Solidity – 组装
汇编或汇编语言是一种低级编程语言,可以使用汇编程序将其转换为机器代码。汇编语言与物理机或虚拟机相关联,因为它们的实现是一个指令集,这些指令告诉 CPU 执行基本任务,例如添加两个数字。
Solidity 可以选择在智能合约的源代码中编写汇编语言代码。在 Solidity 组装的帮助下,我们可以使用操作码直接与 EVM 交互。汇编提供了对某些仅使用solidity 无法实现的逻辑的更多控制,例如指向特定的内存块。主要优点之一是它降低了用于部署合约的 gas 成本。 Solidity 有两种方式来实现汇编语言:
内联汇编:内联汇编代码可以写在solidity代码中,以实现更细粒度的控制,特别是用于通过创建新库来增强语言。内联汇编可以以 EVM 可以理解的方式插入到 Solidity 语句之间。当优化器无法生成高效代码时,也可以使用它。当使用汇编局部变量、函数调用、switch 语句、if 语句、循环等功能时,Solidity 变得更容易。
句法:
assembly{
// assembly language statements
}
示例:在下面的示例中,创建了一个带有函数的合约,其中内联汇编代码位于函数内部。
Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Inline Assembly
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
// Creating a contract
contract InlineAssembly {
// Defining function
function add(uint a) view returns (uint b) {
// Inline assembly code
assembly {
// Creating a new variable 'c'
// Calculate the sum of 'a+16'
// with the 'add' opcode
// assign the value to the 'c'
let c := add(a, 16)
// Use 'mstore' opcode to
// store 'c' in memory
// at memory address 0x80
mstore(0x80, c)
{
// Creating a new variable'
// Calculate the sum of 'sload(c)+12'
// means values in variable 'c'
// with the 'add' opcode
// assign the value to 'd'
let d := add(sload(c), 12)
// assign the value of 'd' to 'b'
b := d
// 'd' is deallocated now
}
// Calculate the sum of 'b+c' with the 'add' opcode
// assign the value to 'b'
b := add(b, c)
// 'c' is deallocated here
}
}
}Solidity
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Standalone Assembly
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
// Creating a contract
contract StandaloneAssembly {
// Defining a function
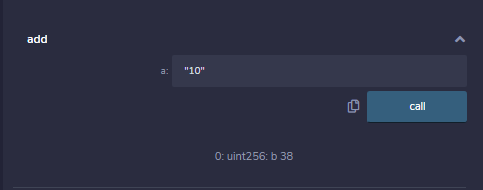
function add(uint a) view returns (uint b) {
// Initializing the variable b
b = 10;
// Executing for loop till the condition is met
for (uint n = 0; n < a; n++)
b = b + a;
}
}
输出 :
有时编写汇编代码比较困难,因为不会执行检查,这就是为什么最好仅在事情复杂并且您知道自己在做什么时使用。
独立程序集:独立程序集计划用于为solidity 编译器制作中间语言。它支持最近的兼容性,但它不再记录在solidity文档中。即使代码是由 Solidity 编译器生成的,以独立程序集编写的程序也是可读的。控制流应该很容易,用于优化和形式验证。
示例:在下面的示例中,创建了合约和函数来演示独立程序集的概念。
坚固性
// Solidity program to demonstrate
// Standalone Assembly
pragma solidity ^0.4.0;
// Creating a contract
contract StandaloneAssembly {
// Defining a function
function add(uint a) view returns (uint b) {
// Initializing the variable b
b = 10;
// Executing for loop till the condition is met
for (uint n = 0; n < a; n++)
b = b + a;
}
}
上述示例的汇编级代码是:
mstore(0x40, 0x60) // this line will store the “free memory pointer”
// dispatch function
switch div(calldataload(0), exp(2, 226))
case 0xb3de649b {
let (retData) = func(calldataload(4))
let retVal := $memAllocate(0x20)
mstore(retVal, retData)
return(retVal, 0x20)
}
default { revert(0, 0) }
// allocate memory
function $memAllocate(size) -> pos {
pos := mload(0x40)
mstore(0x40, add(pos, size))
}
// function of the contract
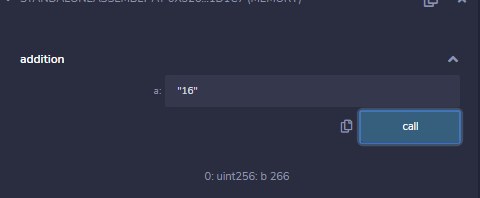
function addition(a) -> b {
b := 10
for { let n := 0 } lt(n, a) { n := add(n, 1) } {
b := add(a, b)
}
}
}
输出 :