给定二维空间中的N个点,我们需要打印穿过所有这N个点并且也经过特定(xO,yO)点的最小线数的计数。
例子:
如果给定的点是(-1、3),(4、3),(2、1),(-1,-2),(3,-3)和(xO,yO)点是(1、0)即每一行都必须经过这一点。然后,我们必须至少绘制两条线来覆盖所有经过(xO,yO)的点,如下图所示。 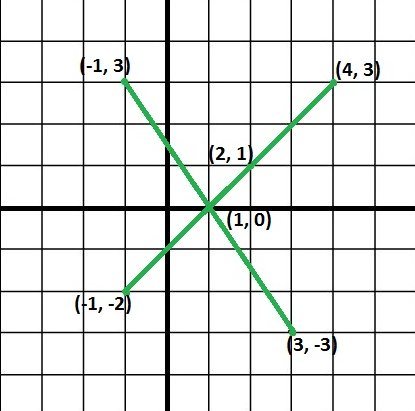
我们可以考虑所有点的斜率(xO,yO)来解决这个问题。如果两个不同的点具有(xO,yO)相同的斜率,则它们只能用同一条线覆盖,因此我们可以跟踪每个点的斜率,并且每当获得新的斜率时,我们的行数就会增加一。
在下面的代码中,斜率存储为一对整数,以消除精度问题,并使用一组跟踪发生的斜率。
请参阅下面的代码,以更好地理解。
CPP
// C++ program to get minimum lines to cover
// all the points
#include
using namespace std;
// Utility method to get gcd of a and b
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
// method returns reduced form of dy/dx as a pair
pair getReducedForm(int dy, int dx)
{
int g = gcd(abs(dy), abs(dx));
// get sign of result
bool sign = (dy < 0) ^ (dx < 0);
if (sign)
return make_pair(-abs(dy) / g, abs(dx) / g);
else
return make_pair(abs(dy) / g, abs(dx) / g);
}
/* method returns minimum number of lines to
cover all points where all lines goes
through (xO, yO) */
int minLinesToCoverPoints(int points[][2], int N,
int xO, int yO)
{
// set to store slope as a pair
set< pair > st;
pair temp;
int minLines = 0;
// loop over all points once
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// get x and y co-ordinate of current point
int curX = points[i][0];
int curY = points[i][1];
temp = getReducedForm(curY - yO, curX - xO);
// if this slope is not there in set,
// increase ans by 1 and insert in set
if (st.find(temp) == st.end())
{
st.insert(temp);
minLines++;
}
}
return minLines;
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
int xO, yO;
xO = 1;
yO = 0;
int points[][2] =
{
{-1, 3},
{4, 3},
{2, 1},
{-1, -2},
{3, -3}
};
int N = sizeof(points) / sizeof(points[0]);
cout << minLinesToCoverPoints(points, N, xO, yO);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to get minimum lines to cover
# all the points
# Utility method to get gcd of a and b
def gcd(a, b):
if (b == 0):
return a
return gcd(b, a % b)
# method returns reduced form of dy/dx as a pair
def getReducedForm(dy, dx):
g = gcd(abs(dy), abs(dx))
# get sign of result
sign = (dy < 0) ^ (dx < 0)
if (sign):
return (-abs(dy) // g, abs(dx) // g)
else:
return (abs(dy) // g, abs(dx) // g)
# /* method returns minimum number of lines to
# cover all points where all lines goes
# through (xO, yO) */
def minLinesToCoverPoints(points, N, xO, yO):
# set to store slope as a pair
st = dict()
minLines = 0
# loop over all points once
for i in range(N):
# get x and y co-ordinate of current point
curX = points[i][0]
curY = points[i][1]
temp = getReducedForm(curY - yO, curX - xO)
# if this slope is not there in set,
# increase ans by 1 and insert in set
if (temp not in st):
st[temp] = 1
minLines += 1
return minLines
# Driver code
xO = 1
yO = 0
points =[[-1, 3],
[4, 3],
[2, 1],
[-1, -2],
[3, -3]]
N = len(points)
print(minLinesToCoverPoints(points, N, xO, yO))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29输出:
2