在流网络中找到最小 st 割
在流网络中,st 割是要求源“s”和汇“t”在不同子集中的割,它由从源端到汇端的边组成。 st 割的容量由割集中每条边的容量之和定义。 (来源:维基)
这里讨论的问题是找到给定网络的最小容量 st cut。预期输出是最小割的所有边。
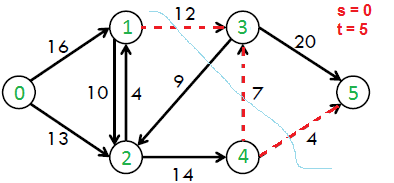
例如,在下面的流网络中,示例 st 割是 {{0 ,1}, {0, 2}}, {{0, 2}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}} 等。最小 st 割是 {{1, 3}, {4, 3}, {4 5}},容量为 12+7+4 = 23。
我们强烈建议您先阅读以下帖子。
最大流量问题的 Ford-Fulkerson 算法
最小切割和最大流量
与最大二分匹配一样,这是另一个可以使用 Ford-Fulkerson 算法解决的问题。这是基于最大流最小割定理。
最大流最小割定理指出,在流网络中,最大流的量等于最小割的容量。有关该定理的证明,请参见 CLRS 书籍。
从 Ford-Fulkerson,我们得到了最小切割容量。如何打印形成最小切口的所有边缘?这个想法是使用残差图。
以下是打印最小切口的所有边缘的步骤。
1)运行 Ford-Fulkerson 算法并考虑最终的残差图。
2)在残差图中找到从源可达的顶点集合。
3)从可达顶点到不可达顶点的所有边都是最小割边。打印所有这些边缘。
以下是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for finding minimum cut using Ford-Fulkerson
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Number of vertices in given graph
#define V 6
/* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path */
int bfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, int t, int parent[])
{
// Create a visited array and mark all vertices as not visited
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark source vertex
// as visited
queue q;
q.push(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int v=0; v 0)
{
q.push(v);
parent[v] = u;
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then return
// true, else false
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// A DFS based function to find all reachable vertices from s. The function
// marks visited[i] as true if i is reachable from s. The initial values in
// visited[] must be false. We can also use BFS to find reachable vertices
void dfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, bool visited[])
{
visited[s] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (rGraph[s][i] && !visited[i])
dfs(rGraph, i, visited);
}
// Prints the minimum s-t cut
void minCut(int graph[V][V], int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the residual graph with
// given capacities in the original graph as residual capacities
// in residual graph
int rGraph[V][V]; // rGraph[i][j] indicates residual capacity of edge i-j
for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
int parent[V]; // This array is filled by BFS and to store path
// Augment the flow while there is a path from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
{
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes along the
// path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
// through the path found.
int path_flow = INT_MAX;
for (v=t; v!=s; v=parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
// along the path
for (v=t; v != s; v=parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
}
}
// Flow is maximum now, find vertices reachable from s
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
dfs(rGraph, s, visited);
// Print all edges that are from a reachable vertex to
// non-reachable vertex in the original graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++)
if (visited[i] && !visited[j] && graph[i][j])
cout << i << " - " << j << endl;
return;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[V][V] = { {0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
{0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
minCut(graph, 0, 5);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for finding min-cut in the given graph
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Graph {
// Returns true if there is a path
// from source 's' to sink 't' in residual
// graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path
private static boolean bfs(int[][] rGraph, int s,
int t, int[] parent) {
// Create a visited array and mark
// all vertices as not visited
boolean[] visited = new boolean[rGraph.length];
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex
// and mark source vertex as visited
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int v = q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < rGraph.length; i++) {
if (rGraph[v][i] > 0 && !visited[i]) {
q.offer(i);
visited[i] = true;
parent[i] = v;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS starting
// from source, then return true, else false
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// A DFS based function to find all reachable
// vertices from s. The function marks visited[i]
// as true if i is reachable from s. The initial
// values in visited[] must be false. We can also
// use BFS to find reachable vertices
private static void dfs(int[][] rGraph, int s,
boolean[] visited) {
visited[s] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < rGraph.length; i++) {
if (rGraph[s][i] > 0 && !visited[i]) {
dfs(rGraph, i, visited);
}
}
}
// Prints the minimum s-t cut
private static void minCut(int[][] graph, int s, int t) {
int u,v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the residual
// graph with given capacities in the original
// graph as residual capacities in residual graph
// rGraph[i][j] indicates residual capacity of edge i-j
int[][] rGraph = new int[graph.length][graph.length];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph.length; j++) {
rGraph[i][j] = graph[i][j];
}
}
// This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int[] parent = new int[graph.length];
// Augment the flow while tere is path from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent)) {
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes
// along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
// find the maximum flow through the path found.
int pathFlow = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
pathFlow = Math.min(pathFlow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v]) {
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] = rGraph[u][v] - pathFlow;
rGraph[v][u] = rGraph[v][u] + pathFlow;
}
}
// Flow is maximum now, find vertices reachable from s
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[graph.length];
dfs(rGraph, s, isVisited);
// Print all edges that are from a reachable vertex to
// non-reachable vertex in the original graph
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph.length; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] > 0 && isVisited[i] && !isVisited[j]) {
System.out.println(i + " - " + j);
}
}
}
}
//Driver Program
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Let us create a graph shown in the above example
int graph[][] = { {0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
{0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
minCut(graph, 0, 5);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Himanshu Shekhar Python
# Python program for finding min-cut in the given graph
# Complexity : (E*(V^3))
# Total augmenting path = VE and BFS
# with adj matrix takes :V^2 times
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency matrix representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self,graph):
self.graph = graph # residual graph
self.org_graph = [i[:] for i in graph]
self. ROW = len(graph)
self.COL = len(graph[0])
'''Returns true if there is a path from
source 's' to sink 't' in
residual graph. Also fills
parent[] to store the path '''
def BFS(self,s, t, parent):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited =[False]*(self.ROW)
# Create a queue for BFS
queue=[]
# Mark the source node as visited and enqueue it
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
# Standard BFS Loop
while queue:
#Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
u = queue.pop(0)
# Get all adjacent vertices of
# the dequeued vertex u
# If a adjacent has not been
# visited, then mark it
# visited and enqueue it
for ind, val in enumerate(self.graph[u]):
if visited[ind] == False and val > 0 :
queue.append(ind)
visited[ind] = True
parent[ind] = u
# If we reached sink in BFS starting
# from source, then return
# true, else false
return True if visited[t] else False
# Function for Depth first search
# Traversal of the graph
def dfs(self, graph,s,visited):
visited[s]=True
for i in range(len(graph)):
if graph[s][i]>0 and not visited[i]:
self.dfs(graph,i,visited)
# Returns the min-cut of the given graph
def minCut(self, source, sink):
# This array is filled by BFS and to store path
parent = [-1]*(self.ROW)
max_flow = 0 # There is no flow initially
# Augment the flow while there is path from source to sink
while self.BFS(source, sink, parent) :
# Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along the
# path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
# through the path found.
path_flow = float("Inf")
s = sink
while(s != source):
path_flow = min (path_flow, self.graph[parent[s]][s])
s = parent[s]
# Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow
# update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
# along the path
v = sink
while(v != source):
u = parent[v]
self.graph[u][v] -= path_flow
self.graph[v][u] += path_flow
v = parent[v]
visited=len(self.graph)*[False]
self.dfs(self.graph,s,visited)
# print the edges which initially had weights
# but now have 0 weight
for i in range(self.ROW):
for j in range(self.COL):
if self.graph[i][j] == 0 and\
self.org_graph[i][j] > 0 and visited[i]:
print str(i) + " - " + str(j)
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
graph = [[0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0],
[0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0],
[0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20],
[0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
g = Graph(graph)
source = 0; sink = 5
g.minCut(source, sink)
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program for finding min-cut in the given graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Graph
{
// Returns true if there is a path
// from source 's' to sink 't' in residual
// graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path
private static bool bfs(int[,] rGraph, int s,
int t, int[] parent)
{
// Create a visited array and mark
// all vertices as not visited
bool[] visited = new bool[rGraph.Length];
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex
// and mark source vertex as visited
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
while (q.Count != 0)
{
int v = q.Dequeue();
for (int i = 0; i < rGraph.GetLength(0); i++)
{
if (rGraph[v,i] > 0 && !visited[i])
{
q.Enqueue(i);
visited[i] = true;
parent[i] = v;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS starting
// from source, then return true, else false
return (visited[t] == true);
}
// A DFS based function to find all reachable
// vertices from s. The function marks visited[i]
// as true if i is reachable from s. The initial
// values in visited[] must be false. We can also
// use BFS to find reachable vertices
private static void dfs(int[,] rGraph, int s,
bool[] visited)
{
visited[s] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < rGraph.GetLength(0); i++)
{
if (rGraph[s,i] > 0 && !visited[i])
{
dfs(rGraph, i, visited);
}
}
}
// Prints the minimum s-t cut
private static void minCut(int[,] graph, int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// Create a residual graph and fill the residual
// graph with given capacities in the original
// graph as residual capacities in residual graph
// rGraph[i,j] indicates residual capacity of edge i-j
int[,] rGraph = new int[graph.Length,graph.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < graph.GetLength(1); j++)
{
rGraph[i, j] = graph[i, j];
}
}
// This array is filled by BFS and to store path
int[] parent = new int[graph.Length];
// Augment the flow while there is path
// from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
{
// Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes
// along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
// find the maximum flow through the path found.
int pathFlow = int.MaxValue;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
pathFlow = Math.Min(pathFlow, rGraph[u, v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and
// reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u, v] = rGraph[u, v] - pathFlow;
rGraph[v, u] = rGraph[v, u] + pathFlow;
}
}
// Flow is maximum now, find vertices reachable from s
bool[] isVisited = new bool[graph.Length];
dfs(rGraph, s, isVisited);
// Print all edges that are from a reachable vertex to
// non-reachable vertex in the original graph
for (int i = 0; i < graph.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < graph.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if (graph[i, j] > 0 &&
isVisited[i] && !isVisited[j])
{
Console.WriteLine(i + " - " + j);
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Let us create a graph shown
// in the above example
int [,]graph = {{0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
{0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}};
minCut(graph, 0, 5);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
1 - 3
4 - 3
4 - 5参考:
http://www.stanford.edu/class/cs97si/08-network-flow-problems.pdf
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spring06/cos226/lectures/maxflow.pdf