先决条件–芬威克树
我们知道,要有效地对一维数组进行范围和查询,二进制索引树(或Fenwick树)是最佳选择(由于内存需求更少,并且比段树更快,因此甚至比段树更好)。
我们是否可以使用二叉索引树有效地回答子矩阵和查询?
答案是肯定的。使用仅是一维BIT数组的2D BIT便可以做到这一点。
算法:
我们考虑以下示例。假设我们必须找到突出显示区域内所有数字的总和- 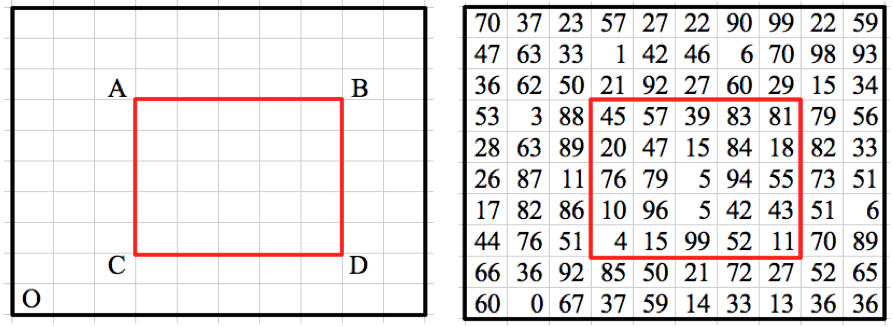
我们假设矩阵的原点位于底部–O。然后,二维BIT利用了以下事实:
Sum under the marked area = Sum(OB) - Sum(OD) -
Sum(OA) + Sum(OC) 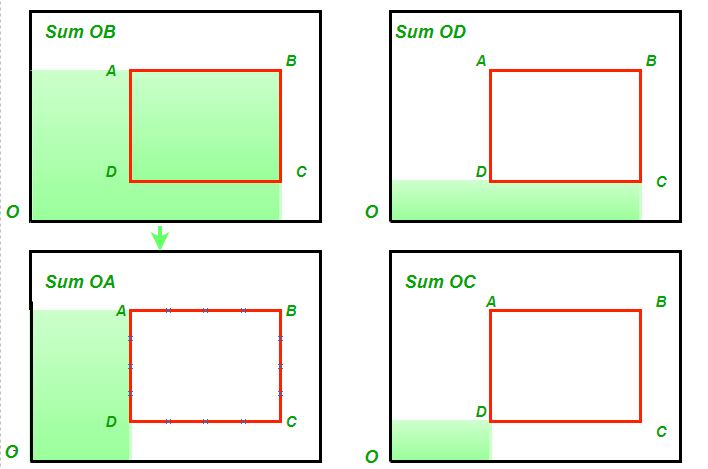
在我们的程序中,我们使用getSum(x,y)函数来查找从(0,0)到(x,y)的矩阵之和。
因此,以下公式:
Sum under the marked area = Sum(OB) - Sum(OD) -
Sum(OA) + Sum(OC)
The above formula gets reduced to,
Query(x1,y1,x2,y2) = getSum(x2, y2) -
getSum(x2, y1-1) -
getSum(x1-1, y2) +
getSum(x1-1, y1-1) 在哪里,
x1,y1 = C的x和y坐标
x2,y2 = B的x和y坐标
updateBIT(x,y,val)函数将区域(x,y)下的所有元素更新为(N,M),其中,
N =整个矩阵的最大X坐标。
M =整个矩阵的最大Y坐标。
其余过程与一维二元索引树的过程非常相似。以下是2D索引树的C++实现
C++
/* C++ program to implement 2D Binary Indexed Tree
2D BIT is basically a BIT where each element is another BIT.
Updating by adding v on (x, y) means it's effect will be found
throughout the rectangle [(x, y), (max_x, max_y)],
and query for (x, y) gives you the result of the rectangle
[(0, 0), (x, y)], assuming the total rectangle is
[(0, 0), (max_x, max_y)]. So when you query and update on
this BIT,you have to be careful about how many times you are
subtracting a rectangle and adding it. Simple set union formula
works here.
So if you want to get the result of a specific rectangle
[(x1, y1), (x2, y2)], the following steps are necessary:
Query(x1,y1,x2,y2) = getSum(x2, y2)-getSum(x2, y1-1) -
getSum(x1-1, y2)+getSum(x1-1, y1-1)
Here 'Query(x1,y1,x2,y2)' means the sum of elements enclosed
in the rectangle with bottom-left corner's co-ordinates
(x1, y1) and top-right corner's co-ordinates - (x2, y2)
Constraints -> x1<=x2 and y1<=y2
/\
y |
| --------(x2,y2)
| | |
| | |
| | |
| ---------
| (x1,y1)
|
|___________________________
(0, 0) x-->
In this program we have assumed a square matrix. The
program can be easily extended to a rectangular one. */
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 4 // N-->max_x and max_y
// A structure to hold the queries
struct Query
{
int x1, y1; // x and y co-ordinates of bottom left
int x2, y2; // x and y co-ordinates of top right
};
// A function to update the 2D BIT
void updateBIT(int BIT[][N+1], int x, int y, int val)
{
for (; x <= N; x += (x & -x))
{
// This loop update all the 1D BIT inside the
// array of 1D BIT = BIT[x]
for (; y <= N; y += (y & -y))
BIT[x][y] += val;
}
return;
}
// A function to get sum from (0, 0) to (x, y)
int getSum(int BIT[][N+1], int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
for(; x > 0; x -= x&-x)
{
// This loop sum through all the 1D BIT
// inside the array of 1D BIT = BIT[x]
for(; y > 0; y -= y&-y)
{
sum += BIT[x][y];
}
}
return sum;
}
// A function to create an auxiliary matrix
// from the given input matrix
void constructAux(int mat[][N], int aux[][N+1])
{
// Initialise Auxiliary array to 0
for (int i=0; i<=N; i++)
for (int j=0; j<=N; j++)
aux[i][j] = 0;
// Construct the Auxiliary Matrix
for (int j=1; j<=N; j++)
for (int i=1; i<=N; i++)
aux[i][j] = mat[N-j][i-1];
return;
}
// A function to construct a 2D BIT
void construct2DBIT(int mat[][N], int BIT[][N+1])
{
// Create an auxiliary matrix
int aux[N+1][N+1];
constructAux(mat, aux);
// Initialise the BIT to 0
for (int i=1; i<=N; i++)
for (int j=1; j<=N; j++)
BIT[i][j] = 0;
for (int j=1; j<=N; j++)
{
for (int i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
// Creating a 2D-BIT using update function
// everytime we/ encounter a value in the
// input 2D-array
int v1 = getSum(BIT, i, j);
int v2 = getSum(BIT, i, j-1);
int v3 = getSum(BIT, i-1, j-1);
int v4 = getSum(BIT, i-1, j);
// Assigning a value to a particular element
// of 2D BIT
updateBIT(BIT, i, j, aux[i][j]-(v1-v2-v4+v3));
}
}
return;
}
// A function to answer the queries
void answerQueries(Query q[], int m, int BIT[][N+1])
{
for (int i=0; i 3 8 1
1 | 4 6 7 5 6 7 5
0 | 2 4 8 9
|
--|------ 0 1 2 3 ----> x
|
Hence sum of the sub-matrix = 3+8+1+6+7+5 = 30
*/
Query q[] = {{1, 1, 3, 2}, {2, 3, 3, 3}, {1, 1, 1, 1}};
int m = sizeof(q)/sizeof(q[0]);
answerQueries(q, m, BIT);
return(0);
} Java
/* Java program to implement 2D Binary Indexed Tree
2D BIT is basically a BIT where each element is another BIT.
Updating by adding v on (x, y) means it's effect will be found
throughout the rectangle [(x, y), (max_x, max_y)],
and query for (x, y) gives you the result of the rectangle
[(0, 0), (x, y)], assuming the total rectangle is
[(0, 0), (max_x, max_y)]. So when you query and update on
this BIT,you have to be careful about how many times you are
subtracting a rectangle and adding it. Simple set union formula
works here.
So if you want to get the result of a specific rectangle
[(x1, y1), (x2, y2)], the following steps are necessary:
Query(x1,y1,x2,y2) = getSum(x2, y2)-getSum(x2, y1-1) -
getSum(x1-1, y2)+getSum(x1-1, y1-1)
Here 'Query(x1,y1,x2,y2)' means the sum of elements enclosed
in the rectangle with bottom-left corner's co-ordinates
(x1, y1) and top-right corner's co-ordinates - (x2, y2)
Constraints -> x1<=x2 and y1<=y2
/\
y |
| --------(x2,y2)
| | |
| | |
| | |
| ---------
| (x1,y1)
|
|___________________________
(0, 0) x-->
In this program we have assumed a square matrix. The
program can be easily extended to a rectangular one. */
class GFG
{
static final int N = 4; // N-.max_x and max_y
// A structure to hold the queries
static class Query
{
int x1, y1; // x and y co-ordinates of bottom left
int x2, y2; // x and y co-ordinates of top right
public Query(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
}
};
// A function to update the 2D BIT
static void updateBIT(int BIT[][], int x,
int y, int val)
{
for (; x <= N; x += (x & -x))
{
// This loop update all the 1D BIT inside the
// array of 1D BIT = BIT[x]
for (; y <= N; y += (y & -y))
BIT[x][y] += val;
}
return;
}
// A function to get sum from (0, 0) to (x, y)
static int getSum(int BIT[][], int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
for(; x > 0; x -= x&-x)
{
// This loop sum through all the 1D BIT
// inside the array of 1D BIT = BIT[x]
for(; y > 0; y -= y&-y)
{
sum += BIT[x][y];
}
}
return sum;
}
// A function to create an auxiliary matrix
// from the given input matrix
static void constructAux(int mat[][], int aux[][])
{
// Initialise Auxiliary array to 0
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j++)
aux[i][j] = 0;
// Conthe Auxiliary Matrix
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
aux[i][j] = mat[N - j][i - 1];
return;
}
// A function to cona 2D BIT
static void construct2DBIT(int mat[][],
int BIT[][])
{
// Create an auxiliary matrix
int [][]aux = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
constructAux(mat, aux);
// Initialise the BIT to 0
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
BIT[i][j] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
// Creating a 2D-BIT using update function
// everytime we/ encounter a value in the
// input 2D-array
int v1 = getSum(BIT, i, j);
int v2 = getSum(BIT, i, j - 1);
int v3 = getSum(BIT, i - 1, j - 1);
int v4 = getSum(BIT, i - 1, j);
// Assigning a value to a particular element
// of 2D BIT
updateBIT(BIT, i, j, aux[i][j] -
(v1 - v2 - v4 + v3));
}
}
return;
}
// A function to answer the queries
static void answerQueries(Query q[], int m, int BIT[][])
{
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x1 = q[i].x1 + 1;
int y1 = q[i].y1 + 1;
int x2 = q[i].x2 + 1;
int y2 = q[i].y2 + 1;
int ans = getSum(BIT, x2, y2) -
getSum(BIT, x2, y1 - 1) -
getSum(BIT, x1 - 1, y2) +
getSum(BIT, x1 - 1, y1 - 1);
System.out.printf("Query(%d, %d, %d, %d) = %d\n",
q[i].x1, q[i].y1, q[i].x2, q[i].y2, ans);
}
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int mat[][] = { {1, 2, 3, 4},
{5, 3, 8, 1},
{4, 6, 7, 5},
{2, 4, 8, 9} };
// Create a 2D Binary Indexed Tree
int [][]BIT = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
construct2DBIT(mat, BIT);
/* Queries of the form - x1, y1, x2, y2
For example the query- {1, 1, 3, 2} means the sub-matrix-
y
/\
3 | 1 2 3 4 Sub-matrix
2 | 5 3 8 1 {1,1,3,2} --. 3 8 1
1 | 4 6 7 5 6 7 5
0 | 2 4 8 9
|
--|------ 0 1 2 3 ---. x
|
Hence sum of the sub-matrix = 3+8+1+6+7+5 = 30
*/
Query q[] = {new Query(1, 1, 3, 2),
new Query(2, 3, 3, 3),
new Query(1, 1, 1, 1)};
int m = q.length;
answerQueries(q, m, BIT);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC#
/* C# program to implement 2D Binary Indexed Tree
2D BIT is basically a BIT where each element is another BIT.
Updating by.Adding v on (x, y) means it's effect will be found
throughout the rectangle [(x, y), (max_x, max_y)],
and query for (x, y) gives you the result of the rectangle
[(0, 0), (x, y)], assuming the total rectangle is
[(0, 0), (max_x, max_y)]. So when you query and update on
this BIT,you have to be careful about how many times you are
subtracting a rectangle and.Adding it. Simple set union formula
works here.
So if you want to get the result of a specific rectangle
[(x1, y1), (x2, y2)], the following steps are necessary:
Query(x1,y1,x2,y2) = getSum(x2, y2)-getSum(x2, y1-1) -
getSum(x1-1, y2)+getSum(x1-1, y1-1)
Here 'Query(x1,y1,x2,y2)' means the sum of elements enclosed
in the rectangle with bottom-left corner's co-ordinates
(x1, y1) and top-right corner's co-ordinates - (x2, y2)
Constraints -> x1<=x2 and y1<=y2
/\
y |
| --------(x2,y2)
| | |
| | |
| | |
| ---------
| (x1,y1)
|
|___________________________
(0, 0) x-->
In this program we have assumed a square matrix. The
program can be easily extended to a rectangular one. */
using System;
class GFG
{
static readonly int N = 4; // N-.max_x and max_y
// A structure to hold the queries
public class Query
{
public int x1, y1; // x and y co-ordinates of bottom left
public int x2, y2; // x and y co-ordinates of top right
public Query(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
}
};
// A function to update the 2D BIT
static void updateBIT(int [,]BIT, int x,
int y, int val)
{
for (; x <= N; x += (x & -x))
{
// This loop update all the 1D BIT inside the
// array of 1D BIT = BIT[x]
for (; y <= N; y += (y & -y))
BIT[x,y] += val;
}
return;
}
// A function to get sum from (0, 0) to (x, y)
static int getSum(int [,]BIT, int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
for(; x > 0; x -= x&-x)
{
// This loop sum through all the 1D BIT
// inside the array of 1D BIT = BIT[x]
for(; y > 0; y -= y&-y)
{
sum += BIT[x, y];
}
}
return sum;
}
// A function to create an auxiliary matrix
// from the given input matrix
static void constructAux(int [,]mat, int [,]aux)
{
// Initialise Auxiliary array to 0
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= N; j++)
aux[i, j] = 0;
// Conthe Auxiliary Matrix
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
aux[i, j] = mat[N - j, i - 1];
return;
}
// A function to cona 2D BIT
static void construct2DBIT(int [,]mat,
int [,]BIT)
{
// Create an auxiliary matrix
int [,]aux = new int[N + 1, N + 1];
constructAux(mat, aux);
// Initialise the BIT to 0
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
BIT[i, j] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
// Creating a 2D-BIT using update function
// everytime we/ encounter a value in the
// input 2D-array
int v1 = getSum(BIT, i, j);
int v2 = getSum(BIT, i, j - 1);
int v3 = getSum(BIT, i - 1, j - 1);
int v4 = getSum(BIT, i - 1, j);
// Assigning a value to a particular element
// of 2D BIT
updateBIT(BIT, i, j, aux[i,j] -
(v1 - v2 - v4 + v3));
}
}
return;
}
// A function to answer the queries
static void answerQueries(Query []q, int m, int [,]BIT)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x1 = q[i].x1 + 1;
int y1 = q[i].y1 + 1;
int x2 = q[i].x2 + 1;
int y2 = q[i].y2 + 1;
int ans = getSum(BIT, x2, y2) -
getSum(BIT, x2, y1 - 1) -
getSum(BIT, x1 - 1, y2) +
getSum(BIT, x1 - 1, y1 - 1);
Console.Write("Query({0}, {1}, {2}, {3}) = {4}\n",
q[i].x1, q[i].y1, q[i].x2, q[i].y2, ans);
}
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]mat = { {1, 2, 3, 4},
{5, 3, 8, 1},
{4, 6, 7, 5},
{2, 4, 8, 9} };
// Create a 2D Binary Indexed Tree
int [,]BIT = new int[N + 1,N + 1];
construct2DBIT(mat, BIT);
/* Queries of the form - x1, y1, x2, y2
For example the query- {1, 1, 3, 2} means the sub-matrix-
y
/\
3 | 1 2 3 4 Sub-matrix
2 | 5 3 8 1 {1,1,3,2} --. 3 8 1
1 | 4 6 7 5 6 7 5
0 | 2 4 8 9
|
--|------ 0 1 2 3 ---. x
|
Hence sum of the sub-matrix = 3+8+1+6+7+5 = 30
*/
Query []q = {new Query(1, 1, 3, 2),
new Query(2, 3, 3, 3),
new Query(1, 1, 1, 1)};
int m = q.Length;
answerQueries(q, m, BIT);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji输出:
Query(1, 1, 3, 2) = 30
Query(2, 3, 3, 3) = 7
Query(1, 1, 1, 1) = 6
时间复杂度:
- updateBIT(x,y,val)函数和getSum(x,y)函数需要O(log(NM))时间。
- 建立2D BIT需要O(NM log(NM))。
- 由于在每个查询中我们都调用getSum(x,y)函数,因此回答所有Q个查询需要O(Q.log(NM))时间。
因此,该程序的整体时间复杂度为O((NM + Q).log(NM)) ,其中,
N =整个矩阵的最大X坐标。
M =整个矩阵的最大Y坐标。
Q =查询数。
辅助空间: O(NM)用于存储BIT和辅助数组
参考: https : //www.topcoder.com/community/data-science/data-science-tutorials/binary-indexed-trees/