Python中的文本预处理 |设置 2
先决条件:NLP 简介, Python中的文本预处理 |设置 1
在上一篇文章中,我们看到了处理文本数据时的基本预处理步骤。在本文中,我们将介绍一些更高级的文本预处理技术。我们可以使用这些技术来更深入地了解我们拥有的数据。
让我们导入必要的库。
# import the necessary libraries
import nltk
import string
import re
部分语音标记:
词性解释了一个词在句子中的使用方式。在一个句子中,一个词可以有不同的上下文和语义含义。像词袋这样的基本自然语言处理模型无法识别单词之间的这些关系。因此,我们使用词性标记来根据其在数据中的上下文将单词标记为其词性标记。它还用于提取单词之间的关系。
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk import pos_tag
# convert text into word_tokens with their tags
def pos_tagging(text):
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
return pos_tag(word_tokens)
pos_tagging('You just gave me a scare')
例子:
Input: ‘You just gave me a scare’
Output: [(‘You’, ‘PRP’), (‘just’, ‘RB’), (‘gave’, ‘VBD’), (‘me’, ‘PRP’),
(‘a’, ‘DT’), (‘scare’, ‘NN’)]
在给定的示例中,PRP 代表人称代词,RB 代表副词,VBD 代表动词过去时,DT 代表限定词,NN 代表名词。我们可以使用 Penn Treebank 标签集获取所有词性标签的详细信息。
# download the tagset
nltk.download('tagsets')
# extract information about the tag
nltk.help.upenn_tagset('NN')
例子:
Input: ‘NN’
Output: NN: noun, common, singular or mass
common-carrier cabbage knuckle-duster Casino afghan shed thermostat
investment slide humour falloff slick wind hyena override subhumanity
machinist …
分块:
分块是从非结构化文本中提取短语和更多结构的过程。它也被称为浅解析。它是在词性标记之上完成的。它将单词分组为“块”,主要是名词短语。分块是使用正则表达式完成的。
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk import pos_tag
# define chunking function with text and regular
# expression representing grammar as parameter
def chunking(text, grammar):
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
# label words with part of speech
word_pos = pos_tag(word_tokens)
# create a chunk parser using grammar
chunkParser = nltk.RegexpParser(grammar)
# test it on the list of word tokens with tagged pos
tree = chunkParser.parse(word_pos)
for subtree in tree.subtrees():
print(subtree)
tree.draw()
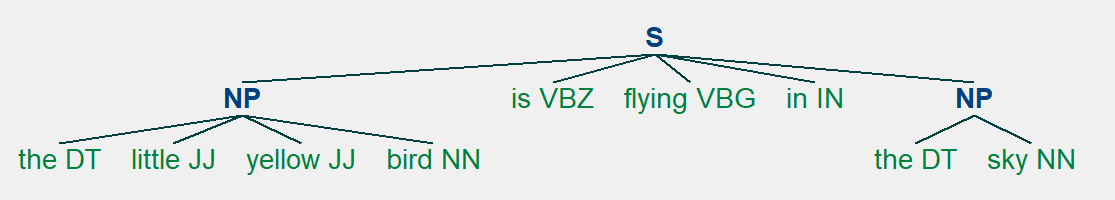
sentence = 'the little yellow bird is flying in the sky'
grammar = "NP: {?*}"
chunking(sentence, grammar)
在给定的示例中,语法是使用简单的正则表达式规则定义的。这条规则说,只要分块器找到一个可选的限定词 (DT) 后跟任意数量的形容词 (JJ) 和一个名词 (NN),就应该形成一个 NP(名词短语)块。
spaCy 和 Textblob 等库更适合分块。
例子:
Input: ‘the little yellow bird is flying in the sky’
Output:
(S
(NP the/DT little/JJ yellow/JJ bird/NN)
is/VBZ
flying/VBG
in/IN
(NP the/DT sky/NN))
(NP the/DT little/JJ yellow/JJ bird/NN)
(NP the/DT sky/NN)
命名实体识别:
命名实体识别用于从非结构化文本中提取信息。它用于将文本中存在的实体分类为人、组织、事件、地点等类别。它为我们提供了有关文本和不同实体之间关系的详细知识。
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk import pos_tag, ne_chunk
def named_entity_recognition(text):
# tokenize the text
word_tokens = word_tokenize(text)
# part of speech tagging of words
word_pos = pos_tag(word_tokens)
# tree of word entities
print(ne_chunk(word_pos))
text = 'Bill works for GeeksforGeeks so he went to Delhi for a meetup.'
named_entity_recognition(text)
例子:
Input: ‘Bill works for GeeksforGeeks so he went to Delhi for a meetup.’
Output:
(S
(PERSON Bill/NNP)
works/VBZ
for/IN
(ORGANIZATION GeeksforGeeks/NNP)
so/RB
he/PRP
went/VBD
to/TO
(GPE Delhi/NNP)
for/IN
a/DT
meetup/NN
./.)
在评论中写代码?请使用 ide.geeksforgeeks.org,生成链接并在此处分享链接。