Python的文本预处理 |套装 – 1
先决条件:NLP 简介
每当我们有文本数据时,我们都需要对数据应用几个预处理步骤,将单词转换为可与机器学习算法配合使用的数字特征。问题的预处理步骤主要取决于领域和问题本身,因此,我们不需要将所有步骤应用于每个问题。
在本文中,我们将看到Python的文本预处理。我们将在这里使用 NLTK(自然语言工具包)库。
# import the necessary libraries
import nltk
import string
import re
文字小写:
我们将文本小写以减少文本数据的词汇量。
def text_lowercase(text):
return text.lower()
input_str = "Hey, did you know that the summer break is coming? Amazing right !! It's only 5 more days !!"
text_lowercase(input_str)
例子:
Input: “Hey, did you know that the summer break is coming? Amazing right!! It’s only 5 more days!!”
Output: “hey, did you know that the summer break is coming? amazing right!! it’s only 5 more days!!”
删除数字:
我们可以删除数字或将数字转换为它们的文本表示。
我们可以使用正则表达式来删除数字。
# Remove numbers
def remove_numbers(text):
result = re.sub(r'\d+', '', text)
return result
input_str = "There are 3 balls in this bag, and 12 in the other one."
remove_numbers(input_str)
例子:
Input: “There are 3 balls in this bag, and 12 in the other one.”
Output: ‘There are balls in this bag, and in the other one.’
我们还可以将数字转换为单词。这可以通过使用 inflect 库来完成。
# import the inflect library
import inflect
p = inflect.engine()
# convert number into words
def convert_number(text):
# split string into list of words
temp_str = text.split()
# initialise empty list
new_string = []
for word in temp_str:
# if word is a digit, convert the digit
# to numbers and append into the new_string list
if word.isdigit():
temp = p.number_to_words(word)
new_string.append(temp)
# append the word as it is
else:
new_string.append(word)
# join the words of new_string to form a string
temp_str = ' '.join(new_string)
return temp_str
input_str = 'There are 3 balls in this bag, and 12 in the other one.'
convert_number(input_str)
例子:
Input: “There are 3 balls in this bag, and 12 in the other one.”
Output: “There are three balls in this bag, and twelve in the other one.”
去除标点符号:
我们删除了标点符号,这样同一个词就不会出现不同的形式。如果我们不删除标点符号,那么就是。去过,去过!会分开处理。
# remove punctuation
def remove_punctuation(text):
translator = str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation)
return text.translate(translator)
input_str = "Hey, did you know that the summer break is coming? Amazing right !! It's only 5 more days !!"
remove_punctuation(input_str)
例子:
Input: “Hey, did you know that the summer break is coming? Amazing right!! It’s only 5 more days!!”
Output: “Hey did you know that the summer break is coming Amazing right Its only 5 more days”
删除空格:
我们可以使用 join 和 split函数删除字符串中的所有空格。
# remove whitespace from text
def remove_whitespace(text):
return " ".join(text.split())
input_str = " we don't need the given questions"
remove_whitespace(input_str)
例子:
Input: " we don't need the given questions"
Output: "we don't need the given questions"
删除默认停用词:
停用词是对句子含义没有贡献的词。因此,可以安全地删除它们,而不会导致句子的含义发生任何变化。 NLTK 库有一组停用词,我们可以使用这些停用词从文本中删除停用词并返回单词标记列表。

from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
# remove stopwords function
def remove_stopwords(text):
stop_words = set(stopwords.words("english"))
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
filtered_text = [word for word in word_tokens if word not in stop_words]
return filtered_text
example_text = "This is a sample sentence and we are going to remove the stopwords from this."
remove_stopwords(example_text)
例子:
Input: “This is a sample sentence and we are going to remove the stopwords from this”
Output: [‘This’, ‘sample’, ‘sentence’, ‘going’, ‘remove’, ‘stopwords’]
词干:
词干提取是获取单词词根形式的过程。词干或词根是添加屈折词缀(-ed、-ize、-de、-s 等)的部分。词干是通过去除词的前缀或后缀来创建的。因此,词干化一个词可能不会产生实际的词。
例子:
books ---> book
looked ---> look
denied ---> deni
flies ---> fli
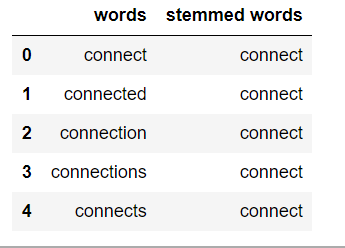
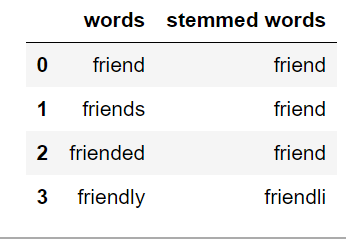
如果文本不在标记中,那么我们需要将其转换为标记。在我们将文本字符串转换为标记之后,我们可以将单词标记转换为其词根形式。主要有三种用于词干的算法。它们是 Porter Stemmer、Snowball Stemmer 和 Lancaster Stemmer。 Porter Stemmer 是其中最常见的。
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
stemmer = PorterStemmer()
# stem words in the list of tokenised words
def stem_words(text):
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
stems = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in word_tokens]
return stems
text = 'data science uses scientific methods algorithms and many types of processes'
stem_words(text)
例子:
Input: ‘data science uses scientific methods algorithms and many types of processes’
Output: [‘data’, ‘scienc’, ‘use’, ‘scientif’, ‘method’, ‘algorithm’, ‘and’, ‘mani’, ‘type’, ‘of’, ‘process’]
词形还原:
与词干提取一样,词形还原也将单词转换为其词根形式。唯一的区别是词形还原确保词根属于该语言。如果我们使用词形还原,我们将得到有效的词。在 NLTK 中,我们使用 WordNetLemmatizer 来获取单词的引理。我们还需要为词形还原提供上下文。因此,我们添加词性作为参数。
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
# lemmatize string
def lemmatize_word(text):
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
# provide context i.e. part-of-speech
lemmas = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(word, pos ='v') for word in word_tokens]
return lemmas
text = 'data science uses scientific methods algorithms and many types of processes'
lemmatize_word(text)
例子:
Input: ‘data science uses scientific methods algorithms and many types of processes’
Output: [‘data’, ‘science’, ‘use’, ‘scientific’, ‘methods’, ‘algorithms’, ‘and’, ‘many’, ‘type’, ‘of’, ‘process’]