使用Python从 Google Drive 存储上传和下载文件
在本文中,我们将了解如何使用Python中的 API 将文件从 Google Drive 下载到我们的 PC 并从我们的 PC 上传文件到 Google Drive。它是一个 REST API,允许您从应用程序或程序中利用 Google Drive 存储。所以,让我们继续编写一个Python脚本来做到这一点。
要求:
- Python (2.6 或更高版本)
- 启用了 Google Drive 的 Google 帐户
- Google API 客户端和 Google OAuth 库
安装:
通过运行以下命令安装所需的库:
pip install –upgrade google-api-python-client google-auth-httplib2 google-auth-oauthlib
设置:
- 现在,要使用 Google Drive API,我们必须设置我们的帐户并启用Google Drive API。
- 要设置您的帐户,您可以按照文章中给出的步骤进行操作。
- 所以,现在我们已经准备好编写Python脚本了。
请确保文件credentials.json位于同一目录中。
入门
首先,我们将导入所需的库。然后我们将定义一个带有构造函数和两个用于上传和下载文件的函数的类DriveAPI 。在构造函数中,我们将检查文件“ token.pickle”是否存在。如果存在,则意味着我们可以访问 Google 云端硬盘存储空间,并且无需再次请求。如果令牌使用时间很长,我们可能需要刷新令牌。如果它不存在或无效,脚本将在浏览器中打开一个新选项卡并要求访问 Google Drive。
授予访问权限后,它将连接到驱动器并为该帐户获取 Google Drive 存储中的文件列表并打印该列表。列表中的每一项都包含 Google Drive 中该文件的 ID 和名称。
现在,在FileDownload函数中,我们将编写下载文件的代码。我们需要做两件事来做到这一点。第一个是该文件在 Drive 中的ID ,第二个是您希望将其保存为的名称。现在,我们将向 Drive 服务发出请求,以获取具有给定ID 的文件。然后,我们将使用一个BytesIO对象将文件写入内存。我们将使用MediaIoBaseDownload类从服务器接收文件并使用BytesIO对象将其写入内存。由于文件大小可能从几个字节到非常大不等,我们更喜欢以块格式下载文件。我们还可以传递块大小 如果我们不想使用默认的。现在,我们将运行一个 while 循环,并且在该循环的每次迭代中,我们将下载文件的一个块。完成后,我们会将文件从内存写入硬盘存储。我们将整个过程包装在一个 try-except 块中,这样如果出现问题,我们的脚本就不会抛出错误。
要上传文件,我们将使用FileUpload函数。我们只需要文件路径来上传文件。从文件路径中,我们可以轻松地提取文件名并使用mimetypes模块找到其 mime-type。我们将使用包含文件名的键“name”创建一个字典。现在,我们将使用MediaFileUpload类来生成媒体文件,然后我们将使用 create函数在驱动器中创建一个新文件,它将我们的文件数据保存到新创建的文件中。
执行:
Python3
# import the required libraries
from __future__ import print_function
import pickle
import os.path
import io
import shutil
import requests
from mimetypes import MimeTypes
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
from google_auth_oauthlib.flow import InstalledAppFlow
from google.auth.transport.requests import Request
from googleapiclient.http import MediaIoBaseDownload, MediaFileUpload
class DriveAPI:
global SCOPES
# Define the scopes
SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive']
def __init__(self):
# Variable self.creds will
# store the user access token.
# If no valid token found
# we will create one.
self.creds = None
# The file token.pickle stores the
# user's access and refresh tokens. It is
# created automatically when the authorization
# flow completes for the first time.
# Check if file token.pickle exists
if os.path.exists('token.pickle'):
# Read the token from the file and
# store it in the variable self.creds
with open('token.pickle', 'rb') as token:
self.creds = pickle.load(token)
# If no valid credentials are available,
# request the user to log in.
if not self.creds or not self.creds.valid:
# If token is expired, it will be refreshed,
# else, we will request a new one.
if self.creds and self.creds.expired and self.creds.refresh_token:
self.creds.refresh(Request())
else:
flow = InstalledAppFlow.from_client_secrets_file(
'credentials.json', SCOPES)
self.creds = flow.run_local_server(port=0)
# Save the access token in token.pickle
# file for future usage
with open('token.pickle', 'wb') as token:
pickle.dump(self.creds, token)
# Connect to the API service
self.service = build('drive', 'v3', credentials=self.creds)
# request a list of first N files or
# folders with name and id from the API.
results = self.service.files().list(
pageSize=100, fields="files(id, name)").execute()
items = results.get('files', [])
# print a list of files
print("Here's a list of files: \n")
print(*items, sep="\n", end="\n\n")
def FileDownload(self, file_id, file_name):
request = self.service.files().get_media(fileId=file_id)
fh = io.BytesIO()
# Initialise a downloader object to download the file
downloader = MediaIoBaseDownload(fh, request, chunksize=204800)
done = False
try:
# Download the data in chunks
while not done:
status, done = downloader.next_chunk()
fh.seek(0)
# Write the received data to the file
with open(file_name, 'wb') as f:
shutil.copyfileobj(fh, f)
print("File Downloaded")
# Return True if file Downloaded successfully
return True
except:
# Return False if something went wrong
print("Something went wrong.")
return False
def FileUpload(self, filepath):
# Extract the file name out of the file path
name = filepath.split('/')[-1]
# Find the MimeType of the file
mimetype = MimeTypes().guess_type(name)[0]
# create file metadata
file_metadata = {'name': name}
try:
media = MediaFileUpload(filepath, mimetype=mimetype)
# Create a new file in the Drive storage
file = self.service.files().create(
body=file_metadata, media_body=media, fields='id').execute()
print("File Uploaded.")
except:
# Raise UploadError if file is not uploaded.
raise UploadError("Can't Upload File.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
obj = DriveAPI()
i = int(input("Enter your choice:
"1 - Download file, 2- Upload File, 3- Exit.\n"))
if i == 1:
f_id = input("Enter file id: ")
f_name = input("Enter file name: ")
obj.FileDownload(f_id, f_name)
elif i == 2:
f_path = input("Enter full file path: ")
obj.FileUpload(f_path)
else:
exit()输出:
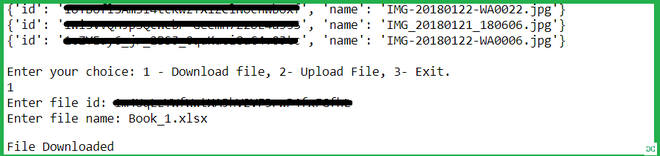
这将尝试在您的默认浏览器中打开一个新窗口。如果失败,请从控制台复制 URL 并在浏览器中手动打开它。现在,如果您尚未登录,请登录您的 Google 帐户。如果有多个帐户,系统会要求您选择其中一个。然后,单击“允许”按钮继续。身份验证完成后,您的浏览器将显示一条消息“身份验证流程已完成。您可以关闭此窗口。 ” 现在,该程序将打印您的 Google 驱动器中的文件列表,并询问您是要上传还是下载文件。