通过遵循单元格值来查找二维数组是否已完全遍历
你得到一个二维数组。我们必须按照单元格的位置遍历给定数组的每个单元格,然后返回 true 否则返回 false。每个单元格的值由 (x, y) 给出,其中 (x, y) 也显示在单元格位置之后。例如。 (0, 0) 显示起始单元格。 'null' 显示遍历每个单元格后的最终目的地。
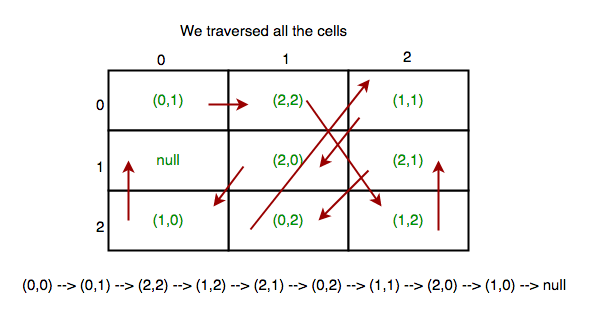
例子:
Input : { 0, 1 1, 2 1, 1
0, 2 2, 0 2, 1
0, 0 1, 0 null }
Output : false
Input : { 0, 1 2, 0
null 1, 0
2, 1 1, 1 }
Output : true如果我们访问一个单元格,我们将获取一个已访问数组,然后在已访问数组中将其值设为真,以便我们可以在下次再次访问它时捕获网格中的循环。如果我们在完成循环之前找到 null ,那么这意味着我们没有遍历给定数组的所有单元格。
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// function which tells all cells are visited or not
bool isAllCellTraversed(vector>>grid, int n, int m)
{
bool visited[n][m];
int total = n*m;
// starting cell values
int startx = grid[0][0].first;
int starty = grid[0][0].second;
for (int i = 0; i < total - 2; i++)
{
// if we get {0,0} before the end of loop
// then returns false. Because it means we
// didn't traverse all the cells
if (grid[startx][starty].first == -1 and
grid[startx][starty].second == -1)
return false;
// If found cycle then return false
if (visited[startx][starty] == true)
return false;
visited[startx][starty] = true;
int x = grid[startx][starty].first;
int y = grid[startx][starty].second;
// Update startx and starty values to next
// cell values
startx = x;
starty = y;
}
// finally if we reach our goal then returns true
if (grid[startx][starty].first == -1 and
grid[startx][starty].second == -1)
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector>> cell(3, vector> (2));
cell[0][0] = {0, 1};
cell[0][1] = {2, 0};
cell[1][0] = {-1,-1};
cell[1][1] = {1, 0};
cell[2][0] = {2, 1};
cell[2][1] = {1, 1};
if(!isAllCellTraversed(cell, 3, 2))
cout << "true";
else
cout << "false";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29. Java
/* Java program to Find a 2-D array is completely
traversed or not by following the cell values */
import java.io.*;
class Cell {
int x;
int y;
// Cell class constructor
Cell(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class MoveCellPerCellValue {
// function which tells all cells are visited or not
public boolean isAllCellTraversed(Cell grid[][])
{
boolean[][] visited =
new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length];
int total = grid.length * grid[0].length;
// starting cell values
int startx = grid[0][0].x;
int starty = grid[0][0].y;
for (int i = 0; i < total - 2; i++) {
// if we get null before the end of loop
// then returns false. Because it means we
// didn't traverse all the cells
if (grid[startx][starty] == null)
return false;
// If found cycle then return false
if (visited[startx][starty] == true)
return false;
visited[startx][starty] = true;
int x = grid[startx][starty].x;
int y = grid[startx][starty].y;
// Update startx and starty values to next
// cell values
startx = x;
starty = y;
}
// finally if we reach our goal then returns true
if (grid[startx][starty] == null)
return true;
return false;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cell cell[][] = new Cell[3][2];
cell[0][0] = new Cell(0, 1);
cell[0][1] = new Cell(2, 0);
cell[1][0] = null;
cell[1][1] = new Cell(1, 0);
cell[2][0] = new Cell(2, 1);
cell[2][1] = new Cell(1, 1);
MoveCellPerCellValue mcp = new MoveCellPerCellValue();
System.out.println(mcp.isAllCellTraversed(cell));
}
}Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# function which tells all cells are visited or not
def isAllCellTraversed(grid, n, m):
visited = [[True for j in range(m)] for i in range(n)];
total = n*m;
# starting cell values
startx = grid[0][0][0];
starty = grid[0][0][1];
for i in range(total-2):
# if we get {0,0} before the end of loop
# then returns False. Because it means we
# didn't traverse all the cells
if (grid[startx][starty][0] == -1 and
grid[startx][starty][1] == -1):
return False;
# If found cycle then return False
if (visited[startx][starty] == True):
return False;
visited[startx][starty] = True;
x = grid[startx][starty][0];
y = grid[startx][starty][1];
# Update startx and starty values to next
# cell values
startx = x;
starty = y;
# finally if we reach our goal then returns True
if (grid[startx][starty][0] == -1 and
grid[startx][starty][1] == -1):
return True;
return False;
# Driver code
cell = [[[] for j in range(3)] for i in range(3)]
cell[0][0] = [0, 1];
cell[0][1] = [2, 0];
cell[1][0] = [-1,-1];
cell[1][1] = [1, 0];
cell[2][0] = [2, 1];
cell[2][1] = [1, 1];
if(not isAllCellTraversed(cell, 3, 2)):
print("True");
else:
print("False");
# This code is contributed by rrrtnx.C#
/* C# program to Find a 2-D array is completely
traversed or not by following the cell values */
using System;
public class Cell
{
public int x;
public int y;
// Cell class constructor
public Cell(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class MoveCellPerCellValue
{
// function which tells all cells are visited or not
public Boolean isAllCellTraversed(Cell [,]grid)
{
Boolean[,] visited =
new Boolean[grid.GetLength(0),
grid.GetLength(1)];
int total = grid.GetLength(0) *
grid.GetLength(1);
// starting cell values
int startx = grid[0, 0].x;
int starty = grid[0, 0].y;
for (int i = 0; i < total - 2; i++)
{
// if we get null before the end of loop
// then returns false. Because it means we
// didn't traverse all the cells
if (grid[startx, starty] == null)
return false;
// If found cycle then return false
if (visited[startx, starty] == true)
return false;
visited[startx, starty] = true;
int x = grid[startx, starty].x;
int y = grid[startx, starty].y;
// Update startx and starty values
// to next cell values
startx = x;
starty = y;
}
// finally if we reach our goal
// then returns true
if (grid[startx, starty] == null)
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Cell [,]cell = new Cell[3, 2];
cell[0, 0] = new Cell(0, 1);
cell[0, 1] = new Cell(2, 0);
cell[1, 0] = null;
cell[1, 1] = new Cell(1, 0);
cell[2, 0] = new Cell(2, 1);
cell[2, 1] = new Cell(1, 1);
MoveCellPerCellValue mcp = new MoveCellPerCellValue();
Console.WriteLine(mcp.isAllCellTraversed(cell));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
输出:
true