先决条件:创建虚拟机并在Google Cloud中设置API
在上一篇文章中,我们已经了解了如何使用Vision API使用Vision的面部检测,徽标检测,标签检测和地标检测功能,现在让我们看看诸如光学字符识别,手写文本检测,图像属性检测等更多功能。
文本检测(光学字符识别):
它检测并提取图像中的文本。
import os
import io
from google.cloud import vision
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import patches as pch
os.environ['GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS'] =
os.path.join(os.curdir, 'credentials.json')
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
f = 'image_filename.jpg'
with io.open(f, 'rb') as image:
content = image.read()
image = vision.types.Image(content = content)
response = client.text_detection(image = image)
texts = response.text_annotations
a = plt.imread(f)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1)
ax.imshow(a)
for text in texts:
print(text.description)
vertices = ([(vertex.x, vertex.y)
for vertex in text.bounding_poly.vertices])
print('Vertices covering text: {}\n\n'.format(vertices))
rect = pch.Rectangle(vertices[0], (vertices[1][0] - vertices[0][0]),
(vertices[2][1] - vertices[0][1]), linewidth = 1,
edgecolor ='r', facecolor ='none')
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
上面的代码从给定的图像中提取文本,并打印包含文本的矩形的顶点坐标。
例如,当以下图像作为输入给出时: 
输出:
MY MORNING
ROUTINE
How Successful People Start
Every Day Inspired
BENJAMIN SPALL and MICHAEL XANDER
Vertices covering text: [(38, 71), (348, 71), (348, 602), (38, 602)]
MY
Vertices covering text: [(46, 71), (108, 82), (100, 128), (38, 117)]
MORNING
Vertices covering text: [(129, 79), (348, 118), (338, 170), (120, 131)]
ROUTINE
Vertices covering text: [(96, 135), (292, 170), (283, 219), (87, 184)]
How
Vertices covering text: [(68, 200), (101, 205), (98, 221), (65, 216)]
Successful
Vertices covering text: [(104, 207), (196, 222), (193, 238), (101, 224)]
People
Vertices covering text: [(202, 222), (257, 231), (254, 251), (199, 242)]
Start
Vertices covering text: [(265, 232), (311, 239), (309, 255), (262, 248)]
Every
Vertices covering text: [(112, 238), (155, 246), (152, 265), (109, 258)]
Day
Vertices covering text: [(160, 246), (189, 251), (185, 271), (157, 266)]
Inspired
Vertices covering text: [(194, 251), (262, 263), (258, 283), (191, 271)]
BENJAMIN
Vertices covering text: [(57, 534), (118, 546), (115, 561), (54, 549)]
SPALL
Vertices covering text: [(122, 550), (160, 558), (157, 572), (119, 564)]
and
Vertices covering text: [(165, 560), (185, 564), (182, 577), (162, 573)]
MICHAEL
Vertices covering text: [(190, 564), (250, 576), (247, 590), (187, 578)]
XANDER
Vertices covering text: [(254, 575), (311, 587), (308, 602), (251, 591)]
文档/手写文字检测:
此功能还可以对密集的文档(包括手写体)执行光学字符识别。
import os
import io
from google.cloud import vision
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
os.environ['GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS'] =
os.path.join(os.curdir, 'credentials.json')
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
f = 'image_filename.jpg'
with io.open(f, 'rb') as image:
content = image.read()
image = vision.types.Image(content = content)
response = client.document_text_detection(image = image)
a = plt.imread(f)
plt.imshow(a)
txt = []
for page in response.full_text_annotation.pages:
for block in page.blocks:
print('\nConfidence: {}%\n'.format(block.confidence * 100))
for paragraph in block.paragraphs:
for word in paragraph.words:
word_text = ''.join([symbol.text for symbol in word.symbols])
txt.append(word_text)
print(txt)
上面的代码从图像中识别并提取手写文本,然后将其输出。
例如,当我们提供以下图像作为输入时: 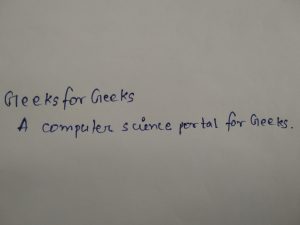
输出:
Block confidence: 97.00000286102295%
['Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks', 'A', 'computer', 'science', 'portal', 'for', 'Geeks', '.']图像属性检测:
此功能可检测图像的一般属性,例如主色。
import os
import io
from google.cloud import vision
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
os.environ['GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS'] =
os.path.join(os.curdir, 'credentials.json')
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
f = 'image_filename.jpeg'
with io.open(f, 'rb') as image:
content = image.read()
image = vision.types.Image(content = content)
response = client.image_properties(image = image)
properties = response.image_properties_annotation
a = plt.imread(f)
plt.imshow(a)
for color in properties.dominant_colors.colors:
print('fraction: {}'.format(color.pixel_fraction))
print('\tr: {}'.format(color.color.red))
print('\tg: {}'.format(color.color.green))
print('\tb: {}'.format(color.color.blue))
该代码将图像作为输入,并返回其颜色属性,即红色,绿色和蓝色的数量。例如,当以下图像作为输入给出时: 
输出:
fraction: 0.036332178860902786
r: 5.0
g: 185.0
b: 6.0
fraction: 0.03337658569216728
r: 131.0
g: 207.0
b: 13.0
fraction: 0.029988465830683708
r: 253.0
g: 169.0
b: 5.0
fraction: 0.0262399073690176
r: 254.0
g: 123.0
b: 5.0
fraction: 0.03553921729326248
r: 253.0
g: 248.0
b: 12.0
fraction: 0.02104959636926651
r: 249.0
g: 36.0
b: 6.0
fraction: 0.024581892415881157
r: 3.0
g: 35.0
b: 188.0
fraction: 0.03424163907766342
r: 6.0
g: 122.0
b: 200.0
fraction: 0.027032872661948204
r: 140.0
g: 32.0
b: 185.0
fraction: 0.029411764815449715
r: 10.0
g: 177.0
b: 217.0安全搜索属性检测:
检测图像中的露骨内容,例如成人内容或暴力内容。此功能使用五个类别(“成人”,“欺骗”,“医疗”,“暴力”和“犯罪”),并返回给定图像中存在每种可能性。
import os
import io
from google.cloud import vision
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
os.environ['GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS'] =
os.path.join(os.curdir, 'credentials.json')
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
f = 'image_filename.jpg'
with io.open(f, 'rb') as image:
content = image.read()
image = vision.types.Image(content = content)
a = plt.imread(f)
plt.imshow(a)
response = client.safe_search_detection(image = image)
safe = response.safe_search_annotation
likelihood_name = ('UNKNOWN', 'VERY_UNLIKELY', 'UNLIKELY',
'POSSIBLE', 'LIKELY', 'VERY_LIKELY')
print('Adult: {}'.format(likelihood_name[safe.adult]))
print('Medical: {}'.format(likelihood_name[safe.medical]))
print('Spoofed: {}'.format(likelihood_name[safe.spoof]))
print('Violence: {}'.format(likelihood_name[safe.violence]))
print('Racy: {}'.format(likelihood_name[safe.racy]))
对于给定的图像,代码将确定其为具有图形或成人内容的图像的可能性。
物体检测:
从图像中检测并提取多个对象。它定位多个对象并返回其坐标。
import os
import io
from google.cloud import vision
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
os.environ['GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS'] =
os.path.join(os.curdir, 'credentials.json')
client = vision.ImageAnnotatorClient()
f = 'image_filename.jpg'
with io.open(f, 'rb') as image:
content = image.read()
image = vision.types.Image(content = content)
a = plt.imread(f)
plt.imshow(a)
response = client.object_localization(image = image)
objects = response.localized_object_annotations
print('Number of objects found: ', len(objects))
for object_ in objects:
print('Object: ', object_.name)
print('Confidence: ', object_.score)
例如,当我们输入以下图像时: 
输出:
Number of objects found: 1
Object: Scissors
Confidence: 0.540185272693634有关更多信息,请在此处访问Cloud Vision API文档。