本文介绍了一种通过将其简化为RMQ问题来解决在树中找到两个节点的LCA的问题的方法。
根树T中两个节点u和v的最低共同祖先(LCA)定义为距离根最远的节点,该节点同时具有u和v作为后代。
例如,在下图中,节点4和节点9的LCA是节点2。
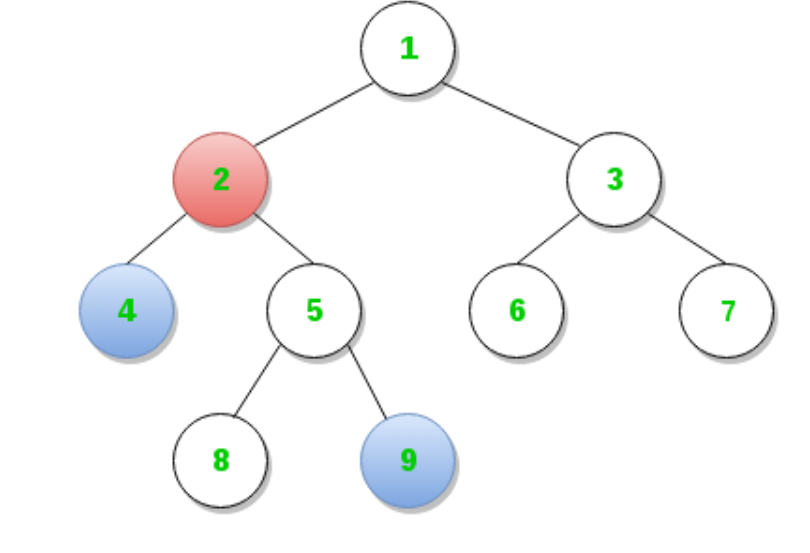
有很多解决LCA问题的方法。这些方法的时间和空间复杂性不同。这是其中几个的链接(这些不涉及降低RMQ)。
数组上使用范围最小查询(Range Minimum Query,RMQ)查找元素在两个指定索引之间具有最小值的位置。这里和这里讨论了解决RMQ的不同方法。在本文中,讨论了基于分段树的方法。对于段树,预处理时间为O(n),范围最小查询到的时间为O(Logn)。存储段树所需的额外空间为O(n)。
将LCA减少为RMQ:
这个想法是通过Euler游览(无需举起铅笔进行遍历)从根开始遍历树,这是一种具有预遍历特性的DFS型遍历。
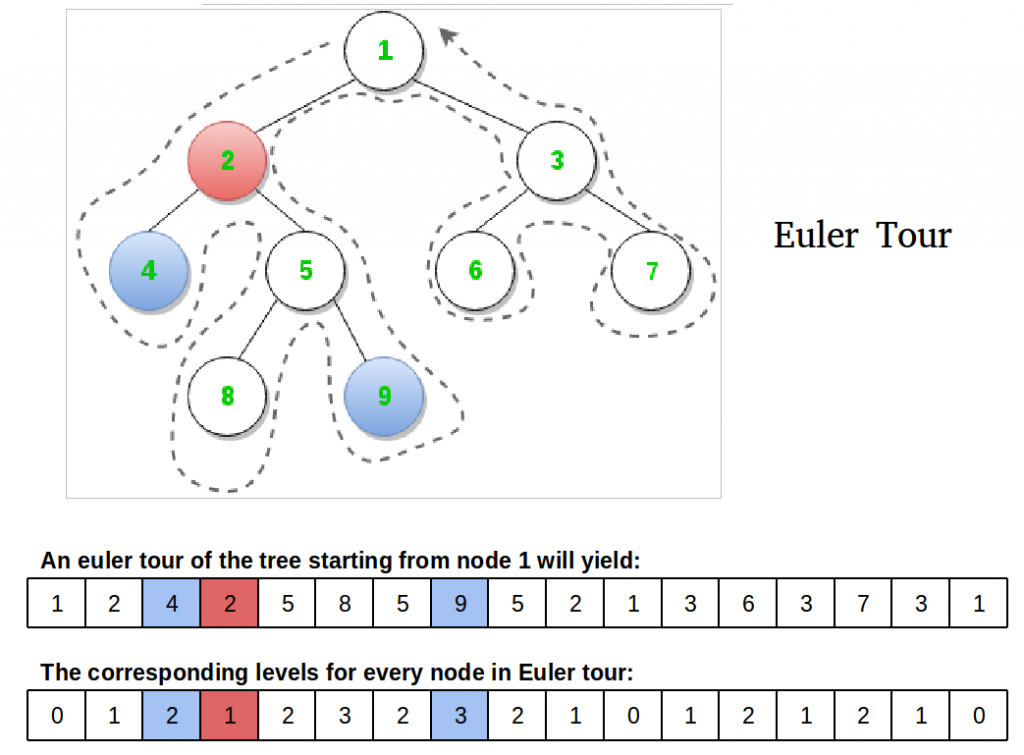
观察:节点4和9的LCA是节点2,它恰好是在D的TFS期间4和9的访问之间遇到的所有根中最靠近根的节点。此观察是减少的关键。让我们重新表述一下:在Euler环游T中,在u和v的连续出现(任意)之间发生的所有节点中,我们的节点是最小级别的节点,并且是该级别上的唯一节点。
我们需要三个数组来实现:
- 按照Euler T巡回的顺序访问了节点
- 欧拉T游览中访问的每个节点的级别
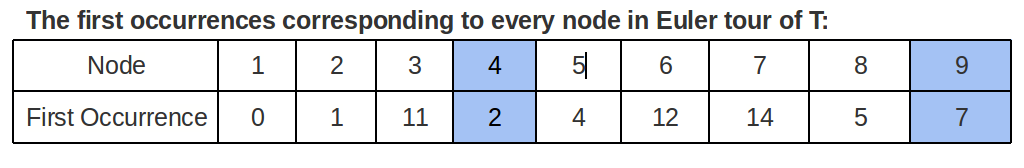
- 欧拉巡回T中第一次出现的节点的索引(因为任何出现都很好,让我们跟踪第一个)
算法:
- 在树上进行Euler游览,并填充Euler,Level和首次出现的数组。
- 使用第一个出现数组,获取与两个节点相对应的索引,这两个节点将成为级别数组中范围的角,该级别数组将馈给RMQ算法以获取最小值。
- 一旦算法返回该范围内最小级别的索引,我们就可以使用它通过Euler巡回数组确定LCA。
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
/* C++ Program to find LCA of u and v by reducing the problem to RMQ */
#include
#define V 9 // number of nodes in input tree
int euler[2*V - 1]; // For Euler tour sequence
int level[2*V - 1]; // Level of nodes in tour sequence
int firstOccurrence[V+1]; // First occurrences of nodes in tour
int ind; // Variable to fill-in euler and level arrays
// A Binary Tree node
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function creates a new binary tree node with given key
Node * newNode(int k)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = k;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// log base 2 of x
int Log2(int x)
{
int ans = 0 ;
while (x>>=1) ans++;
return ans ;
}
/* A recursive function to get the minimum value in a given range
of array indexes. The following are parameters for this function.
st --> Pointer to segment tree
index --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
0 is passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range */
int RMQUtil(int index, int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int *st)
{
// If segment of this node is a part of given range, then return
// the min of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st[index];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
else if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return -1;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = (ss + se)/2;
int q1 = RMQUtil(2*index+1, ss, mid, qs, qe, st);
int q2 = RMQUtil(2*index+2, mid+1, se, qs, qe, st);
if (q1==-1) return q2;
else if (q2==-1) return q1;
return (level[q1] < level[q2]) ? q1 : q2;
}
// Return minimum of elements in range from index qs (query start) to
// qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
int RMQ(int *st, int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n-1 || qs > qe)
{
printf("Invalid Input");
return -1;
}
return RMQUtil(0, 0, n-1, qs, qe, st);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
void constructSTUtil(int si, int ss, int se, int arr[], int *st)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se)st[si] = ss;
else
{
// If there are more than one elements, then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the minimum of two values in this node
int mid = (ss + se)/2;
constructSTUtil(si*2+1, ss, mid, arr, st);
constructSTUtil(si*2+2, mid+1, se, arr, st);
if (arr[st[2*si+1]] < arr[st[2*si+2]])
st[si] = st[2*si+1];
else
st[si] = st[2*si+2];
}
}
/* Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
fill the allocated memory */
int *constructST(int arr[], int n)
{
// Allocate memory for segment tree
// Height of segment tree
int x = Log2(n)+1;
// Maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2*(1<key; // insert in euler array
level[ind] = l; // insert l in level array
ind++; // increment index
/* if unvisited, mark first occurrence */
if (firstOccurrence[root->key] == -1)
firstOccurrence[root->key] = ind-1;
/* tour left subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (root->left)
{
eulerTour(root->left, l+1);
euler[ind]=root->key;
level[ind] = l;
ind++;
}
/* tour right subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (root->right)
{
eulerTour(root->right, l+1);
euler[ind]=root->key;
level[ind] = l;
ind++;
}
}
}
// Returns LCA of nodes n1, n2 (assuming they are
// present in the tree)
int findLCA(Node *root, int u, int v)
{
/* Mark all nodes unvisited. Note that the size of
firstOccurrence is 1 as node values which vary from
1 to 9 are used as indexes */
memset(firstOccurrence, -1, sizeof(int)*(V+1));
/* To start filling euler and level arrays from index 0 */
ind = 0;
/* Start Euler tour with root node on level 0 */
eulerTour(root, 0);
/* construct segment tree on level array */
int *st = constructST(level, 2*V-1);
/* If v before u in Euler tour. For RMQ to work, first
parameter 'u' must be smaller than second 'v' */
if (firstOccurrence[u]>firstOccurrence[v])
std::swap(u, v);
// Starting and ending indexes of query range
int qs = firstOccurrence[u];
int qe = firstOccurrence[v];
// query for index of LCA in tour
int index = RMQ(st, 2*V-1, qs, qe);
/* return LCA node */
return euler[index];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create the Binary Tree as shown in the diagram.
Node * root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->right->left = newNode(8);
root->left->right->right = newNode(9);
int u = 4, v = 9;
printf("The LCA of node %d and node %d is node %d.\n",
u, v, findLCA(root, u, v));
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find LCA of u and v by reducing problem to RMQ
import java.util.*;
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
Node left, right;
int data;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class St_class
{
int st;
int stt[] = new int[10000];
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
int v = 9; // v is the highest value of node in our tree
int euler[] = new int[2 * v - 1]; // for euler tour sequence
int level[] = new int[2 * v - 1]; // level of nodes in tour sequence
int f_occur[] = new int[2 * v - 1]; // to store 1st occurrence of nodes
int fill; // variable to fill euler and level arrays
St_class sc = new St_class();
// log base 2 of x
int Log2(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
int y = x >>= 1;
while (y-- != 0)
ans++;
return ans;
}
int swap(int a, int b)
{
return a;
}
/* A recursive function to get the minimum value in a given range
of array indexes. The following are parameters for this function.
st --> Pointer to segment tree
index --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
0 is passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range */
int RMQUtil(int index, int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, St_class st)
{
// If segment of this node is a part of given range, then return
// the min of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st.stt[index];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
else if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return -1;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = (ss + se) / 2;
int q1 = RMQUtil(2 * index + 1, ss, mid, qs, qe, st);
int q2 = RMQUtil(2 * index + 2, mid + 1, se, qs, qe, st);
if (q1 == -1)
return q2;
else if (q2 == -1)
return q1;
return (level[q1] < level[q2]) ? q1 : q2;
}
// Return minimum of elements in range from index qs (query start) to
// qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
int RMQ(St_class st, int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n - 1 || qs > qe)
{
System.out.println("Invalid input");
return -1;
}
return RMQUtil(0, 0, n - 1, qs, qe, st);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
void constructSTUtil(int si, int ss, int se, int arr[], St_class st)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se)
st.stt[si] = ss;
else
{
// If there are more than one elements, then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the minimum of two values in this node
int mid = (ss + se) / 2;
constructSTUtil(si * 2 + 1, ss, mid, arr, st);
constructSTUtil(si * 2 + 2, mid + 1, se, arr, st);
if (arr[st.stt[2 * si + 1]] < arr[st.stt[2 * si + 2]])
st.stt[si] = st.stt[2 * si + 1];
else
st.stt[si] = st.stt[2 * si + 2];
}
}
/* Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
fill the allocated memory */
int constructST(int arr[], int n)
{
// Allocate memory for segment tree
// Height of segment tree
int x = Log2(n) + 1;
// Maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2 * (1 << x) - 1; // 2*pow(2,x) -1
sc.stt = new int[max_size];
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructSTUtil(0, 0, n - 1, arr, sc);
// Return the constructed segment tree
return sc.st;
}
// Recursive version of the Euler tour of T
void eulerTour(Node node, int l)
{
/* if the passed node exists */
if (node != null)
{
euler[fill] = node.data; // insert in euler array
level[fill] = l; // insert l in level array
fill++; // increment index
/* if unvisited, mark first occurrence */
if (f_occur[node.data] == -1)
f_occur[node.data] = fill - 1;
/* tour left subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (node.left != null)
{
eulerTour(node.left, l + 1);
euler[fill] = node.data;
level[fill] = l;
fill++;
}
/* tour right subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (node.right != null)
{
eulerTour(node.right, l + 1);
euler[fill] = node.data;
level[fill] = l;
fill++;
}
}
}
// returns LCA of node n1 and n2 assuming they are present in tree
int findLCA(Node node, int u, int v)
{
/* Mark all nodes unvisited. Note that the size of
firstOccurrence is 1 as node values which vary from
1 to 9 are used as indexes */
Arrays.fill(f_occur, -1);
/* To start filling euler and level arrays from index 0 */
fill = 0;
/* Start Euler tour with root node on level 0 */
eulerTour(root, 0);
/* construct segment tree on level array */
sc.st = constructST(level, 2 * v - 1);
/* If v before u in Euler tour. For RMQ to work, first
parameter 'u' must be smaller than second 'v' */
if (f_occur[u] > f_occur[v])
u = swap(u, u = v);
// Starting and ending indexes of query range
int qs = f_occur[u];
int qe = f_occur[v];
// query for index of LCA in tour
int index = RMQ(sc, 2 * v - 1, qs, qe);
/* return LCA node */
return euler[index];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create the Binary Tree as shown in the diagram.
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
int u = 4, v = 9;
System.out.println("The LCA of node " + u + " and " + v + " is "
+ tree.findLCA(tree.root, u, v));
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython3
# Python3 program to find LCA of u and v by
# reducing the problem to RMQ
from math import log2, floor
from typing import List
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: int):
self.val, self.left, self.right = val, None, None
class BinaryTree:
def __init__(self, root: Node):
self.root = root
self.val_max = self._get_max_val()
self.euler = [0] * (2 * self.val_max - 1)
self.level = [0] * (2 * self.val_max - 1)
self.f_occur = [-1] * (self.val_max + 1)
self.fill = 0
self.segment_tree = []
def _get_max_val(self):
stack = [self.root]
max_val = -1
while stack:
x = stack.pop()
if x.val > max_val:
max_val = x.val
if x.left:
stack.append(x.left)
if x.right:
stack.append(x.right)
return max_val
''' A recursive function to get the minimum value in a given range
of array indexes. The following are parameters for this function.
st --> Pointer to segment tree
index --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially
0 is passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented
by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range '''
def rmq_util(self, index, ss, se, qs, qe) -> int:
# If segment of this node is part of given range
# then return the min of the segment
if qs <= ss and qe >= se:
return self.segment_tree[index]
# If segment of this node is outside
# the given range
elif se < qs or ss > qe:
return -1
# If part of this segment overlaps with
# given range
mid = (ss + se) // 2
q1 = self.rmq_util(2 * index + 1,
ss, mid, qs, qe)
q2 = self.rmq_util(2 * index + 2, mid + 1,
se, qs, qe)
if q1 == -1:
return q2
if q2 == -1:
return q1
return (q1 if self.level[q1] <
self.level[q2] else q2)
# Return minimum of elements in range from
# index qs (query start) to qe (query end).
# It mainly uses rmq_util()
def rmq(self, n: int, qs: int, qe: int) -> int:
if qs < 0 or qe > n - 1 or qs > qe:
print('invalid input')
return -1
return self.rmq_util(0, 0, n - 1, qs, qe)
# A recursive function that constructs Segment
# Tree for array[ss..se]. si is index of
# current node in segment tree st
def construct_segment_tree_util(self, si, ss,
se, arr):
# If there is one element in array,
# store it in current node of segment tree
# and return
if ss == se:
self.segment_tree[si] = ss
else:
# If there are more than one elements,
# then recur for left and right subtrees and
# store the min of two values in this node
mid = (ss + se) // 2
index_left, index_right = si * 2 + 1, si * 2 + 2
self.construct_segment_tree_util(
index_left, ss, mid, arr)
self.construct_segment_tree_util(
index_right, mid+1, se, arr)
if (arr[self.segment_tree[index_left]] <
arr[self.segment_tree[index_right]]):
self.segment_tree[si] = self.segment_tree[index_left]
else:
self.segment_tree[si] = self.segment_tree[index_right]
# Function to construct segment tree from given
# array. This function allocates memory for segment
# tree and calls construct_segment_tree_util()
# to fill the allocated memory
def construct_segment_tree(self, arr: List, n: int):
# Height of segment tree
x = floor(log2(n) + 1)
# Maximum size of segment tree
max_size = 2 * (1 << x) - 1 # 2*pow(2,x) -1
self.segment_tree = [0] * max_size
# Fill the allocated memory st
self.construct_segment_tree_util(
0, 0, n - 1, arr)
# Recursive version of the Euler tour of T
def euler_tour(self, node: Node, lev: int):
# If the passed node exists
if node is not None:
self.euler[self.fill] = node.val
self.level[self.fill] = lev
self.fill += 1
# If unvisited, mark first occurence
if self.f_occur[node.val] == -1:
self.f_occur[node.val] = self.fill - 1
# Tour left subtree if exists and remark
# euler and level arrays for parent on
# return
if node.left is not None:
self.euler_tour(node.left, lev + 1)
self.euler[self.fill] = node.val
self.level[self.fill] = lev
self.fill += 1
# Tour right subtree if exists and
# remark euler and level arrays for
# parent on return
if node.right is not None:
self.euler_tour(node.right, lev + 1)
self.euler[self.fill] = node.val
self.level[self.fill] = lev
self.fill += 1
# Returns LCA of nodes n1, n2 (assuming they are
# present in the tree)
def find_lca(self, u: int, v: int):
# Start euler tour with root node on level 0
self.euler_tour(self.root, 0)
# Construct segment tree on level array
self.construct_segment_tree(self.level,
2 * self.val_max - 1)
# For rmq to work, u must be smaller than v
if self.f_occur[u] > self.f_occur[v]:
u, v = v, u
# Start and end of query range
qs = self.f_occur[u]
qe = self.f_occur[v]
# Query for index of lca in tour
index = self.rmq(2 * self.val_max - 1, qs, qe)
# Return lca node
return self.euler[index]
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.left.right.left = Node(8)
root.left.right.right = Node(9)
tree = BinaryTree(root)
u, v = 4, 9
print('The lca of node {} and {} is node {}'.format(
u, v, tree.find_lca(u, v)))
# This code is contributed by Rajat SrivastavaC#
// C# program to find LCA of u and
// v by reducing problem to RMQ
using System;
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
public Node left, right;
public int data;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class St_class
{
public int st;
public int []stt = new int[10000];
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
static int v = 9; // v is the highest value of node in our tree
int []euler = new int[2 * v - 1]; // for euler tour sequence
int []level = new int[2 * v - 1]; // level of nodes in tour sequence
int []f_occur = new int[2 * v - 1]; // to store 1st occurrence of nodes
int fill; // variable to fill euler and level arrays
St_class sc = new St_class();
// log base 2 of x
int Log2(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
int y = x >>= 1;
while (y-- != 0)
ans++;
return ans;
}
int swap(int a, int b)
{
return a;
}
/* A recursive function to get
the minimum value in a given range
of array indexes. The following
are parameters for this function.
st --> Pointer to segment tree
index --> Index of current node
in the segment tree. Initially
0 is passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> Starting and ending
indexes of the segment represented
by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> Starting and ending
indexes of query range */
int RMQUtil(int index, int ss, int se,
int qs, int qe, St_class st)
{
// If segment of this node is a part
// of given range, then return
// the min of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st.stt[index];
// If segment of this node is
// outside the given range
else if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return -1;
// If a part of this segment
// overlaps with the given range
int mid = (ss + se) / 2;
int q1 = RMQUtil(2 * index + 1,
ss, mid, qs, qe, st);
int q2 = RMQUtil(2 * index + 2,
mid + 1, se, qs, qe, st);
if (q1 == -1)
return q2;
else if (q2 == -1)
return q1;
return (level[q1] < level[q2]) ? q1 : q2;
}
// Return minimum of elements in
// range from index qs (query start) to
// qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
int RMQ(St_class st, int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n - 1 || qs > qe)
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid input");
return -1;
}
return RMQUtil(0, 0, n - 1, qs, qe, st);
}
// A recursive function that constructs
// Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
void constructSTUtil(int si, int ss, int se,
int []arr, St_class st)
{
// If there is one element in array,
// store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se)
st.stt[si] = ss;
else
{
// If there are more than one elements,
// then recur for left and right subtrees
// and store the minimum of two values in this node
int mid = (ss + se) / 2;
constructSTUtil(si * 2 + 1, ss, mid, arr, st);
constructSTUtil(si * 2 + 2, mid + 1, se, arr, st);
if (arr[st.stt[2 * si + 1]] < arr[st.stt[2 * si + 2]])
st.stt[si] = st.stt[2 * si + 1];
else
st.stt[si] = st.stt[2 * si + 2];
}
}
/* Function to construct segment tree
from given array. This function
allocates memory for segment tree
and calls constructSTUtil() to
fill the allocated memory */
int constructST(int []arr, int n)
{
// Allocate memory for segment tree
// Height of segment tree
int x = Log2(n) + 1;
// Maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2 * (1 << x) - 1; // 2*pow(2,x) -1
sc.stt = new int[max_size];
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructSTUtil(0, 0, n - 1, arr, sc);
// Return the constructed segment tree
return sc.st;
}
// Recursive version of the Euler tour of T
void eulerTour(Node node, int l)
{
/* if the passed node exists */
if (node != null)
{
euler[fill] = node.data; // insert in euler array
level[fill] = l; // insert l in level array
fill++; // increment index
/* if unvisited, mark first occurrence */
if (f_occur[node.data] == -1)
f_occur[node.data] = fill - 1;
/* tour left subtree if exists,
and remark euler and level
arrays for parent on return */
if (node.left != null)
{
eulerTour(node.left, l + 1);
euler[fill] = node.data;
level[fill] = l;
fill++;
}
/* tour right subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (node.right != null)
{
eulerTour(node.right, l + 1);
euler[fill] = node.data;
level[fill] = l;
fill++;
}
}
}
// returns LCA of node n1 and n2
// assuming they are present in tree
int findLCA(Node node, int u, int v)
{
/* Mark all nodes unvisited. Note
that the size of firstOccurrence
is 1 as node values which
vary from 1 to 9 are used as indexes */
//Arrays.fill(f_occur, -1);
for(int i = 0; i < f_occur.Length; i++)
f_occur[i] = -1;
/* To start filling euler and
level arrays from index 0 */
fill = 0;
/* Start Euler tour with
root node on level 0 */
eulerTour(root, 0);
/* construct segment tree on level array */
sc.st = constructST(level, 2 * v - 1);
/* If v before u in Euler tour.
For RMQ to work, first parameter
'u' must be smaller than
second 'v' */
if (f_occur[u] > f_occur[v])
u = swap(u, u = v);
// Starting and ending indexes of query range
int qs = f_occur[u];
int qe = f_occur[v];
// query for index of LCA in tour
int index = RMQ(sc, 2 * v - 1, qs, qe);
/* return LCA node */
return euler[index];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String []args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
// Let us create the Binary Tree
// as shown in the diagram.
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(9);
int u = 4, v = 9;
Console.WriteLine("The LCA of node " + u + " and " + v + " is "
+ tree.findLCA(tree.root, u, v));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar输出:
The LCA of node 4 and node 9 is node 2.笔记:
- 我们假设查询的节点存在于树中。
- 我们还假设如果树中有V个节点,则这些节点的键(或数据)的范围是1到V。
时间复杂度:
- 欧拉巡回:节点数为V。对于树,E = V-1。欧拉巡视(DFS)将取O(V + E),即O(2 * V),可以写为O(V)。
- 段树结构:O(n),其中n = V + E = 2 * V – 1。
- 范围最小查询:O(log(n))
总体而言,此方法花费O(n)的时间进行预处理,但是花费O(Log n)的时间进行查询。因此,当我们要在其上执行大量LCA查询的一棵树时,这很有用(请注意,LCA对于查找二叉树的两个节点之间的最短路径很有用)
辅助空间:
- 欧拉巡视数组:O(n)其中n = 2 * V – 1
- 节点级别数组:O(n)
- 第一次出现数组:O(V)
- 细分树:O(n)