给定一个由N个整数组成的数组arr [] ,任务是从第一个和最后一个开始,删除每隔一个第二个元素,然后找到最后剩余的数组元素。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
Output: 8
Explanation: Elements in the list are: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Starting from first array element, removing every second element from arr[] = {1, 2. 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} modifies arr[] to {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}.
Starting from last array element, removing every second element from arr[] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10} modifies arr[] to {4, 8}.
Starting from first array element, removing every second element from arr[] = {4, 8} modifies arr[] to {8}.
Therefore, the last remaining element in the array is 8.
Input: arr[] = {2, 3, 5, 6}
Output: 3
天真的方法:解决此问题的最简单方法是从第一个索引和最后一个索引开始依次删除数组中的每个第二个元素,直到数组的大小减小为1为止。执行给定操作后,打印剩余的最后一个数组元素。
时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
辅助空间: O(1)
高效方法:还可以通过下图中观察到的N = 20来优化上述方法:
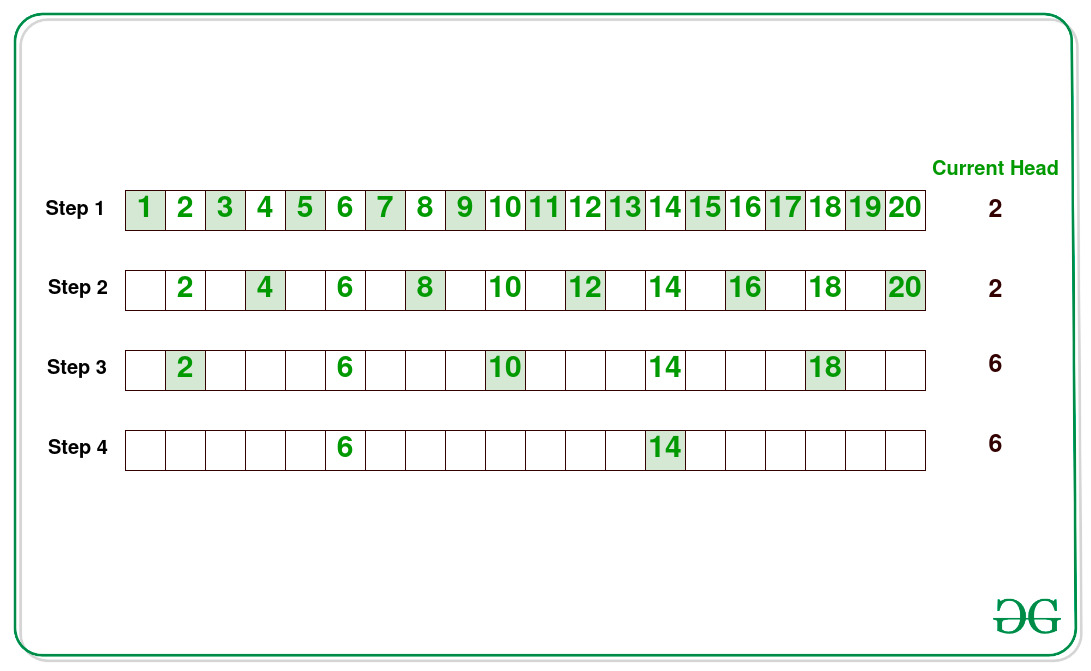
从上面的插图中可以得出以下结论:
- 每次消除N / 2个数字。
- 如果转弯方向是从左到右(→),则序列的第一个元素更改为(currentFirstElement + 2 step – 1 ) 。
- 如果转弯方向是从右到左(←),并且列表中的其余数字为奇数,则序列的第一个元素将更改为(currentFirstElement + 2 step – 1 ) 。
- 通过上述步骤获得currentFirstElement的最终值后,将值打印为序列中的其余元素。
脚步:
- 初始化一个变量,例如leftTurn ,以检查是否要从左侧或右侧删除元素。
- 将变量resetElements初始化为N ,将步骤初始化为1 ,将head初始化为1 ,以存储序列中的其余元素,执行的步骤数以及序列的第一个元素。
- 进行迭代,直到keepElements大于1 :
- 如果leftTurn的值为true ,则将head更新为(head + 2 step – 1 ) 。否则,如果其余元素为奇数,则将head更新为(head + 2 step – 1 ) 。
- 将maintainElement的值更新为maintainElement / 2 。
- 将步骤更新为2 *步骤。
- 切换leftTurn可以从右边移除元素。
- 完成上述步骤后,将索引(头– 1)上的值打印为剩余元素。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the last element
// remaining in the array after
// performing the given operations
void printLastElement(int arr[], int N)
{
// Checks if traversal is from
// left to right or vice versa
bool leftTurn = true;
// Store the elements currently
// present in the array
int remainElements = N;
// Store the distance between 2
// consecutive array elements
int step = 1;
// Store the first element
// of the remaining array
int head = 1;
// Iterate while elements
// are greater than 1
while (remainElements > 1) {
// If left to right turn
if (leftTurn) {
// Update head
head = head + step;
}
// Otherwise, check if the
// remaining elements are odd
else {
// If true, update head
if (remainElements % 2 == 1)
head = head + step;
}
// Eleminate half of the array elements
remainElements = remainElements / 2;
// Double the steps after each turn
step = step * 2;
// Alter the turn
leftTurn = !leftTurn;
}
// Print the remaining element
cout << arr[head - 1];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 5, 6 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printLastElement(arr, N);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to find the last element
# remaining in the array after
# performing the given operations
def printLastElement(arr, N):
# Checks if traversal is from
# left to right or vice versa
leftTurn = True
# Store the elements currently
# present in the array
remainElements = N
# Store the distance between 2
# consecutive array elements
step = 1
# Store the first element
# of the remaining array
head = 1
# Iterate while elements
# are greater than 1
while (remainElements > 1):
# If left to right turn
if (leftTurn):
# Update head
head = head + step
# Otherwise, check if the
# remaining elements are odd
else:
# If true, update head
if (remainElements % 2 == 1):
head = head + step
# Eleminate half of the array elements
remainElements = remainElements // 2
# Double the steps after each turn
step = step * 2
# Alter the turn
leftTurn = not leftTurn
# Print the remaining element
print(arr[head - 1])
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [ 2, 3, 5, 6 ]
N = len(arr)
printLastElement(arr, N)
# This code is contributed by ukasp3时间复杂度: O(log N)
辅助空间: O(1)