遍历 N 叉树的方法数
给定一个 n 元树,计算从根顶点开始遍历 n 元(或有向无环图)树的方法数。
假设我们有一个给定的 N 叉树,如下所示。
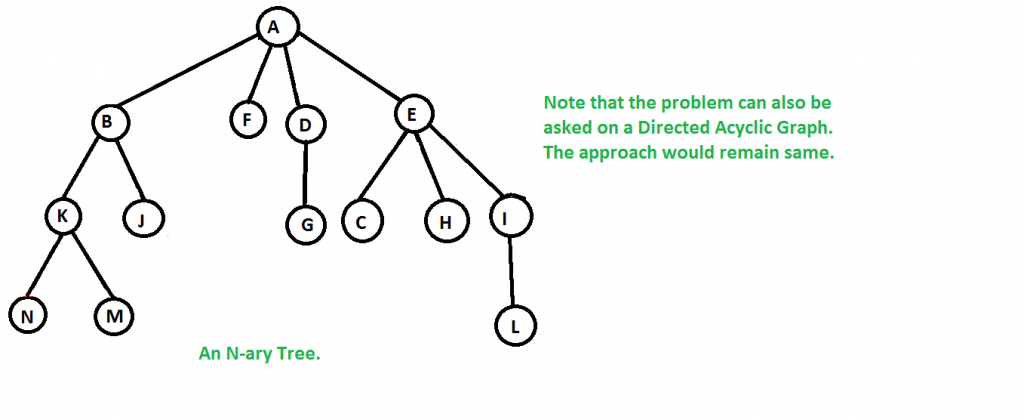
现在我们必须找到从根顶点开始遍历整棵树的方法数。可以有很多这样的方式。下面列出了其中一些。
1) N->M->K->J->B->F->D->E->C->H->I->L->A(一种深度优先遍历)。
2) A->B->F->D->E->K->J->G->C->H->I->N->M->L(层序遍历)
3) …………
4) …………
.
.
.
等等…。
我们强烈建议您最小化您的浏览器并首先自己尝试。
所有遍历方式的计数是每个节点的子节点数的阶乘乘积。请参阅下图以清楚地了解-
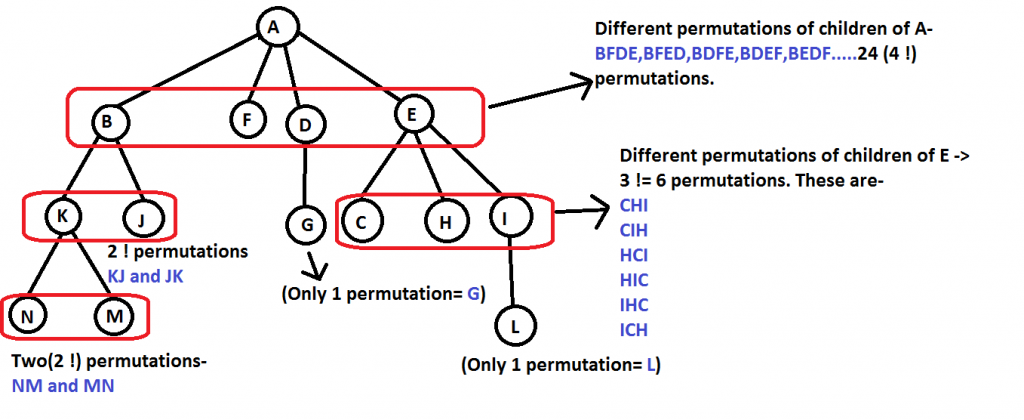
这里,
'A' 有四个孩子,所以 4!可能的排列
'B' 有两个孩子,所以 2!可能的排列
'F' 没有孩子,所以 0!可能的排列
……
等等
因此,所有这些方式都是- 4! * 2! * 0! * 1! * 3! * 2! * 0! * 0! * 0! * 0! * 1! * 0! * 0! = 576 路
那是大量的方式,其中只有少数被证明是有用的,比如-inorder,level-order,preorder,postorder(根据这些遍历的流行度排列)
C++
// C++ program to find the number of ways to traverse a
// n-ary tree starting from the root node
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node of an n-ary tree
struct Node
{
char key;
vector child;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node *newNode(int key)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
// Untility Function to find factorial of given number
int factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
// Function to calculate the number of ways of traversing
// the n-ary starting from root.
// This function is just a modified breadth-first search.
// We can use a depth-first search too.
int calculateWays(Node * root)
{
int ways = 1; // Initialize result
// If the tree is empty there is no way of traversing
// the tree.
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Create a queue and enqueue root to it.
queueq;
q.push(root);
// Level order traversal.
while (!q.empty())
{
// Dequeue an item from queue and print it
Node * p = q.front();
q.pop();
// The number of ways is the product of
// factorials of number of children of each node.
ways = ways*(factorial(p->child.size()));
// Enqueue all childrent of the dequeued item
for (int i=0; ichild.size(); i++)
q.push(p->child[i]);
}
return(ways);
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
/* Let us create below tree
* A
* / / \ \
* B F D E
* / \ | /|\
* K J G C H I
* /\ \
* N M L
*/
Node *root = newNode('A');
(root->child).push_back(newNode('B'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('F'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('D'));
(root->child).push_back(newNode('E'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('K'));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('J'));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('G'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('C'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('H'));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode('I'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('N'));
(root->child[0]->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode('M'));
(root->child[3]->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode('L'));
cout << calculateWays(root); ;
return 0;
} Javascript
输出:
576时间复杂度:我们在级别顺序遍历期间访问每个节点一次,并花费 O(n) 时间来计算每个节点的阶乘。总时间为 O(Nn),其中 N = n 叉树中的节点数。我们可以通过计算从 1 到 n 的所有数字的阶乘来优化解决方案以在 O(N) 时间内工作。
辅助空间:由于我们只为每个节点使用一个队列和一个结构,所以整体空间复杂度也是 O(N)。
常见陷阱:由于阶乘的乘积往往会变得非常巨大,因此可能会溢出。最好在 C/C++ 中使用 unsigned long long int 等数据类型,因为路数永远不能是负数。在Java和Python中有 Big Integer 来处理溢出问题。