Python|使用 XlsxWriter 模块在 Excel 工作表中添加图表表
先决条件:在 Excel 工作表上创建和书写
XlsxWriter是一个Python库,使用它可以对 excel 文件执行多种操作,例如创建、写入、算术运算和绘图。让我们看看如何使用实时数据在 Excel 工作表中添加图表并在其上绘制折线图。
图表由至少一系列的一个或多个数据点组成。系列本身由对单元格范围的引用组成。为了在图表表上绘制图表,首先,创建特定图表类型的图表对象(即折线图等)。创建图表对象后,在其中插入数据,最后,将该图表对象添加到图表对象中。
代码:在 Excel 表中添加图表表。
为了创建仅包含图表的工作表,我们使用工作簿对象的add_chartsheet()方法。
# Python3 program for adding a chartsheet
# in an excel sheet using xlsxwriter
# we import xlsxwriter module
import xlsxwriter
# Workbook() takes one, non-optional, argument
# which is the filename that we want to create.
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('chartsheet.xlsx')
# The workbook object is then used to add new
# worksheet via the add_worksheet() method.
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
# create a worksheet that only holds a chart
# using add_chartsheet() method of workbook object.
chartsheet = workbook.add_chartsheet()
# Create a new Format object to formats cells
# in worksheets using add_format() method .
# here we create bold format object
bold = workbook.add_format({'bold': 1})
# Add the worksheet data that the charts will refer to.
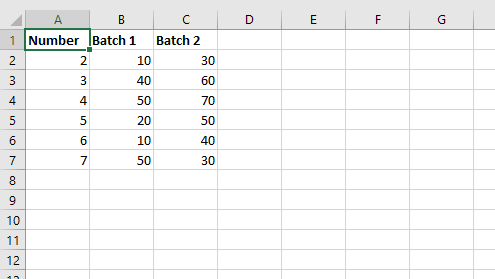
headings = ['Number', 'Batch 1', 'Batch 2']
data = [
[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[10, 40, 50, 20, 10, 50],
[30, 60, 70, 50, 40, 30],
]
# Write a row of data starting from 'A1'
# with bold format .
worksheet.write_row('A1', headings, bold)
# Write a column of data starting from
# 'A2', 'B2', 'C2' respectively .
worksheet.write_column('A2', data[0])
worksheet.write_column('B2', data[1])
worksheet.write_column('C2', data[2])
# Create a chart object that can be added
# to a worksheet using add_chart() method.
# here we create a line chart object .
chart1 = workbook.add_chart({'type': 'line'})
# Add a data series to a chart
# using add_series method.
# Configure the first series.
# = Sheet1 !$A$1 is equivalent to ['Sheet1', 0, 0].
# note : spaces is not inserted in b / w
# = and Sheet1, Sheet1 and !
# if space is inserted it throws warning.
chart1.add_series({
'name': '= Sheet1 !$B$1',
'categories': '= Sheet1 !$A$2:$A$7',
'values': '= Sheet1 !$B$2:$B$7',})
# Configure a second series.
# Note use of alternative syntax to define ranges.
# [sheetname, first_row, first_col, last_row, last_col].
chart1.add_series({
'name': ['Sheet1', 0, 2],
'categories': ['Sheet1', 1, 0, 6, 0],
'values': ['Sheet1', 1, 2, 6, 2],})
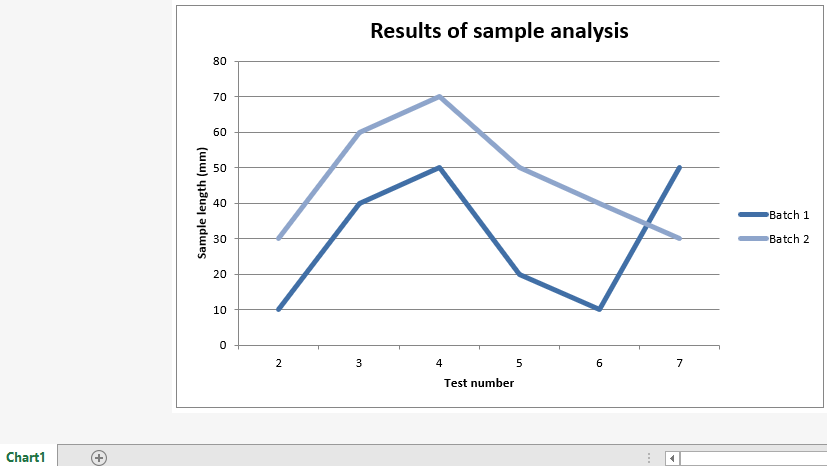
# Add a chart title
chart1.set_title ({'name': 'Results of sample analysis'})
# Add x-axis label
chart1.set_x_axis({'name': 'Test number'})
# Add y-axis label
chart1.set_y_axis({'name': 'Sample length (mm)'})
# Set an Excel chart style.
chart1.set_style(11)
# Add the chart to the chartsheet.
chartsheet.set_chart(chart1)
# Display the chartsheet as the
# active sheet when the workbook is opened.
chartsheet.activate();
# Finally, close the Excel file
# via the close() method.
workbook.close()
输出 :