Julia 中的序列化
与其他编程语言一样,Julia 也提供对序列化和反序列化的支持。为了将对象存储到内存、文件或数据库中,将对象转换为字节流(IO 缓冲区)的过程称为序列化。执行它是为了保存对象状态以备后用。反向过程称为反序列化。
在 Julia 中执行序列化的方法:
- 序列化是通过 Julia 中的序列化模块实现的。
- Julia 中的 JLD2 模块以包含 HDF5 子集的格式保存和加载 Julia 数据结构,而不依赖于 HDF5 C 库。它优于 Julia 的内置序列化器。
- BSON 模块也可以用来提供序列化的特性。
Serialization.serialize()函数
句法:
serialize(stream::IO, value)
and
serialize(filename::AbstractString, value)
Serialization.deserialize()函数
句法:
deserialize(stream)
and
deserialize(filename::AbstractString)
Note:
- serialize and deserialize functions perform read and write operations using iobuffer object. IOBuffer acts as an in-memory I/O stream.
- The function take! fetches iobuffer contents as a byte array and resets it to its initial state.
使用各种模块执行序列化
使用序列化模块:
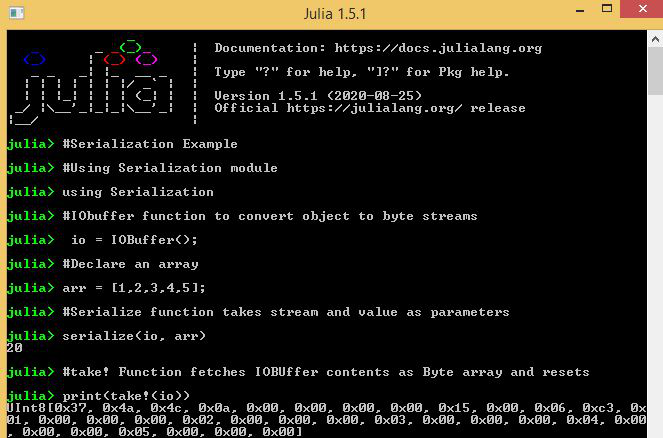
Julia
# Serialization Example
# Using Serialization module
using Serialization
# IObuffer function to convert
# object to byte streams
io = IOBuffer();
# Declare an array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
# Serialize function takes stream
# and value as parameters
serialize(io, arr)
# take! function fetches IOBUffer
# contents as Byte array and resets
print(take!(io))Julia
# Serialization using JLD2 module
# Using JLD2 module
using JLD2
# Using FileIO module
using FileIO
# Declare an array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
# Create a file
file = File(format"JLD2", "array.jld2")
# Save data into the file
save(file, "arr", arr)
# Load the file
data = load(file)
# Display user-visible data
dump(data["arr"])Julia
# Serialization using BSON module
# Using BSON module
using BSON
bson("test.bson",
Dict(:arr => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
:str => "GfG!"))
BSON.load("test.bson")Julia
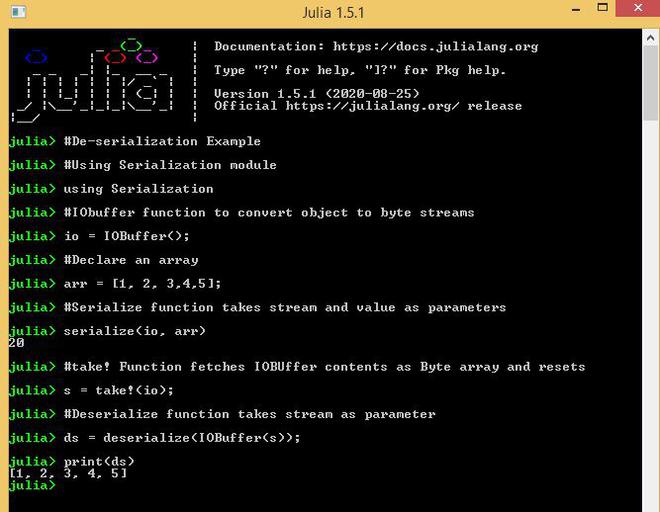
# De-serialization Example
# Using Serialization module
using Serialization
# IObuffer function to convert
# object to byte streams
io = IOBuffer();
# Declare an array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
# Serialize function takes stream
# and value as parameters
serialize(io, arr)
# take! Function fetches IOBUffer contents
# as Byte array and resets
s = take!(io);
# Deserialize function takes stream as parameter
ds = deserialize(IOBuffer(s));
print(ds)输出:
使用 JLD2 模块:
朱莉娅
# Serialization using JLD2 module
# Using JLD2 module
using JLD2
# Using FileIO module
using FileIO
# Declare an array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
# Create a file
file = File(format"JLD2", "array.jld2")
# Save data into the file
save(file, "arr", arr)
# Load the file
data = load(file)
# Display user-visible data
dump(data["arr"])
输出:

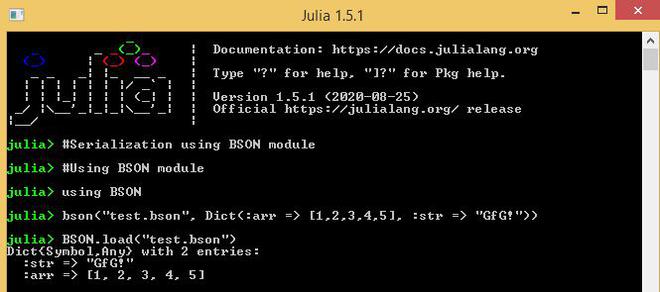
使用 BSON 模块:
朱莉娅
# Serialization using BSON module
# Using BSON module
using BSON
bson("test.bson",
Dict(:arr => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
:str => "GfG!"))
BSON.load("test.bson")
输出:
使用序列化模块执行反序列化
朱莉娅
# De-serialization Example
# Using Serialization module
using Serialization
# IObuffer function to convert
# object to byte streams
io = IOBuffer();
# Declare an array
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
# Serialize function takes stream
# and value as parameters
serialize(io, arr)
# take! Function fetches IOBUffer contents
# as Byte array and resets
s = take!(io);
# Deserialize function takes stream as parameter
ds = deserialize(IOBuffer(s));
print(ds)
输出: