给定两个数字x和n,找到x的第n个根。
例子:
Input : 5 2
Output : 2.2360679768025875
Input : x = 5, n = 3
Output : 1.70997594668
为了计算数字的第n个根,我们可以使用以下过程。
- 如果x处于[0,1)范围内,则我们将下限值low = x设置为上限值high = 1 ,因为在此数字范围内,第n个根始终大于给定的数字,并且永远不能超过1。
例如-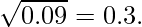
- 否则,我们取low = 1和high = x 。
- 声明一个名为epsilon的变量,并对其进行初始化以实现所需的准确性。
假设epsilon = 0.01,那么我们可以保证对给定数字的第n个根的猜测为
更正最多2个小数位。 - 声明变量guess,并将其初始化为guess =(low + high)/ 2。
- 运行一个循环,以便:
- 如果我们猜测的绝对误差大于epsilon,则执行以下操作:
- 如果猜测n > x ,则high = guesss
- 否则低估
- 做出新的更好的猜测,即guess =(low + high)/ 2。
- 如果我们猜测的绝对误差小于epsilon,则退出循环。
- 如果我们猜测的绝对误差大于epsilon,则执行以下操作:
绝对误差:可以将绝对误差计算为abs(guess n -x)
C++
// C++ Program to find
// n-th real root of x
#include
using namespace std;
void findNthRoot(double x, int n)
{
// Initialize boundary values
double low, high;
if (x >= 0 and x <= 1)
{
low = x;
high = 1;
}
else
{
low = 1;
high = x;
}
// Used for taking approximations
// of the answer
double epsilon = 0.00000001;
// Do binary search
double guess = (low + high) / 2;
while (abs((pow(guess, n)) - x) >= epsilon)
{
if (pow(guess, n) > x)
{
high = guess;
}
else
{
low = guess;
}
guess = (low + high) / 2;
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(16) << guess;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
double x = 5;
int n = 2;
findNthRoot(x, n);
}
// This code is contributed
// by Subhadeep Java
// Java Program to find n-th real root of x
class GFG
{
static void findNthRoot(double x, int n)
{
// Initialize boundary values
double low, high;
if (x >= 0 && x <= 1)
{
low = x;
high = 1;
}
else
{
low = 1;
high = x;
}
// used for taking approximations
// of the answer
double epsilon = 0.00000001;
// Do binary search
double guess = (low + high) / 2;
while (Math.abs((Math.pow(guess, n)) - x)
>= epsilon)
{
if (Math.pow(guess, n) > x)
{
high = guess;
}
else
{
low = guess;
}
guess = (low + high) / 2;
}
System.out.println(guess);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double x = 5;
int n = 2;
findNthRoot(x, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by mitsPython3
# Python Program to find n-th real root
# of x
def findNthRoot(x, n):
# Initialize boundary values
x = float(x)
n = int(n)
if (x >= 0 and x <= 1):
low = x
high = 1
else:
low = 1
high = x
# used for taking approximations
# of the answer
epsilon = 0.00000001
# Do binary search
guess = (low + high) / 2
while abs(guess ** n - x) >= epsilon:
if guess ** n > x:
high = guess
else:
low = guess
guess = (low + high) / 2
print(guess)
# Driver code
x = 5
n = 2
findNthRoot(x, n)C#
// C# Program to find n-th real root of x
using System;
public class GFG {
static void findNthRoot(double x, int n)
{
// Initialize boundary values
double low, high;
if (x >= 0 && x <= 1)
{
low = x;
high = 1;
}
else
{
low = 1;
high = x;
}
// used for taking approximations
// of the answer
double epsilon = 0.00000001;
// Do binary search
double guess = (low + high) / 2;
while (Math.Abs((Math.Pow(guess, n)) - x)
>= epsilon)
{
if (Math.Pow(guess, n) > x)
{
high = guess;
}
else
{
low = guess;
}
guess = (low + high) / 2;
}
Console.WriteLine(guess);
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
double x = 5;
int n = 2;
findNthRoot(x, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by akt_mit输出
2.2360679768025875epsilon = 0.01的第一个示例的说明
由于在程序中采用太小的epsilon值可能无法解释,因为它将大大增加步骤数,因此为简单起见,我们采用epsilon = 0.01以上过程将按如下方式进行:计算![]() 然后x = 5,低= 1,高=5。以epsilon = 0.01首先猜测:猜测=(1 + 5)/ 2 = 3绝对误差= | 3 2 -5 | = 4>的ε-猜2 = 9> 5(x)的,然后在高=猜- >高= 3第二次猜测:猜测=(1 + 3)/ 2 = 2绝对误差= | 2 2 – 5 | = 1>小量猜2 = 4> 5(x)的后低=猜- >低= 2个第三猜测:猜测=(2 + 3)/ 2 = 2.5绝对误差= | 2.5 2 – 5 | = 1.25> epsilon猜测2 = 6.25> 5(x)然后高=猜测->高= 2.5并继续进行下去,我们将得到
然后x = 5,低= 1,高=5。以epsilon = 0.01首先猜测:猜测=(1 + 5)/ 2 = 3绝对误差= | 3 2 -5 | = 4>的ε-猜2 = 9> 5(x)的,然后在高=猜- >高= 3第二次猜测:猜测=(1 + 3)/ 2 = 2绝对误差= | 2 2 – 5 | = 1>小量猜2 = 4> 5(x)的后低=猜- >低= 2个第三猜测:猜测=(2 + 3)/ 2 = 2.5绝对误差= | 2.5 2 – 5 | = 1.25> epsilon猜测2 = 6.25> 5(x)然后高=猜测->高= 2.5并继续进行下去,我们将得到![]() 更正最多2个小数位,即
更正最多2个小数位,即![]() = 2.23600456我们将忽略小数点后2位的数字,因为它们可能正确或错误。
= 2.23600456我们将忽略小数点后2位的数字,因为它们可能正确或错误。