- Linux终止
- Linux终止(1)
- 工作流程流程
- 工作流程流程(1)
- 流程,父流程和子流程之间的差异
- 流程,父流程和子流程之间的差异(1)
- 终止 cmd (1)
- 如何终止 JavaScript 中的脚本?(1)
- 如何终止 JavaScript 中的脚本?
- 如何在 js 中终止程序 - Javascript (1)
- 如何在C#中终止线程(1)
- 如何在C#中终止线程
- 如何在 js 中终止程序 - Javascript 代码示例
- 在 jquery 中终止执行 - Javascript (1)
- 终止 cmd - 任何代码示例
- 流程操作
- 流程操作(1)
- 在 jquery 中终止执行 - Javascript 代码示例
- 流程资源
- 命名空间卡在终止 (1)
- Node.js流程(1)
- Node.js流程
- c# 如何终止控制台应用程序 - C# (1)
- 流程信息
- c# 如何终止控制台应用程序 - C# 代码示例
- 在java中终止函数调用(1)
- TCP 连接终止(1)
- TCP 连接终止
- Apache NiFi-创建流程(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2021-01-18 06:32:03 🧑 作者: Mango
到现在为止,我们知道无论何时执行程序,都会创建一个流程,并且该流程将在执行完成后终止。如果我们需要在程序中创建一个流程,并且可能希望为其安排其他任务,该怎么办?能做到吗?是的,显然是通过流程创建的。当然,工作完成后,它将自动终止,或者您可以根据需要终止它。
流程创建是通过fork()系统调用实现的。新创建的进程称为子进程,而将其初始化的进程(或开始执行时的进程)称为父进程。在fork()系统调用之后,现在我们有两个进程-父进程和子进程。如何区分它们?很简单,就是通过它们的返回值。
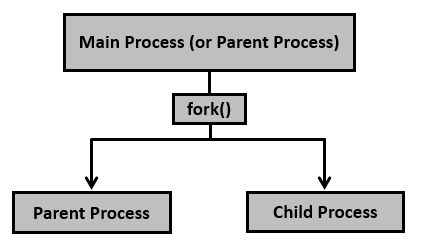
创建子进程后,让我们看到fork()系统调用详细信息。
#include
#include
pid_t fork(void);
创建子进程。此调用之后,有两个进程,现有的一个称为父进程,而新创建的一个称为子进程。
fork()系统调用返回以下三个值之一:
-
表示错误的负值,即创建子进程失败。
-
为子进程返回零。
-
返回父进程的正值。该值是新创建的子进程的进程ID。
让我们考虑一个简单的程序。
File name: basicfork.c
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
fork();
printf("Called fork() system call\n");
return 0;
}
执行步骤
汇编
gcc basicfork.c -o basicfork
执行/输出
Called fork() system call
Called fork() system call
注–通常在fork()调用之后,子进程和父进程将执行不同的任务。如果需要运行同一任务,则对于每个fork()调用,它将运行2次幂n次,其中n是调用fork()的次数。
在上述情况下,fork()被调用一次,因此输出被打印两次(2次幂1)。如果fork()被调用了3次,那么输出将被打印8次(2次幂3)。如果调用了5次,那么它将打印32次,依此类推。
看到fork()创建了子进程之后,就该查看父进程和子进程的详细信息了。
文件名:pids_after_fork.c
#include
#include
#include
int main() {
pid_t pid, mypid, myppid;
pid = getpid();
printf("Before fork: Process id is %d\n", pid);
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork() failure\n");
return 1;
}
// Child process
if (pid == 0) {
printf("This is child process\n");
mypid = getpid();
myppid = getppid();
printf("Process id is %d and PPID is %d\n", mypid, myppid);
} else { // Parent process
sleep(2);
printf("This is parent process\n");
mypid = getpid();
myppid = getppid();
printf("Process id is %d and PPID is %d\n", mypid, myppid);
printf("Newly created process id or child pid is %d\n", pid);
}
return 0;
}
编译和执行步骤
Before fork: Process id is 166629
This is child process
Process id is 166630 and PPID is 166629
Before fork: Process id is 166629
This is parent process
Process id is 166629 and PPID is 166628
Newly created process id or child pid is 166630
进程可以通过以下两种方式之一终止:
-
异常发生在某些信号(例如终止信号)的传递上。
-
通常,使用_exit()系统调用(或_Exit()系统调用)或exit()库函数。
_exit()和exit()之间的区别主要是清理活动。 exit()在将控件返回内核之前会进行一些清理,而_exit() (或_Exit())会将控件立即返回内核。
考虑以下带有exit()的示例程序。
档案名称:atexit_sample.c
#include
#include
void exitfunc() {
printf("Called cleanup function - exitfunc()\n");
return;
}
int main() {
atexit(exitfunc);
printf("Hello, World!\n");
exit (0);
}
编译和执行步骤
Hello, World!
Called cleanup function - exitfunc()
考虑以下带有_exit()的示例程序。
档案名称:at_exit_sample.c
#include
#include
void exitfunc() {
printf("Called cleanup function - exitfunc()\n");
return;
}
int main() {
atexit(exitfunc);
printf("Hello, World!\n");
_exit (0);
}
编译和执行步骤
Hello, World!