计算文本文件中空格数的Python程序
所有程序都需要输入来处理,处理后给出输出。 Python支持文件处理并允许用户处理文件。文件处理的概念已经扩展到各种其他语言,但实现要么冗长要么复杂。 Python将文件视为文本和二进制文件,
将数据写入文件时要注意的一件事是应保持其一致性和完整性。一旦您将数据存储在文件中,现在最重要的事情就是对其进行检索,因为计算机数据存储为 1 和 0 的位,如果检索不正确,则它变得完全无用,数据被称为已损坏。因此,写和读也是Python文件处理的一个重要方面。
如何计算空格或任何字符的数量?
' '(空格)也属于可打印 ASCII字符类型,而 NULL 不是可打印 ASCII字符类型。
方法 :
如何使用Python写入文件?
- 打开要写入的文件。
- 计算该文本文件中的空格数。
- 关闭一个文件。
这是我们的文本文件。
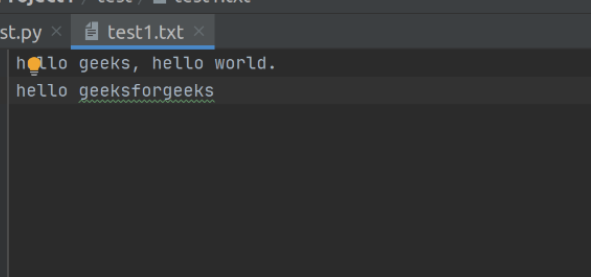
实施:
方法#1:使用 isspace()函数。
首先,我们将打开我们的文本文件并将该文本文件存储在该变量中。循环用于计算文本文件中的空格。 if condition ( char.isspace()) 测试所有条件,如果它返回 True 则计数将增加 1。测试完所有字符的循环将返回 False 并终止自身。最后,程序将显示空格的总数。
Python3
# this will open the file and store
# in "file" variable
file = open("test1.txt", "r")
count = 0
while True:
# this will read each character
# and store in char
char = file.read(1)
if char.isspace():
count += 1
if not char:
break
print(count)Python3
# this will open the file and store in
# "file" variable
file = open("test1.txt", "r")
count = 0
while True:
# this will read each character
# and store in char
char = file.read(1)
if char == " ":
count += 1
if not char:
break
print(count)Python3
import functools
with open("test1.txt") as file:
file_char = functools.partial(file.read, 1)
for char in iter(file_char, " "):
if char == " ":
count += 1
print("count: ", count)输出:
5
注意 – isspace() 也计算字符,因此它显示输出为 6。
方法#2:使用循环:
首先,我们将打开我们的文本文件并将该文本文件存储在该变量中。循环用于计算文本文件中的空格。 if condition ( char == ” ” ) 测试所有条件,如果它返回 True 则计数将增加 1。测试完所有字符的循环将返回 False 并终止自身。最后,程序将显示空格的总数。
蟒蛇3
# this will open the file and store in
# "file" variable
file = open("test1.txt", "r")
count = 0
while True:
# this will read each character
# and store in char
char = file.read(1)
if char == " ":
count += 1
if not char:
break
print(count)
输出:
4
方法#3:使用Python模块“functools”。
Partial函数是用于特定参数值的函数。它们可以通过使用“functools”库中的“partial”在Python中创建。
蟒蛇3
import functools
with open("test1.txt") as file:
file_char = functools.partial(file.read, 1)
for char in iter(file_char, " "):
if char == " ":
count += 1
print("count: ", count)
输出:
4