在 Julia 中使用 Excel 文件
Julia 是一种高级开源编程语言,这意味着它的源代码是免费提供的。它是一种用于在科学计算中执行操作的语言。 Julia 用于统计计算和数据分析。 Julia 为其用户提供了一些预定义的函数和内置包,借助这些功能,Julia 可以轻松地使用 Excel 文件。
读取 Excel 文件
在 Packages 的帮助下,Julia 可以更轻松地读取 Excel 文件。首先,需要添加以获取其读取 Excel 文件的功能的包是
XLSX.jl package
可以通过将其作为参数传递给 Pkg 对象中存在的add(" ")函数来添加所有包
Pkg.add("")
一次读取一行
为了从 Excel 文件中一次读取一行,Julia 提供了一个函数eachrow()来迭代文件的每一行并将其存储在一个变量中。
方法:
- 首先,添加包XLSX
- 使用openxlsx()函数打开文件,参数以字符串形式作为文件名传递,访问缓存的内存。
- 现在我们将在循环和变量的帮助下遍历存储数据的工作表,并在传递时存储(工作表)。
- 现在要访问表的每一行,我们需要在名为eachrow()的函数的帮助下逐行迭代,并将工作表作为参数传递给其中。
- for 循环使用的迭代变量称为“ SheetRow ”值,使用列引用读取值。
- row_number(iterating_variable)函数用于访问行号,并在其中传递迭代变量,这将有助于遍历。
- 现在要读取引用的列,传递的变量应该具有与特定标题中包含的值相同类型的参数并存储在另一个变量中。 r[“B”] 用于字符串,r[1] 用于 int 值等。
- 现在只需打印存储这些数据的变量并结束两个循环
Julia
using Pkg
Pkg.add("XLSX")
XLSX.openxlsx("sample1.xlsx", enable_cache=false) do f
sheet = f["Sheet1"]
for r in XLSX.eachrow(sheet)
# r is a `SheetRow`, values are read
# using column references
rn = XLSX.row_number(r) # `SheetRow` row number
v1 = r[1] # will read value at column 1
v2 = r[2]# will read value at column 2
v3 = r["B"]
v4 = r[3]
println("v1=$v1, v2=$v2, v3=$v3, v4=$v4")
end
endJulia
using Pkg
Pkg.add("XLSX")
import XLSX
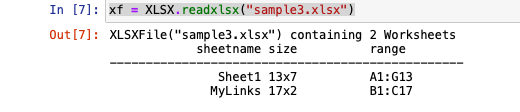
xf = XLSX.readxlsx("sample3.xlsx")Julia
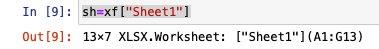
sh = xf["Sheet1"]
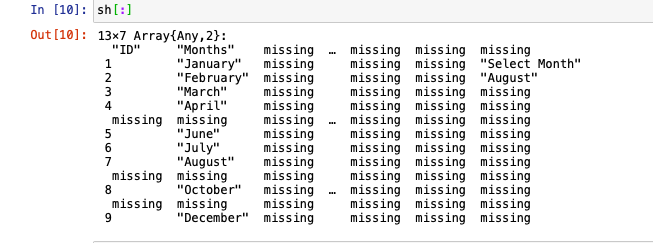
sh[:]Julia
# Modifying contents of a file
using Pkg
Pkg.add("XLSX")
XLSX.openxlsx("sample3.xlsx", mode="rw") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
sheet["B2"] = "March" #row number = B2
endJulia
# Only 10 columns are present
df2 = DataFrame(XLSX.readtable("sample2.xlsx", "Sheet1")...)
# add a new column to an existing file
# and makes it 11 columns
XLSX.openxlsx("sample2.xlsx", mode="rw") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
# add a column from "K1" to "K3"
sheet["K1", dim=1] = collect(1:3)
endJulia
# deleting from an existing column
row = 2
df = df[setdiff(1:end, row), :]Julia
# Only 10 columns are present
df2 = DataFrame(XLSX.readtable("sample2.xlsx", "Sheet1")...)
# Add a new column to an existing file
# and makes it 11 columns
XLSX.openxlsx("sample2.xlsx", mode="rw") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
# will add a column from "K1" to "K3"
sheet["K1", dim=1] = collect(1:3)
end
# Updated columns and stored in new dataframe df3
df3 = DataFrame(XLSX.readtable("sample2.xlsx", "Sheet1")...)
# Appended df2 rows to the end of df3
# with same column names
df3 = append!(df2,df3)Julia
# Writing a new xlsx file and
# the mode is w means(write)
# and created a new one.
XLSX.openxlsx("sample5.xlsx", mode="w") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
# add a row from "A5" to "E5"
# equivalent to `sheet["A5", dim=2] = collect(1:4)`
sheet["A5"] = collect(1:5)
# will add a column from "B1" to "B4"
sheet["B1", dim=1] = collect(1:3)
# will add a matrix from "A7" to "C9"
sheet["A7:C9"] = [ 1 2 3 ; 4 5 6 ; 7 8 9 ]
end
一次读取整个文件
Julia 提供了一个函数readxlsx()来一次读取文件的所有内容。
方法:
- 首先,添加包Pkg
- 然后使用 add函数添加 XLSX 包并将包名称作为参数传递
- 可以通过读取 xlsx 文件的函数readxlsx()读取文件及其所有信息的输出
- 现在此函数返回 xlsx 文件中所有工作表的尺寸。
- 所有工作表的这些维度可以存储在一个单独的变量中,然后可以通过传递一个字符串来访问它。
- 现在,可以使用双冒号查看传递的此表中单独变量的所有数据,从而可以读取此特定表中的所有数据。
朱莉娅
using Pkg
Pkg.add("XLSX")
import XLSX
xf = XLSX.readxlsx("sample3.xlsx")
朱莉娅
sh = xf["Sheet1"]
sh[:]
修改文件内容
可以通过以“rw”即读写模式打开文件,然后在迭代器的帮助下进一步更新值来修改 Excel 文件的内容。
方法:
- 首先,添加包Pkg
- 现在使用 add函数添加包 XLSX
- 现在以“ rw ”模式打开文件以对现有文件进行更改。
- 现在在循环的帮助下遍历工作表变量
- 现在将行号传递给工作表变量以访问该行
- 用新的数字或字符串替换它
- 使用“ end”结束循环。
朱莉娅
# Modifying contents of a file
using Pkg
Pkg.add("XLSX")
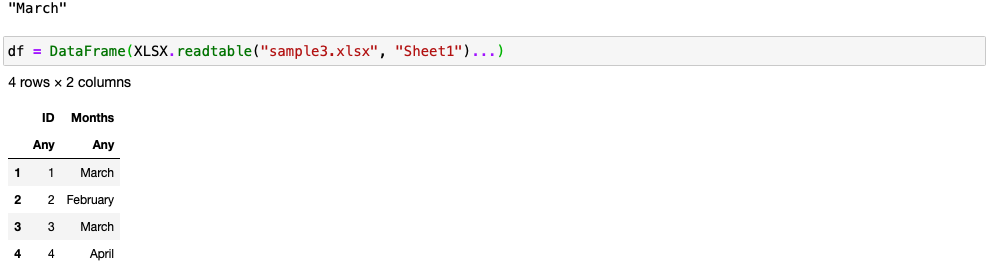
XLSX.openxlsx("sample3.xlsx", mode="rw") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
sheet["B2"] = "March" #row number = B2
end
创建新列
在 Excel 文件中添加列是通过在“rw”模式下打开文件然后使用collect()函数来完成的。
方法:
- 首先,添加包 Pkg、XLSX 和 DataFrames。
- 现在以 ' rw ' 模式打开文件意味着编辑现有文件
- 现在使用变量遍历工作表
- 将参数作为要在其中添加列和维度的列号传递
- 并通过函数收集传递参数,告诉范围
- 然后结束循环
朱莉娅
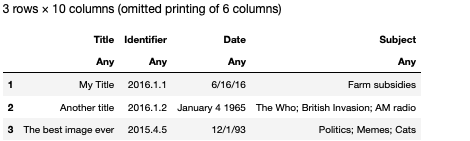
# Only 10 columns are present
df2 = DataFrame(XLSX.readtable("sample2.xlsx", "Sheet1")...)
# add a new column to an existing file
# and makes it 11 columns
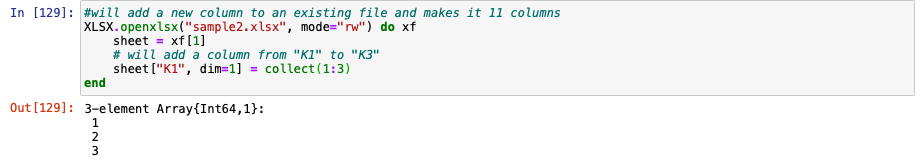
XLSX.openxlsx("sample2.xlsx", mode="rw") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
# add a column from "K1" to "K3"
sheet["K1", dim=1] = collect(1:3)
end
删除文件的内容
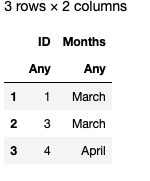
可以使用setdiff()函数从 Excel 文件中删除内容。此函数比较所有行并删除作为参数传递的行。
方法:
- 首先告诉需要删除的行。
- 现在在同一个 DataFrames ' df'中使用setdiff()函数传递参数,它从开始读取所有行并删除传递的行。
朱莉娅
# deleting from an existing column
row = 2
df = df[setdiff(1:end, row), :]
原始文件:
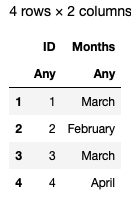
更新后的文件:
附加到文件
Julia 提供了一个函数append()来对文件执行追加操作。此函数将两个数据帧作为参数并返回附加的数据帧。
方法:
- 要附加文件,请使用将 DataFrames (df2,df3) 作为参数传递的append()函数
- append()函数的作用是在 df3 数据帧的后面添加 df2 数据帧
- 但请记住,两个数据帧(df2,df3)中的列应该相同
朱莉娅
# Only 10 columns are present
df2 = DataFrame(XLSX.readtable("sample2.xlsx", "Sheet1")...)
# Add a new column to an existing file
# and makes it 11 columns
XLSX.openxlsx("sample2.xlsx", mode="rw") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
# will add a column from "K1" to "K3"
sheet["K1", dim=1] = collect(1:3)
end
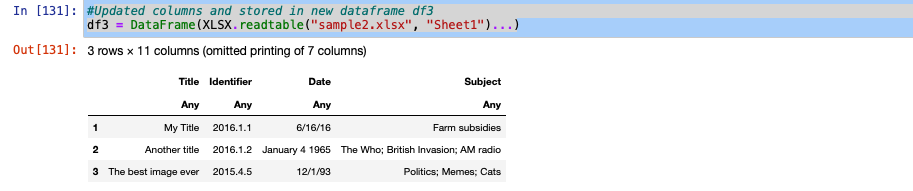
# Updated columns and stored in new dataframe df3
df3 = DataFrame(XLSX.readtable("sample2.xlsx", "Sheet1")...)
# Appended df2 rows to the end of df3
# with same column names
df3 = append!(df2,df3)
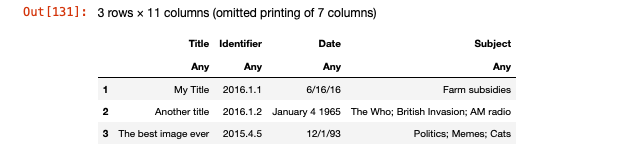
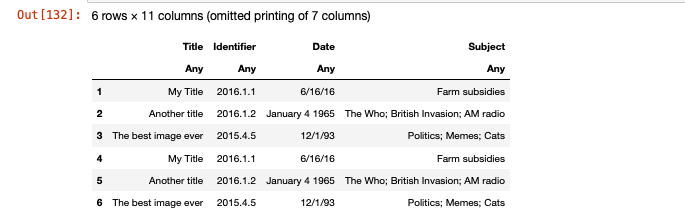
编写一个新的excel文件
要将内容写入新的 Excel 文件,请以“w”即写入模式打开文件,然后使用collect()函数将列添加到文件并进一步分配要添加到变量的值。
方法:
- 首先,以写入模式'w'打开文件并开始循环
- 现在要在新文件中添加一行,将行号作为参数在工作表变量中传递,并传递收集函数,给出范围直到我们想要一行并将它们作为参数传递
- 现在要将列添加到文件中,将行号和维度作为 1 传递给列
- 将 collect()函数传递给 sheet 变量,并在 collect()函数中传递范围,直到我们想要我们的列,在特定的行号上
- 现在在方括号中传递由分号(;)分隔的工作表变量中的数字矩阵,并传递工作表变量中的行号范围,直到我们想要我们的矩阵。
朱莉娅
# Writing a new xlsx file and
# the mode is w means(write)
# and created a new one.
XLSX.openxlsx("sample5.xlsx", mode="w") do xf
sheet = xf[1]
# add a row from "A5" to "E5"
# equivalent to `sheet["A5", dim=2] = collect(1:4)`
sheet["A5"] = collect(1:5)
# will add a column from "B1" to "B4"
sheet["B1", dim=1] = collect(1:3)
# will add a matrix from "A7" to "C9"
sheet["A7:C9"] = [ 1 2 3 ; 4 5 6 ; 7 8 9 ]
end
