给定一棵二叉树,将其平整化为就地链表。不允许使用辅助数据结构。展平后,每个节点的左侧应指向NULL,右侧应包含按顺序排列的下一个节点。
例子:
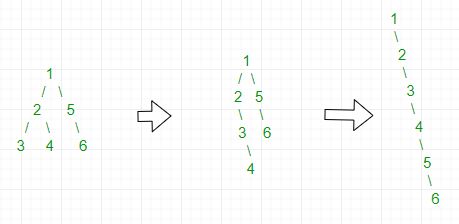
Input :
1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
Output :
1
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
Input :
1
/ \
3 4
/
2
\
5
Output :
1
\
3
\
4
\
2
\
5简单方法:一个简单的解决方案是通过“队列”使用“级别顺序遍历”。在级别顺序遍历中,跟踪先前的节点。将当前节点作为上一个节点的右子节点,将上一个节点的左节点作为NULL。该解决方案需要队列,但问题要求解决而无需其他数据结构。
无需附加数据结构即可高效地在左子树中递归查找没有孙子代且左子代和右子代都没有的节点。然后将node-> right存储在临时目录中,并使node-> right = node-> left。通过node = node-> right在节点右边的第一个节点NULL中插入temp。重复直到将其转换为链接列表。
例如,
C++
/* C++ Program to flatten a given Binary
Tree into linked list */
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* utility that allocates a new Node
with the given key */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->key = key;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Function to convert binary tree into
// linked list by altering the right node
// and making left node point to NULL
void flatten(struct Node* root)
{
// base condition- return if root is NULL
// or if it is a leaf node
if (root == NULL || root->left == NULL &&
root->right == NULL) {
return;
}
// if root->left exists then we have
// to make it root->right
if (root->left != NULL) {
// move left recursively
flatten(root->left);
// store the node root->right
struct Node* tmpRight = root->right;
root->right = root->left;
root->left = NULL;
// find the position to insert
// the stored value
struct Node* t = root->right;
while (t->right != NULL) {
t = t->right;
}
// insert the stored value
t->right = tmpRight;
}
// now call the same function
// for root->right
flatten(root->right);
}
// To find the inorder traversal
void inorder(struct Node* root)
{
// base condition
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->key << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6 */
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(5);
root->left->left = newNode(3);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
root->right->right = newNode(6);
flatten(root);
cout << "The Inorder traversal after "
"flattening binary tree ";
inorder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to flatten a given
// Binary Tree into linked list
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int key)
{
data = key;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree{
Node root;
// Function to convert binary tree into
// linked list by altering the right node
// and making left node NULL
public void flatten(Node node)
{
// Base case - return if root is NULL
if (node == null)
return;
// Or if it is a leaf node
if (node.left == null &&
node.right == null)
return;
// If root.left children exists then we have
// to make it node.right (where node is root)
if (node.left != null)
{
// Move left recursively
flatten(node.left);
// Store the node.right in
// Node named tempNode
Node tempNode = node.right;
node.right = node.left;
node.left = null;
// Find the position to insert
// the stored value
Node curr = node.right;
while (curr.right != null)
{
curr = curr.right;
}
// Insert the stored value
curr.right = tempNode;
}
// Now call the same function
// for node.right
flatten(node.right);
}
// Function for Inorder traversal
public void inOrder(Node node)
{
// Base Condition
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inOrder(node.right);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6 */
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(6);
System.out.println("The Inorder traversal after " +
"flattening binary tree ");
tree.flatten(tree.root);
tree.inOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Yash SinghalPython3
# Python3 program to flatten a given Binary
# Tree into linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.key = 0
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Utility that allocates a new Node
# with the given key
def newNode(key):
node = Node()
node.key = key
node.left = node.right = None
return (node)
# Function to convert binary tree into
# linked list by altering the right node
# and making left node point to None
def flatten(root):
# Base condition- return if root is None
# or if it is a leaf node
if (root == None or root.left == None and
root.right == None):
return
# If root.left exists then we have
# to make it root.right
if (root.left != None):
# Move left recursively
flatten(root.left)
# Store the node root.right
tmpRight = root.right
root.right = root.left
root.left = None
# Find the position to insert
# the stored value
t = root.right
while (t.right != None):
t = t.right
# Insert the stored value
t.right = tmpRight
# Now call the same function
# for root.right
flatten(root.right)
# To find the inorder traversal
def inorder(root):
# Base condition
if (root == None):
return
inorder(root.left)
print(root.key, end = ' ')
inorder(root.right)
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
''' 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6 '''
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(5)
root.left.left = newNode(3)
root.left.right = newNode(4)
root.right.right = newNode(6)
flatten(root)
print("The Inorder traversal after "
"flattening binary tree ",
end = '')
inorder(root)
# This code is contributed by pratham76C#
// C# program to flatten a given
// Binary Tree into linked list
using System;
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int key)
{
data = key;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
// Function to convert binary tree into
// linked list by altering the right node
// and making left node NULL
public void flatten(Node node)
{
// Base case - return if root is NULL
if (node == null)
return;
// Or if it is a leaf node
if (node.left == null &&
node.right == null)
return;
// If root.left children exists then we have
// to make it node.right (where node is root)
if (node.left != null)
{
// Move left recursively
flatten(node.left);
// Store the node.right in
// Node named tempNode
Node tempNode = node.right;
node.right = node.left;
node.left = null;
// Find the position to insert
// the stored value
Node curr = node.right;
while (curr.right != null)
{
curr = curr.right;
}
// Insert the stored value
curr.right = tempNode;
}
// Now call the same function
// for node.right
flatten(node.right);
}
// Function for Inorder traversal
public void inOrder(Node node)
{
// Base Condition
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.left);
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
inOrder(node.right);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* 1
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6 */
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(6);
Console.Write("The Inorder traversal after " +
"flattening binary tree ");
tree.flatten(tree.root);
tree.inOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56输出:
The Inorder traversal after flattening
binary tree 1 2 3 4 5 6