先决条件:
- 插入元素圆双链表。
- 将数组转换为圆形双链表。
给定起始指针指向圆形双链表,元素和位置的起点。任务是将元素插入到给定的“环形双链表”中的指定位置。
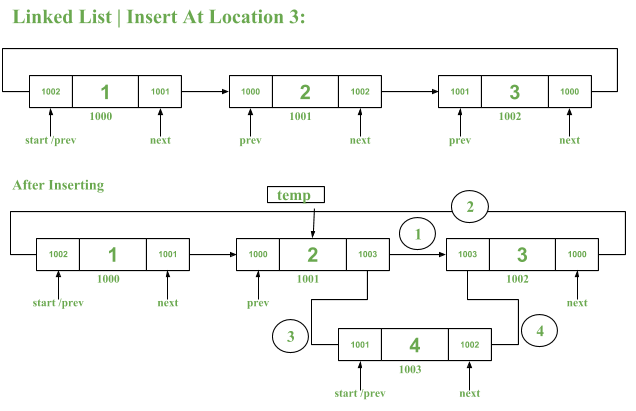
这个想法是计算列表中元素的总数。检查指定的位置是否有效,即位置在计数范围内。
如果位置有效:
- 在内存中创建一个newNode。
- 使用临时指针( temp )在列表中遍历,直到节点刚好在需要插入新节点的给定位置之前。
- 通过执行以下操作来插入新节点:
- 分配newNode-> next = temp-> next
- 将newNode-> prev分配为temp-> next
- 将temp-> next分配为newNode
- 假设(temp-> next)-> prev as newNode-> next
下面是上述想法的实现:
C++
// CPP program to convert insert an element at a specific
// position in a circular doubly linked list
#include
using namespace std;
// Doubly linked list node
struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
struct node* prev;
};
// Utility function to create a node in memory
struct node* getNode()
{
return ((struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)));
}
// Function to display the list
int displayList(struct node* temp)
{
struct node* t = temp;
if (temp == NULL)
return 0;
else {
cout << "The list is: ";
while (temp->next != t) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << temp->data << endl;
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count nunmber of
// elements in the list
int countList(struct node* start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
struct node* temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
int count = 0;
// Iterate the list and increment the count
while (temp->next != start) {
temp = temp->next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment the
// counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at a given position
// in the circular doubly linked list
bool insertAtLocation(struct node* start, int data, int loc)
{
// Declare two pointers
struct node *temp, *newNode;
int i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == NULL || count < loc)
return false;
else {
// Assign the data
newNode->data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++) {
temp = temp->next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode->next = temp->next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
(temp->next)->prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp->next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode->prev = temp;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Function to create circular doubly linked list
// from array elements
void createList(int arr[], int n, struct node** start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
struct node *newNode, *temp;
int i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode->data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0) {
*start = newNode;
newNode->prev = *start;
newNode->next = *start;
}
else {
// Find the last node
temp = (*start)->prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *start;
newNode->prev = temp;
temp = *start;
temp->prev = newNode;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Start Pointer
struct node* start = NULL;
// Create the List
createList(arr, n, &start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to convert insert
// an element at a specific position
// in a circular doubly linked listing,
// end and middle
class GFG
{
// Doubly linked list node
static class node
{
int data;
node next;
node prev;
};
// Utility function to create a node in memory
static node getNode()
{
return new node();
}
// Function to display the list
static int displayList( node temp)
{
node t = temp;
if (temp == null)
return 0;
else
{
System.out.println( "The list is: ");
while (temp.next != t)
{
System.out.print( temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println( temp.data );
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count nunmber of
// elements in the list
static int countList( node start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
node temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
int count = 0;
// Iterate the list and
// increment the count
while (temp.next != start)
{
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment
// the counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at
// a given position in the
// circular doubly linked list
static node insertAtLocation( node start,
int data, int loc)
{
// Declare two pointers
node temp, newNode;
int i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == null || count < loc)
return start;
else
{
// Assign the data
newNode.data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
(temp.next).prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp;
return start;
}
}
// Function to create circular doubly
// linked list from array elements
static node createList(int arr[], int n, node start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
node newNode, temp;
int i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0)
{
start = newNode;
newNode.prev = start;
newNode.next = start;
}
else
{
// Find the last node
temp = (start).prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = start;
newNode.prev = temp;
temp = start;
temp.prev = newNode;
}
}
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
// Start Pointer
node start = null;
// Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
# Python3 program to insert an element
# at a specific position in a
# circular doubly linked list
# Node of the doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
# Utility function to create
# a node in memory
def getNode():
return (Node(0))
# Function to display the list
def displayList(temp):
t = temp
if (temp == None):
return 0
else :
print("The list is: ", end = " ")
while (temp.next != t):
print( temp.data, end = " ")
temp = temp.next
print(temp.data )
return 1
# Function to count nunmber of
# elements in the list
def countList( start):
# Declare temp pointer to
# traverse the list
temp = start
# Variable to store the count
count = 0
# Iterate the list and increment the count
while (temp.next != start) :
temp = temp.next
count = count + 1
# As the list is circular, increment the
# counter at last
count = count + 1
return count
# Function to insert a node at a given position
# in the circular doubly linked list
def insertAtLocation(start, data, loc):
# Declare two pointers
temp = None
newNode = None
i = 0
count = 0
# Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode()
# Point temp to start
temp = start
# count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start)
# If list is empty or the position is
# not valid, return False
if (temp == None or count < loc):
return start
else :
# Assign the data
newNode.data = data
# Iterate till the loc
i = 1;
while(i < loc - 1) :
temp = temp.next
i = i + 1
# See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next
# See in Image, Circle 2
(temp.next).prev = newNode
# See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode
# See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp
return start
return start
# Function to create circular
# doubly linked list from array elements
def createList(arr, n, start):
# Declare newNode and temporary pointer
newNode = None
temp = None
i = 0
# Iterate the loop until array length
while (i < n) :
# Create new node
newNode = getNode()
# Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i]
# If it is first element
# Put that node prev and next as start
# as it is circular
if (i == 0) :
start = newNode
newNode.prev = start
newNode.next = start
else :
# Find the last node
temp = (start).prev
# Add the last node to make them
# in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode
newNode.next = start
newNode.prev = temp
temp = start
temp.prev = newNode
i = i + 1;
return start
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Array elements to create
# circular doubly linked list
arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
n = len(arr)
# Start Pointer
start = None
# Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start)
# Display the list before insertion
displayList(start)
# Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3)
# Display the list after insertion
displayList(start)
# This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC#
// C# program to convert insert
// an element at a specific position
// in a circular doubly linked listing,
// end and middle
using System;
class GFG
{
// Doubly linked list node
public class node
{
public int data;
public node next;
public node prev;
};
// Utility function to create a node in memory
static node getNode()
{
return new node();
}
// Function to display the list
static int displayList( node temp)
{
node t = temp;
if (temp == null)
return 0;
else
{
Console.WriteLine( "The list is: ");
while (temp.next != t)
{
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine( temp.data );
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count nunmber of
// elements in the list
static int countList( node start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
node temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
int count = 0;
// Iterate the list and
// increment the count
while (temp.next != start)
{
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment
// the counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at
// a given position in the
// circular doubly linked list
static node insertAtLocation( node start,
int data, int loc)
{
// Declare two pointers
node temp, newNode;
int i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == null || count < loc)
return start;
else
{
// Assign the data
newNode.data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
(temp.next).prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp;
return start;
}
}
// Function to create circular doubly
// linked list from array elements
static node createList(int []arr, int n, node start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
node newNode, temp;
int i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0)
{
start = newNode;
newNode.prev = start;
newNode.next = start;
}
else
{
// Find the last node
temp = (start).prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = start;
newNode.prev = temp;
temp = start;
temp.prev = newNode;
}
}
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Start Pointer
node start = null;
// Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */输出:
The list is: 1 2 3 4 5 6
The list is: 1 2 8 3 4 5 6
时间复杂度: O(n)=>用于计数列表,O(n)=>插入元素。因此,总复杂度为O(n + n)= O(n)