找到给定链表的中间
给定一个单向链表,找到链表的中间部分。例如,如果给定的链表是 1->2->3->4->5,那么输出应该是 3。
如果有偶数个节点,那么就会有两个中间节点,我们需要打印第二个中间元素。例如,如果给定的链表是 1->2->3->4->5->6,那么输出应该是 4。
方法一:
遍历整个链表并计算编号。的节点。现在再次遍历列表直到 count/2 并返回 count/2 处的节点。
方法二:
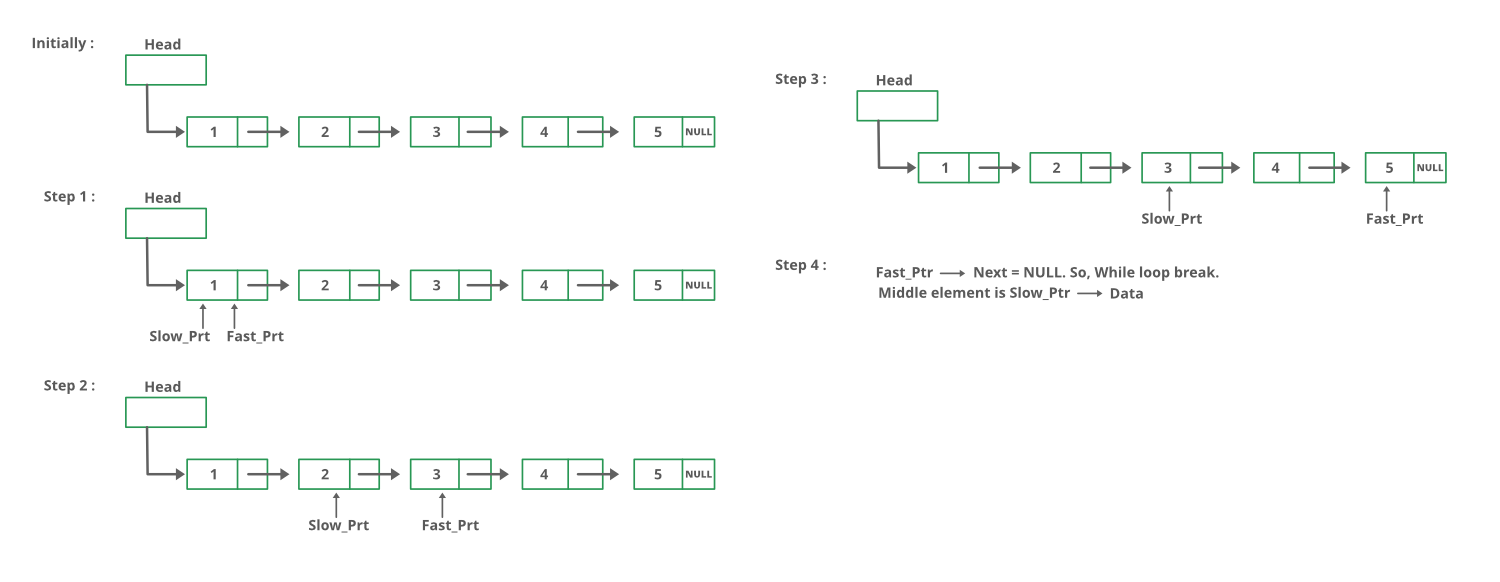
使用两个指针遍历链表。一个指针一个一个地移动,另一个指针两个一个地移动。当快指针到达末尾时,慢指针会到达链表的中间。
下图显示了 printMiddle函数在代码中的工作方式:
Java
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class NodeOperation{
public:
// Function to add a new node
void pushNode(class Node** head_ref,int data_val){
// Allocate node
class Node *new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node->data = data_val;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = *head_ref;
// move the head to point to the new node
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a given linked list
void printNode(class Node *head){
while(head != NULL){
cout <data << "->";
head = head->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
}
void printMiddle(class Node *head){
struct Node *slow_ptr = head;
struct Node *fast_ptr = head;
if (head!=NULL)
{
while (fast_ptr != NULL && fast_ptr->next != NULL)
{
fast_ptr = fast_ptr->next->next;
slow_ptr = slow_ptr->next;
}
cout << "The middle element is [" << slow_ptr->data << "]" << endl;
}
}
};
// Driver Code
int main(){
class Node *head = NULL;
class NodeOperation *temp = new NodeOperation();
for(int i=5; i>0; i--){
temp->pushNode(&head, i);
temp->printNode(head);
temp->printMiddle(head);
}
return 0;
} C
// C program to find middle of linked list
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to get the middle of the linked list*/
void printMiddle(struct Node *head)
{
struct Node *slow_ptr = head;
struct Node *fast_ptr = head;
if (head!=NULL)
{
while (fast_ptr != NULL && fast_ptr->next != NULL)
{
fast_ptr = fast_ptr->next->next;
slow_ptr = slow_ptr->next;
}
printf("The middle element is [%d]\n\n", slow_ptr->data);
}
}
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a given linked list
void printList(struct Node *ptr)
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
int i;
for (i=5; i>0; i--)
{
push(&head, i);
printList(head);
printMiddle(head);
}
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find middle of linked list
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of linked list
/* Linked list node */
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to print middle of linked list */
void printMiddle()
{
Node slow_ptr = head;
Node fast_ptr = head;
while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null)
{
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next;
slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("The middle element is [" +
slow_ptr.data + "] \n");
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/* This function prints contents of linked list
starting from the given node */
public void printList()
{
Node tnode = head;
while (tnode != null)
{
System.out.print(tnode.data+"->");
tnode = tnode.next;
}
System.out.println("NULL");
}
public static void main(String [] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
for (int i=5; i>0; --i)
{
llist.push(i);
llist.printList();
llist.printMiddle();
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajat MishraC#
// C# program to find middle of linked list
using System;
class LinkedList{
// Head of linked list
Node head;
// Linked list node
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// Function to print middle of linked list
void printMiddle()
{
Node slow_ptr = head;
Node fast_ptr = head;
if (head != null)
{
while (fast_ptr != null &&
fast_ptr.next != null)
{
fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next;
slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("The middle element is [" +
slow_ptr.data + "] \n");
}
}
// Inserts a new Node at front of the list.
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// This function prints contents of linked
// list starting from the given node
public void printList()
{
Node tnode = head;
while (tnode != null)
{
Console.Write(tnode.data + "->");
tnode = tnode.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("NULL");
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
for(int i = 5; i > 0; --i)
{
llist.push(i);
llist.printList();
llist.printMiddle();
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.Python3
# Python3 program to find middle of linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialise the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # Assign data
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Linked List class contains a Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Print the linked list
def printList(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(str(node.data) + "->", end="")
node = node.next
print("NULL")
# Function that returns middle.
def printMiddle(self):
# Initialize two pointers, one will go one step a time (slow), another two at a time (fast)
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
# Iterate till fast's next is null (fast reaches end)
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# return the slow's data, which would be the middle element.
print("The middle element is ", slow.data)
# Code execution starts here
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
llist = LinkedList()
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
llist.push(i)
llist.printList()
llist.printMiddle()
# Code is contributed by Kumar Shivam (kshivi99)Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Link list node
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* next;
};
// Function to get the middle of
// the linked list
void printMiddle(struct node* head)
{
int count = 0;
struct node* mid = head;
while (head != NULL)
{
// Update mid, when 'count'
// is odd number
if (count & 1)
mid = mid->next;
++count;
head = head->next;
}
// If empty list is provided
if (mid != NULL)
printf("The middle element is [%d]\n\n",
mid->data);
}
void push(struct node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct node* new_node = (struct node*)malloc(
sizeof(struct node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print
// a given linked list
void printList(struct node* ptr)
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct node* head = NULL;
int i;
for(i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
push(&head, i);
printList(head);
printMiddle(head);
}
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by ac121102 C
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
};
/* Function to get the middle of the linked list*/
void printMiddle(struct node* head)
{
int count = 0;
struct node* mid = head;
while (head != NULL) {
/* update mid, when 'count' is odd number */
if (count & 1)
mid = mid->next;
++count;
head = head->next;
}
/* if empty list is provided */
if (mid != NULL)
printf("The middle element is [%d]\n\n", mid->data);
}
void push(struct node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct node* new_node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a given linked list
void printList(struct node* ptr)
{
while (ptr != NULL) {
printf("%d->", ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct node* head = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
push(&head, i);
printList(head);
printMiddle(head);
}
return 0;
} Java
class GFG{
static Node head;
// Link list node
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
public Node(Node next, int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
// Function to get the middle of
// the linked list
void printMiddle(Node head)
{
int count = 0;
Node mid = head;
while (head != null)
{
// Update mid, when 'count'
// is odd number
if ((count % 2) == 1)
mid = mid.next;
++count;
head = head.next;
}
// If empty list is provided
if (mid != null)
System.out.println("The middle element is [" +
mid.data + "]\n");
}
void push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(head_ref, new_data);
// Move the head to point to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a
// given linked list
void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.data + "-> ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG ll = new GFG();
for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
ll.push(head, i);
ll.printList(head);
ll.printMiddle(head);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by mark_3Python3
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialise the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # Assign data
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Linked List class contains a Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Print the linked list
def printList(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(str(node.data) + "->", end = "")
node = node.next
print("NULL")
# Function to get the middle of
# the linked list
def printMiddle(self):
count = 0
mid = self.head
heads = self.head
while(heads != None):
# Update mid, when 'count'
# is odd number
if count&1:
mid = mid.next
count += 1
heads = heads.next
# If empty list is provided
if mid!=None:
print("The middle element is ", mid.data)
# Code execution starts here
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
llist = LinkedList()
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
llist.push(i)
llist.printList()
llist.printMiddle()
# This Code is contributed by Manisha_EdigaC#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static Node head;
// Link list node
public
class Node {
public
int data;
public
Node next;
// Constructor
public Node(Node next, int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
// Function to get the middle of
// the linked list
void printMiddle(Node head) {
int count = 0;
Node mid = head;
while (head != null) {
// Update mid, when 'count'
// is odd number
if ((count % 2) == 1)
mid = mid.next;
++count;
head = head.next;
}
// If empty list is provided
if (mid != null)
Console.WriteLine("The middle element is [" + mid.data + "]\n");
}
public void Push(Node head_ref, int new_data) {
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(head_ref, new_data);
// Move the head to point to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a
// given linked list
void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
Console.Write(head.data + "-> ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("null");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
GFG ll = new GFG();
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
ll.Push(head, i);
ll.printList(head);
ll.printMiddle(head);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
输出
5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
4->5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [3]方法三:
将 mid 元素初始化为 head 并将计数器初始化为 0。从 head 开始遍历列表,遍历时递增计数器并在计数器为奇数时将 mid 更改为 mid->next。所以 mid 只会移动列表总长度的一半。
感谢 Narendra Kangralkar 提出这种方法。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
// Link list node
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* next;
};
// Function to get the middle of
// the linked list
void printMiddle(struct node* head)
{
int count = 0;
struct node* mid = head;
while (head != NULL)
{
// Update mid, when 'count'
// is odd number
if (count & 1)
mid = mid->next;
++count;
head = head->next;
}
// If empty list is provided
if (mid != NULL)
printf("The middle element is [%d]\n\n",
mid->data);
}
void push(struct node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct node* new_node = (struct node*)malloc(
sizeof(struct node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print
// a given linked list
void printList(struct node* ptr)
{
while (ptr != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct node* head = NULL;
int i;
for(i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
push(&head, i);
printList(head);
printMiddle(head);
}
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by ac121102
C
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
};
/* Function to get the middle of the linked list*/
void printMiddle(struct node* head)
{
int count = 0;
struct node* mid = head;
while (head != NULL) {
/* update mid, when 'count' is odd number */
if (count & 1)
mid = mid->next;
++count;
head = head->next;
}
/* if empty list is provided */
if (mid != NULL)
printf("The middle element is [%d]\n\n", mid->data);
}
void push(struct node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct node* new_node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a given linked list
void printList(struct node* ptr)
{
while (ptr != NULL) {
printf("%d->", ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct node* head = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
push(&head, i);
printList(head);
printMiddle(head);
}
return 0;
}
Java
class GFG{
static Node head;
// Link list node
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor
public Node(Node next, int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
// Function to get the middle of
// the linked list
void printMiddle(Node head)
{
int count = 0;
Node mid = head;
while (head != null)
{
// Update mid, when 'count'
// is odd number
if ((count % 2) == 1)
mid = mid.next;
++count;
head = head.next;
}
// If empty list is provided
if (mid != null)
System.out.println("The middle element is [" +
mid.data + "]\n");
}
void push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(head_ref, new_data);
// Move the head to point to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a
// given linked list
void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.data + "-> ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GFG ll = new GFG();
for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
ll.push(head, i);
ll.printList(head);
ll.printMiddle(head);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by mark_3
蟒蛇3
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialise the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data # Assign data
self.next = None # Initialize next as null
# Linked List class contains a Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Print the linked list
def printList(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(str(node.data) + "->", end = "")
node = node.next
print("NULL")
# Function to get the middle of
# the linked list
def printMiddle(self):
count = 0
mid = self.head
heads = self.head
while(heads != None):
# Update mid, when 'count'
# is odd number
if count&1:
mid = mid.next
count += 1
heads = heads.next
# If empty list is provided
if mid!=None:
print("The middle element is ", mid.data)
# Code execution starts here
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
llist = LinkedList()
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
llist.push(i)
llist.printList()
llist.printMiddle()
# This Code is contributed by Manisha_Ediga
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static Node head;
// Link list node
public
class Node {
public
int data;
public
Node next;
// Constructor
public Node(Node next, int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
// Function to get the middle of
// the linked list
void printMiddle(Node head) {
int count = 0;
Node mid = head;
while (head != null) {
// Update mid, when 'count'
// is odd number
if ((count % 2) == 1)
mid = mid.next;
++count;
head = head.next;
}
// If empty list is provided
if (mid != null)
Console.WriteLine("The middle element is [" + mid.data + "]\n");
}
public void Push(Node head_ref, int new_data) {
// Allocate node
Node new_node = new Node(head_ref, new_data);
// Move the head to point to the new node
head = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print a
// given linked list
void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
Console.Write(head.data + "-> ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine("null");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
GFG ll = new GFG();
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--) {
ll.Push(head, i);
ll.printList(head);
ll.printMiddle(head);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
输出
5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
4->5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [3]如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。