平衡氧化还原反应
氧化还原反应是一种化学反应,其中原子的氧化态发生变化,并且在两种相关反应物之间交换电子。这是一个涉及电子传输的反应,它结合了两个反应:氧化和还原。反应性化学物质的氧化态在该反应中发生变化,一种化学物质失去电子,而另一种化学物质同时获得电子。
生活的方方面面都需要一种平衡感。吃太多巧克力也不是一个好主意。甚至反应也必须平衡。氧化还原反应的平衡是化学的重要组成部分。什么是氧化还原反应,它们是如何工作的?由于氧化还原过程,铁会生锈。在我们周围可能会发现其他氧化还原反应。让我们更多地了解它们并检查氧化还原反应平衡所涉及的步骤。
氧化还原反应
术语“氧化还原反应”是指同时发生氧化和还原的反应。
氧化是什么意思?
- 向物质中添加氧气称为氧化。
- 从物质中除去氢也称为氧化。
例如- 2Cu + O 2 → 2Cuo
在这个反应中,氧气被添加到铜中。因此,铜被氧化。
还原反应是什么意思?
- 将氢添加到物质中称为还原。
- 从物质中去除氧气也称为还原。
例如- CuO + H 2 → Cu + H 2 O
在该反应中,氧气从氧化铜中除去。因此,氧化铜(CuO)被还原。
电子的获得称为还原,电子的损失称为氧化。氧化还原反应/氧化还原过程是指还原和氧化反应的组合。如前所述,了解“平衡氧化还原反应”至关重要。
在氧化还原过程中,通常有两种平衡氧化还原反应的技术(化学方程式)。氧化数法和半反应法是两种方法。
氧化还原反应的平衡
使用两种方法平衡氧化还原过程的化学方程式。一种技术基于改变还原剂和氧化剂的氧化数,而另一种方法基于将氧化还原反应分成两个半反应,一个涉及氧化,另一个涉及还原。这两种方式都在使用中,由使用它们的个人决定使用哪一种。
使用两种方法来平衡氧化还原反应。其中一种方法基于氧化数法,第二种方法基于半反应法。
氧化数法
在为氧化还原过程创建方程式时,必须知道反应物和产物的组成和公式,就像其他反应一样。氧化数法在以下步骤中得到了最好的证明:
有两种培养基,酸性培养基和碱性培养基。
用氧化数法平衡酸性介质中氧化还原反应的步骤:
步骤 1:将氧化数分配给反应中的所有元素,以识别在反应过程中改变氧化数的原子。
How to find an Oxidation Number? Elements Oxidation State Exceptions Group 1 Metals Always +1 Group 2 Metals Always +2 Fluorine Always -1 Oxygen Mostly -2 Peroxides and F2O Hydrogen Mostly +1 Metal hydrides (-1) Chlorine Mostly -1 Compounds with O or F
- The oxidation number of an atom or molecule is 0 (Zero). Eg, Cu, N2.
- Sum of oxidation number in compound is 0. eg, CuO : Oxidation number (O.N.) of Cu = +2 and O.N. of O is -2. ∴ +2 + (-2) = 0.
- More Electronegative atom = -ve O.S.
- Less Electronegative atom = +ve O.S.
Examples: To find oxidation number.
- Cr2O72-
2(x)+7(-2)=-2, (Here, x is O.N. of Cu and -2 is O.N. of O)
∴2x-14=-2
∴2x=-2+14
∴x=6 (Oxidation number of Cu)
- Na3PO3
3(+1)+(x)+3(-2)=0
∴3+x-6=0
∴x=+3 (Oxidation number of P)
第 2 步:识别发生氧化和还原的元素/原子。
步骤3:平衡经过氧化和还原的原子后,通过交叉乘法平衡电荷。
第 4 步:平衡除氧和氢以外的所有其他原子。
步骤 5:加入 H 2 O 以平衡氧气。
第6步:通过在反应物或产物中加入H +分子,可以使表达式两边的氢原子数相等。
让我们一直使用下面的示例来解释该方法中涉及的步骤。
示例:通过氧化数法平衡酸性介质中的氧化还原反应。
P + HNO 3 → HPO 3 + NO + H 2 O
Solution:
Step 1: Assign the oxidation number to all elements in the reaction to identify atoms that change oxidation number during the reaction.

Step 2: Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation: P → HPO3
Reduction: HNO3 → NO
Step 3: After balancing atoms that have undergone oxidation and reduction, balance charge by cross multiplication.
P + HNO3 → HPO3 + NO + H2O
There is an increase in the O.N. of P from 0 to +5 which is an increase of 5 in O.N. and there is a decrease in the O.N. of N from +5 to +2 which is a decrease of 3 in O.N.
Cross multiplication: 3P + 5HNO3 → 3HPO3 + 5NO + H2O
Step 4: Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
3P + 5HNO3 → 3HPO3 + 5NO + H2O
Step 5: Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
3P + 5HNO3 → 3HPO3 + 5NO + H2O
Step 6: By adding H+ molecules to the reactants or products, you can make the number of hydrogen atoms in the expression on both sides equal.
3P + 5HNO3 → 3HPO3 + 5NO + H2O
Hence, the equation is balanced.
用氧化数法平衡碱性介质中氧化还原反应的步骤:
步骤 1:将氧化数分配给反应中的所有元素,以识别在反应过程中改变氧化数的原子。
第 2 步:识别发生氧化和还原的元素/原子。
第 3 步:平衡除氧和氢以外的所有其他原子。
第四步:平衡经过氧化和还原的原子后,通过交叉乘法平衡电荷。
步骤 5:加入 H 2 O 以平衡氧气。
第6步:通过在反应物或产物中加入H +分子,可以使表达式两边的氢原子数相等。
第 7 步:在两侧添加尽可能多的 OH -离子,就像在一侧添加 H +离子一样多。
让我们一直使用下面的示例来解释该方法中涉及的步骤。
示例:通过氧化数法平衡碱性介质中的氧化还原反应。
Cl 2 + IO 3 – + OH – → IO 4 – + Cl – + H 2 O
解决方案:
Step 1: Assign the oxidation number to all elements in the reaction to identify atoms that change oxidation number during the reaction.

Step 2: Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation: IO3– → IO4–
Reduction: Cl2 → Cl–
Step 3: Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
Cl2 + IO3– +OH → IO4– + 2Cl– + H2O
Step 4: After balancing atom that have undergone oxidation and reduction, balance charge by cross multiplication.
Cl2 + IO3– +OH– → IO4– + 2Cl– + H2O
There is an increase in the O.N. of I from +5 to +7 that is an increase of 2 in O.N. and there is a decrease in the O.N. of Cl from 0 to -2 that is a decrease of 2 in O.N.
Cancel both difference (2) to each other.
Cl2 + IO3– +OH– → IO4– + 2Cl– + H2O
Step 5: Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
Cl2 + IO3– + H2O → IO4– + 2Cl–
Step 6: By adding H+ molecules to the reactants or products, you can make the number of hydrogen atoms in the expression on both sides equal.
Cl2 + IO3– + H2O → IO4– + 2Cl– + 2H+
Step 7: Add as many OH- ions on both sides as number of H+ ions on one side.
Cl2 + IO3– + H2O + 2OH– → IO4– + 2Cl– + 2H+ + 2OH–
∴ Cl2 + IO3– + H2O + 2OH– → IO4– + 2Cl– + 2H2O
∴ Cl2 + IO3– + 2OH– → IO4– + 2Cl– + ( 2H2O – H2O )
∴ Cl2 + IO3– + 2OH– → IO4– + 2Cl– + H2O
Hence, the equation is balanced.
半反应法(离子电子法):
两个半方程单独平衡,然后在此方法中组合以创建平衡方程。
有两种介质:酸性介质和碱性介质
用半反应法平衡酸性介质中氧化还原反应的步骤:
第 1 步:以离子形式,生成反应的不平衡方程。
第 2 步:识别发生氧化和还原的元素/原子。
第 3 步:将反应分成两半。
- 氧化半
- 减半
第 4 步:平衡半反应。
- 平衡除氧和氢以外的所有其他原子。
- 添加 H2O 以平衡氧气。
- 用质子平衡氢(添加 H+ 离子)。
- 用电子平衡电荷。
第 5 步:为了平衡电荷,将电子添加到半反应的一侧。如有必要,将一个或两个半反应乘以适当的值,以使两个半反应中的电子数相等。
第6步:为了得到整体反应,我们将两个半反应结合起来,取消两边的共同项。因此获得了净离子方程。
第 7 步:检查等式两边是否具有相同种类和数量的原子,以及相同的电荷。最后的检查证实了方程在原子和电荷方面是完全平衡的。
示例:通过半反应法平衡酸性介质中的氧化还原反应。
Cr 2 O 7 2- (aq) + HNO 2 (aq) → Cr 3+ (aq) + NO 3 – (aq)
解决方案:
Step 1: In ionic form, generate an imbalanced equation for the reaction.
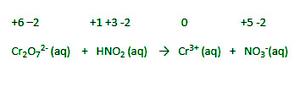
Step 2: Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation: HNO2(aq) → NO3–(aq)
Reduction: Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq)
Step 3: Break the reaction in two halves.
Reduction Half,
Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq)
Oxidation Half,
HNO2(aq) → NO3–(aq)
Step 4: Balance the Half reaction.
- Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
(In 1st reaction, there are 2 moles of Cr on left side so we have to take 2 mole of Cr on right side.)
Cr2O72-(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq)
(In 2nd reaction),
HNO2(aq) → NO3–(aq)
- Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
Cr2O72-(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l)
HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) → NO3–(aq)
- Balance Hydrogen (Add H+ ion) with protons.
Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l)
HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) → NO3–(aq) + 3H+(aq)
- Balance the charge with electron.
In 1st reaction,
Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l)
LHS : (2-) + (14+) = (12+)charges
RHS : 2(3+) = (6+)charges
Therefore,
Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e– → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l)
In 2nd reaction,
HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) → NO3–(aq) + 3H+(aq)
LHS : No charges
RHS : (1-) + (3+) = (2+)charges
Therefore,
HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) → NO3–(aq) + 3H+(aq) + 2e–
Step 5: To balance the charges, add electrons to one side of the half reaction. If necessary, multiply one or both half reactions by an appropriate value to make the number of electrons in the two half reactions equal.
Here, 6 electrons in 1st reaction and 2 electrons in 2nd reaction. so we multiply
1st reaction,
Cr2O72-(aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e– → 2Cr3+(aq) + 7H2O(l)
2nd reaction,
HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) → NO3–(aq) + 3H+(aq) + 2e–
∴ 3( HNO2(aq) + H2O(l) → NO3–(aq) + 3H+(aq) + 2e– )
∴ 3HNO2(aq) + 3H2O(l) → 3NO3–(aq) + 9H+(aq) + 6e–
Step 6: To get the overall reaction, we combine the two half reactions and cancel the common term on both sides. The net ionic equation is thus obtained.

Cr2O72-(aq) + 5H+(aq) + 3HNO2(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 4H2O(l) + 3NO3-(aq)
Step 7] Check that both sides of the equation have the same kind and number of atoms, as well as the same charges. This final check confirms that the equation is perfectly balanced in terms of atoms and charges.
Hence, the equation is balanced.
用半反应法平衡碱性介质中氧化还原反应的步骤:
第 1 步:以离子形式,生成反应的不平衡方程。
第 2 步:识别发生氧化和还原的元素/原子。
第 3 步:将反应分成两半。
- 氧化半
- 减半
第 4 步:平衡半反应。
- 平衡除氧和氢以外的所有其他原子。
- 添加 H2O 以平衡氧气。
- 用质子平衡氢(添加 H+ 离子)。
- 用电子平衡电荷。
第 5 步:为了平衡电荷,将电子添加到半反应的一侧。如有必要,将一个或两个半反应乘以适当的值,以使两个半反应中的电子数相等。
第6步:为了得到整体反应,我们将两个半反应结合起来,取消两边的共同项。因此获得了净离子方程。
第 7 步:在两侧添加与在一侧添加的 H+ 离子一样多的 OH- 离子。
第 8 步:检查等式两边是否具有相同种类和数量的原子,以及相同的电荷。最后的检查证实了方程在原子和电荷方面是完全平衡的。
示例:通过半反应法平衡碱性介质中的氧化还原反应。
MnO 4 – + I – → MnO 2 + I 2
解决方案:
Step 1: In ionic form, generate an imbalanced equation for the reaction.

Step 2: Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation: I– → I2
Reduction: MnO4– → MnO2
Step 3: Break the reaction in two halves.
Oxidation Half
I– → I2
Reduction Half
MnO4– → MnO2
Step 4: Balance the Half reaction.
- Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
2I– → I2
(Here, 2 moles of I on right side so we have to take 2 mole of I on left side.)
MnO4– → MnO2
- Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
2I– → I2
MnO4– → MnO2 + 2H2O
- Balance Hydrogen (Add H+ ion) with protons.
2I– → I2
MnO4– + 4H+ → MnO2 + 2H2O
- Balance the charge with electron.
2I– → I2 + 2e–
MnO4– + 4H+ + 3e– → MnO2 + 2H2O
Step 5: To balance the charges, add electrons to one side of the half reaction. If necessary, multiply one or both half reactions by an appropriate value to make the number of electrons in the two half reactions equal.
Here, 2 electrons in 1st reaction and 3 electrons in 2nd reaction. so we balance the electron.
3( 2I– → I2 + 2e– )
∴ 6I– → 3I2 + 6e–
2( MnO4– + 4H+ + 3e– → MnO2 + 2H2O )
∴ 2MnO4– + 8H+ + 6e– → 2MnO2 + 4H2O
Step 6: To get the overall reaction, we combine the two half reactions and cancel the common term on both sides. The net ionic equation is thus obtained.

Step 7: Add as many OH- ions on both sides as number of H+ ions on one side.
6I– + 2MnO4– + 8H+ + 8OH– → 3I2 + 2MnO2 + 4H2O + 8OH–
∴ 6I– + 2MnO4– + 8H2O → 3I2 + 2MnO2 + 4H2O + 8OH–
∴ 6I– + 2MnO4– + 4H2O → 3I2 + 2MnO2 + 8OH–
Step 8: Check that both sides of the equation have the same kind and number of atoms, as well as the same charges. This final check confirms that the equation is perfectly balanced in terms of atoms and charges.
Hence, the equation is balanced.
示例问题
问题1:通过氧化数法确定酸性介质中的平衡氧化还原反应:
CuO + NH 3 → Cu + N 2 + H 2 O
解决方案:
Step 1] Assign the oxidation number to all elements in the reaction to identify atoms which change oxidation number during the reaction.
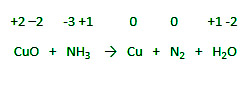
Step 2] Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation:
NH3 → N2
Reduction :
CuO → Cu
Step 3] After balancing atom that have undergone oxidation and reduction, balance charge by cross multiplication.
CuO + NH3 → Cu + N2 + H2O
There is an increase in the O.N. of N from -3 to 0 that is an increase of 3 in O.N. and there is a decrease in the O.N. of Cu from +2 to 0 that is a decrease of 2 in O.N.
Cross multiplication,
3CuO + 2NH3 → 3Cu + 2N2 + H2O
Step 4] Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
3CuO + 4NH3 → 3Cu + 2N2 + H2O
Step 5] Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
3CuO + 4NH3 → 3Cu + 2N2 + H2O +2H2O
Step 6] By adding H+ molecules to the reactants or products, you can make the number of hydrogen atoms in the expression on both sides equal.
3CuO + 4NH3 → 3Cu + 2N2 + H2O +2H2O + 6H+
∴ 3CuO + 2NH3 → 3Cu + N2 + 3H2O
Hence, the equation is balanced.
问题2:用离子电子法求酸性介质中的平衡氧化还原反应:
Fe 2+ + Cr 2 O 7 2- → Cr 3+ + Fe 3+
解决方案:
Step 1] In ionic form, generate an imbalanced equation for the reaction.
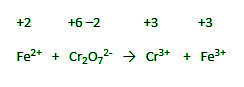
Step 2] Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation,
Fe2+ → Fe3+
Reduction,
Cr2O72- → Cr3+
Step 3] Break the reaction in two halves.
Oxidation Half,
Fe2+ → Fe3+
Reduction Half,
Cr2O72- → Cr3+
Step 4] Balance the Half reaction.
- Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
Fe2+ → Fe3+
Cr2O72- → 2Cr3+
- Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
Fe2+ → Fe3+
Cr2O72- → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
- Balance Hydrogen (Add H+ ion) with protons.
Fe2+ → Fe3+
Cr2O72- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
- Balance the charge with electron.
In 1st reaction,
Fe2+ → Fe3+
LHS : (2+) charges
RHS : (3+)charges
Therefore,
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e–
In 2nd reaction,
Cr2O72- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
LHS : (2-) + (14+) = (12+)charges
RHS : (6+) = (6+)charges
Therefore,
Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Step 5] To balance the charges, add electrons to one side of the half reaction. If necessary, multiply one or both half reactions by an appropriate value to make the number of electrons in the two half reactions equal.
(Here, 1 electrons in 1st reaction and 6 electrons in 2nd reaction. so we balance the electrons.)
1st reaction,
6( Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e– )
∴ 6Fe2+ → 6Fe3+ + 6e–
2nd reaction,
Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Step 6] To get the overall reaction, we combine the two half reactions and cancel the common term on both sides. The net ionic equation is thus obtained.
6Fe2+ + Cr2O72- + 14H+ → 6Fe3+ + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Step 7] Check that both sides of the equation have the same kind and number of atoms, as well as the same charges. This final check confirms that the equation is perfectly balanced in terms of atoms and charges.
Hence, the equation is balanced.
问题 3:通过半反应法确定碱性介质中的平衡氧化还原反应:
Ag(s) + Zn 2+ (aq) → Ag 2 O(aq) + Zn(s)
解决方案:
Step 1] In ionic form, generate an imbalanced equation for the reaction.
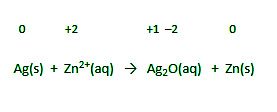
Step 2] Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation,
Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq)
Reduction,
Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s)
Step 3] Break the reaction in two halves.
Oxidation Half,
Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq)
Reduction Half,
Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s)
Step 4] Balance the Half reaction.
- Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
2Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq)
Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s)
- Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
H2O(l) + 2Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq)
Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s)
- Balance Hydrogen (Add H+ ion) with protons.
H2O(l) + 2Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq) + 2H+(aq)
Zn2+(aq) → Zn(s)
- Balance the charge with electron.
H2O(l) + 2Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2e–
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s)
Step 5] To balance the charges, add electrons to one side of the half reaction. If necessary, multiply one or both half reactions by an appropriate value to make the number of electrons in the two half reactions equal.
H2O(l) + 2Ag(s) → Ag2O(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2e–
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s)
Step 6] To get the overall reaction, we combine the two half reactions and cancel the common term on both sides. The net ionic equation is thus obtained.
H2O(l) + 2Ag(s) + Zn2+ → Ag2O(aq) + 2H+(aq) + Zn(s)
Step 7] Add as many OH- ions on both sides as number of H+ ions on one side.
2Ag(s) + Zn2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq) → Zn(s) + Ag2O(aq) + H2O(l)
Step 8] Check that both sides of the equation have the same kind and number of atoms, as well as the same charges. This final check confirms that the equation is perfectly balanced in terms of atoms and charges.
Hence, the equation is balanced.
问题 4:什么是酸性介质中的平衡氧化还原反应,通过氧化数法:
Cu + NO 3 – → NO 2 + Cu 2+
解决方案:
Step 1] Assign the oxidation number to all elements in the reaction to identify atoms which change oxidation number during the reaction.
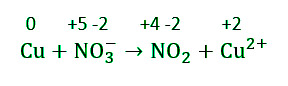
Step 2] Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation,
Cu → Cu2+
Reduction,
NO3– → NO2
Step 3] After balancing atom that have undergone oxidation and reduction, balance charge by cross multiplication.
Cu + NO3– → NO2 + Cu2+
There is an increase in the O.N. of Cu from 0 to +2 that is an increase of 2 in O.N. and there is a decrease in the O.N. of N from +5 to +4 that is a decrease of 1 in O.N.
Cross multiplication,
Cu + 2NO3– → 2NO2 + Cu2+
Step 4] Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
Cu + 2NO3– → 2NO2 + Cu2+
Step 5] Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
Cu + 2NO3– → 2NO2 + Cu2+ + 2H2O
Step 6] By adding H+ molecules to the reactants or products, you can make the number of hydrogen atoms in the expression on both sides equal.
Cu + 2NO3– + 4H+ → 2NO2 + Cu2+ + 2H2O
Hence, the equation is balanced.
问题 5:通过氧化数法找到碱性介质中的平衡氧化还原反应:
[Cr(OH) 4 ] + H 2 O 2 → CrO 4 2- + H 2 O
解决方案:
Step 1] Assign the oxidation number to all elements in the reaction to identify atoms which change oxidation number during the reaction.
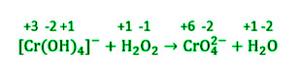
Step 2] Identify the elements/atoms which undergo oxidation and reduction.
Oxidation,
[Cr(OH)4] → CrO42-
Reduction,
H2O2 → H2O
Step 3] Balance all other atoms except oxygen and hydrogen.
[Cr(OH)4] + H2O2 → CrO42- + H2O
Step 4] After balancing atom that have undergone oxidation and reduction, balance charge by cross multiplication.
There is an increase in the O.N. of chromium from +3 to +6 that is an increase of 3 in O.N. and there is a decrease in the O.N. of one oxygen atom in hydrogen peroxide from −1 to −2 that is a decrease of 1 in O.N.
Cross multiplication,
2[Cr(OH)4]– + 3H2OCr2 → CrO42-+ H2O
Step 5] Add H2O to balance the oxygen.
2[Cr(OH)4]– + 3H2O2 → 2CrO42- + 6H2O
Step 6] Add as many OH- ions on both sides as number of H+ ions on one side.
2[Cr(OH)4]– + 3H2O2 + 2OH– → 2CrO42- + 8H2O
Hence the equation is balanced.