Python字典数据类型可以轻松呈现图形。我们将顶点表示为字典的键,并且将顶点之间的连接也称为边作为字典中的值。
看一下下图-
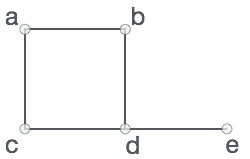
在上图中
V = {a, b, c, d, e}
E = {ab, ac, bd, cd, de}
我们可以在Python程序中显示此图,如下所示。
# Create the dictionary with graph elements
graph = { "a" : ["b","c"],
"b" : ["a", "d"],
"c" : ["a", "d"],
"d" : ["e"],
"e" : ["d"]
}
# Print the graph
print(graph)
执行以上代码后,将产生以下结果-
{'c': ['a', 'd'], 'a': ['b', 'c'], 'e': ['d'], 'd': ['e'], 'b': ['a', 'd']}
显示图顶点
为了显示图顶点,我们简单地找到图字典的键。我们使用keys()方法。
class graph:
def __init__(self,gdict=None):
if gdict is None:
gdict = []
self.gdict = gdict
# Get the keys of the dictionary
def getVertices(self):
return list(self.gdict.keys())
# Create the dictionary with graph elements
graph_elements = { "a" : ["b","c"],
"b" : ["a", "d"],
"c" : ["a", "d"],
"d" : ["e"],
"e" : ["d"]
}
g = graph(graph_elements)
print(g.getVertices())
执行以上代码后,将产生以下结果-
['d', 'b', 'e', 'c', 'a']
显示图形边缘
查找图的边缘比顶点要难得多,因为我们必须找到在一对顶点之间具有边的一对顶点。因此,我们创建了一个空的边列表,然后再遍历与每个顶点关联的边值。形成一个列表,其中包含从顶点找到的不同边缘组。
class graph:
def __init__(self,gdict=None):
if gdict is None:
gdict = {}
self.gdict = gdict
def edges(self):
return self.findedges()
# Find the distinct list of edges
def findedges(self):
edgename = []
for vrtx in self.gdict:
for nxtvrtx in self.gdict[vrtx]:
if {nxtvrtx, vrtx} not in edgename:
edgename.append({vrtx, nxtvrtx})
return edgename
# Create the dictionary with graph elements
graph_elements = { "a" : ["b","c"],
"b" : ["a", "d"],
"c" : ["a", "d"],
"d" : ["e"],
"e" : ["d"]
}
g = graph(graph_elements)
print(g.edges())
执行以上代码后,将产生以下结果-
[{'b', 'a'}, {'b', 'd'}, {'e', 'd'}, {'a', 'c'}, {'c', 'd'}]
添加一个顶点
直接添加顶点是在图字典中添加另一个键的过程。
class graph:
def __init__(self,gdict=None):
if gdict is None:
gdict = {}
self.gdict = gdict
def getVertices(self):
return list(self.gdict.keys())
# Add the vertex as a key
def addVertex(self, vrtx):
if vrtx not in self.gdict:
self.gdict[vrtx] = []
# Create the dictionary with graph elements
graph_elements = { "a" : ["b","c"],
"b" : ["a", "d"],
"c" : ["a", "d"],
"d" : ["e"],
"e" : ["d"]
}
g = graph(graph_elements)
g.addVertex("f")
print(g.getVertices())
执行以上代码后,将产生以下结果-
['f', 'e', 'b', 'a', 'c','d']
添加边缘
将边缘添加到现有图形涉及将新顶点视为元组,并验证边缘是否已存在。如果没有,则添加边缘。
class graph:
def __init__(self,gdict=None):
if gdict is None:
gdict = {}
self.gdict = gdict
def edges(self):
return self.findedges()
# Add the new edge
def AddEdge(self, edge):
edge = set(edge)
(vrtx1, vrtx2) = tuple(edge)
if vrtx1 in self.gdict:
self.gdict[vrtx1].append(vrtx2)
else:
self.gdict[vrtx1] = [vrtx2]
# List the edge names
def findedges(self):
edgename = []
for vrtx in self.gdict:
for nxtvrtx in self.gdict[vrtx]:
if {nxtvrtx, vrtx} not in edgename:
edgename.append({vrtx, nxtvrtx})
return edgename
# Create the dictionary with graph elements
graph_elements = { "a" : ["b","c"],
"b" : ["a", "d"],
"c" : ["a", "d"],
"d" : ["e"],
"e" : ["d"]
}
g = graph(graph_elements)
g.AddEdge({'a','e'})
g.AddEdge({'a','c'})
print(g.edges())
执行以上代码后,将产生以下结果-
[{'e', 'd'}, {'b', 'a'}, {'b', 'd'}, {'a', 'c'}, {'a', 'e'}, {'c', 'd'}]