用于查找给定链表的中间元素的Python程序
给定一个单链表,找到链表的中间。例如,如果给定的链表是 1->2->3->4->5,那么输出应该是 3。
如果有偶数节点,那么就会有两个中间节点,我们需要打印第二个中间元素。例如,如果给定的链表是 1->2->3->4->5->6,那么输出应该是 4。
方法一:
遍历整个链表并计算编号。的节点。现在再次遍历列表直到 count/2 并返回 count/2 处的节点。
方法二:
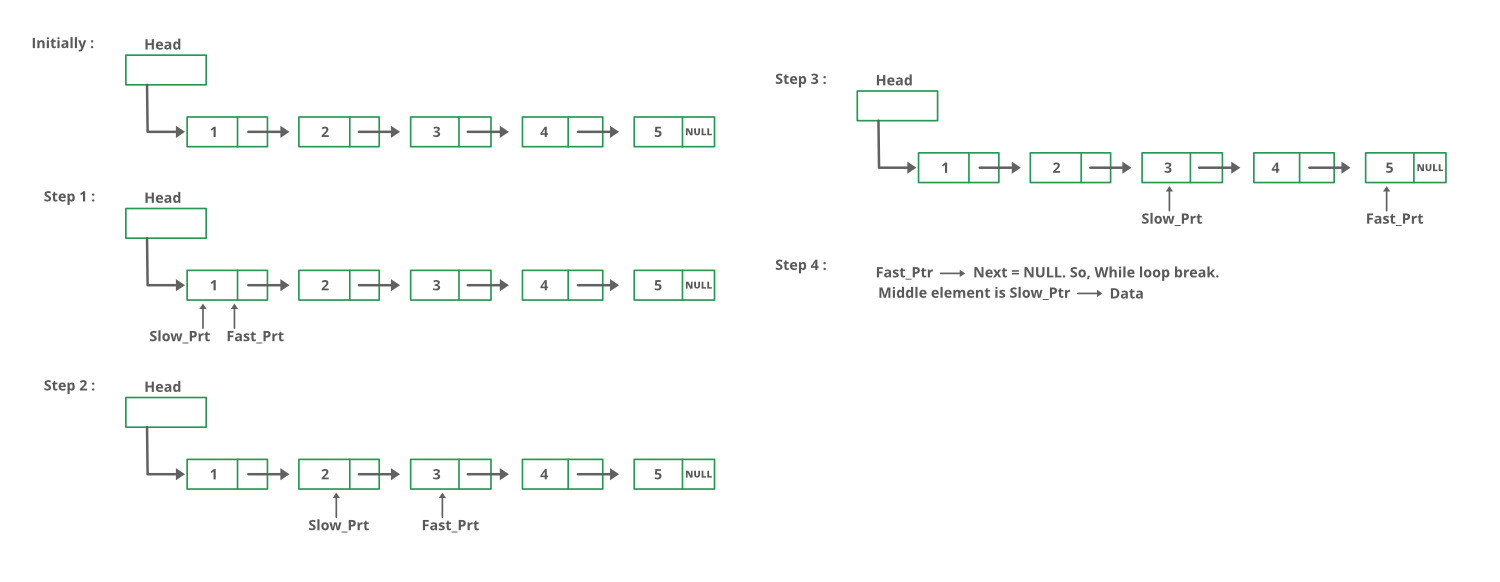
使用两个指针遍历链表。将一个指针移动一格,将其他指针移动二格。当快指针到达末尾时,慢指针将到达链表的中间。
下图显示了 printMiddle函数在代码中的工作方式:
Python3
# Python3 program to find middle of
# the linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialise the
# node object
def __init__(self, data):
# Assign data
self.data = data
# Initialize next as null
self.next = None
# Linked List class contains a
# Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at
# the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Print the linked list
def printList(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(str(node.data) +
"->", end = "")
node = node.next
print("NULL")
# Function that returns middle.
def printMiddle(self):
# Initialize two pointers, one will go
# one step a time (slow), another two
# at a time (fast)
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
# Iterate till fast's next is null (fast
# reaches end)
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Return the slow's data, which would be
# the middle element.
print("The middle element is ", slow.data)
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
llist = LinkedList()
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
llist.push(i)
llist.printList()
llist.printMiddle()
# This code is contributed by Kumar Shivam (kshivi99)Python3
# Python program to implement
# the above approach
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialise the
# node object
def __init__(self, data):
# Assign data
self.data = data
# Initialize next as null
self.next = None
# Linked List class contains a
# Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at
# the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Print the linked list
def printList(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(str(node.data) +
"->", end = "")
node = node.next
print("NULL")
# Function to get the middle of
# the linked list
def printMiddle(self):
count = 0
mid = self.head
heads = self.head
while(heads != None):
# Update mid, when 'count'
# is odd number
if count & 1:
mid = mid.next
count += 1
heads = heads.next
# If empty list is provided
if mid != None:
print("The middle element is ",
mid.data)
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
llist = LinkedList()
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
llist.push(i)
llist.printList()
llist.printMiddle()
# This code is contributed by Manisha_Ediga输出:
5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
4->5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [3]方法三:
将 mid 元素初始化为 head 并将计数器初始化为 0。从 head 遍历列表,同时遍历递增计数器并在计数器为奇数时将 mid 更改为 mid->next。所以中间只会移动列表总长度的一半。
感谢 Narendra Kangralkar 提出这种方法。
Python3
# Python program to implement
# the above approach
# Node class
class Node:
# Function to initialise the
# node object
def __init__(self, data):
# Assign data
self.data = data
# Initialize next as null
self.next = None
# Linked List class contains a
# Node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new node at
# the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Print the linked list
def printList(self):
node = self.head
while node:
print(str(node.data) +
"->", end = "")
node = node.next
print("NULL")
# Function to get the middle of
# the linked list
def printMiddle(self):
count = 0
mid = self.head
heads = self.head
while(heads != None):
# Update mid, when 'count'
# is odd number
if count & 1:
mid = mid.next
count += 1
heads = heads.next
# If empty list is provided
if mid != None:
print("The middle element is ",
mid.data)
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
# Start with the empty list
llist = LinkedList()
for i in range(5, 0, -1):
llist.push(i)
llist.printList()
llist.printMiddle()
# This code is contributed by Manisha_Ediga
输出:
5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
4->5->NULL
The middle element is [5]
3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [4]
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
The middle element is [3]有关详细信息,请参阅有关查找给定链接列表的中间的完整文章!