加权总和法是一种多准则决策方法,其中会有多种选择,我们必须根据多种标准来确定最佳选择。还有其他可用的方法,包括加权乘积法(WPM),与理想解决方案相似的偏好排序技术(TOPSIS),VIKOR,MOORA,GTMA等。让我们了解一下加权求和法与示例结合使用的方法。
考虑一种情况,我们必须在面试的5名候选人中选择最佳候选人。表1包含5名学生的详细信息,其中包括他们的CGPA,他们每月期望的薪水,他们在技术考试中的分数以及他们在能力测验中达到的分数。
表1:样本数据集
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Student 1 | 9 | 12000 | 72 | B1 |
| Student 2 | 7.6 | 8500 | 68 | B1 |
| Student 3 | 8.2 | 9500 | 63 | B2 |
| Student 4 | 8.5 | 10000 | 70 | A2 |
| Student 5 | 9.3 | 14000 | 72 | A2 |
考虑面试小组假设的权重,如下所示:
CGPA = 30%,预期津贴= 20%,技术考试分数= 25%,Aptitute测试成绩= 25%
表2:每个属性的权重
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 9 | 12000 | 72 | B1 |
| Student 2 | 7.6 | 8500 | 68 | B1 |
| Student 3 | 8.2 | 9500 | 63 | B2 |
| Student 4 | 8.5 | 10000 | 70 | A2 |
| Student 5 | 9.3 | 14000 | 72 | A2 |
有益属性是人们渴望获得最大价值的属性。在这里,CGPA,技术考试分数和能力测验分数是有益的属性,因为公司希望学生拥有更多这些属性。
非有益属性是其中需要最小值的属性。在这种情况下,预期的津贴是非受益属性。公司鼓励愿意以低薪工作的人们。
现在,让我们使用加权总和法查看公司要选择哪个学生。
为此,我们必须将表2中的值标准化。
- 对于有益的属性,
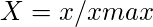
- 对于非受益属性,
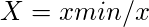
表3:确定有益属性的最大值和非有益属性的最小值
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 9 | 12000 | 72(max) | B1 |
| Student 2 | 7.6 | 8500(min) | 68 | B1 |
| Student 3 | 8.2 | 9500 | 63 | B2 |
| Student 4 | 8.5 | 10000 | 70 | A2(max) |
| Student 5 | 9.3(max) | 14000 | 72 | A2 |
我们将对成绩系统考虑以下几点
A1 – 5
A2 – 4
B1 – 3
B2 – 2
C1 – 1
表4:更新能力测验成绩
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 9 | 12000 | 72(max) | 3 |
| Student 2 | 7.6 | 8500(min) | 68 | 3 |
| Student 3 | 8.2 | 9500 | 63 | 2 |
| Student 4 | 8.5 | 10000 | 70 | 4(max) |
| Student 5 | 9.3(max) | 14000 | 72 | 4 |
根据受益和非受益属性对各个属性的值进行归一化。
表5:归一化
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 9/9.3 | 8500/12000 | 72/72 | 3/4 |
| Student 2 | 7.6/9.3 | 8500/8500 | 68/72 | 3/4 |
| Student 3 | 8.2/9.3 | 8500/9500 | 63/72 | 2/4 |
| Student 4 | 8.5/9.3 | 8500/10000 | 70/72 | 4/4 |
| Student 5 | 9.3/9.3 | 8500/14000 | 72/72 | 4/4 |
表6:权重归一化决策矩阵
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 0.9677 | 0.7083 | 1 | 0.75 |
| Student 2 | 0.8172 | 1 | 0.9444 | 0.75 |
| Student 3 | 0.8817 | 0.8947 | 0.875 | 0.5 |
| Student 4 | 0.9134 | 0.85 | 0.9722 | 1 |
| Student 5 | 1 | 0.6071 | 1 | 1 |
表7:将每个参数与各自的权重相乘
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 0.9677 × 0.3 | 0.7083 × 0.2 | 1 × 0.25 | 0.75 × 0.25 |
| Student 2 | 0.8172 × 0.3 | 1 × 0.2 | 0.9444 × 0.25 | 0.75 × 0.25 |
| Student 3 | 0.8817 × 0.3 | 0.8947 × 0.2 | 0.875 × 0.25 | 0.5 × 0.25 |
| Student 4 | 0.9134 × 0.3 | 0.85 × 0.2 | 0.9722 × 0.25 | 1 × 0.25 |
| Student 5 | 1 × 0.3 | 0.6071 × 0.2 | 1 × 0.25 | 1 × 0.25 |
上表简化如下
表8:表7的简化版本
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Student 1 | 0.29031 | 0.14166 | 0.25 | 0.1875 |
| Student 2 | 0.24516 | 0.2 | 0.2361 | 0.1875 |
| Student 3 | 0.26451 | 0.17894 | 0.21875 | 0.125 |
| Student 4 | 0.27402 | 0.17 | 0.24305 | 0.25 |
| Student 5 | 0.3 | 0.12142 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
我们必须在每一行中添加组成部分,并计算加权总和,即绩效得分,并将优先级给予学生
表9:按成绩得分计算学生的等级
| Attribute | CGPA | Expected Stipend | Technical Exam Score | Aptitude Test Grade | Performance Score | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 | ||
| Student 1 | 0.29031 | 0.14166 | 0.25 | 0.1875 | 0.86947 | 3 |
| Student 2 | 0.24516 | 0.2 | 0.2361 | 0.1875 | 0.86876 | 4 |
| Student 3 | 0.26451 | 0.17894 | 0.21875 | 0.125 | 0.7872 | 5 |
| Student 4 | 0.27402 | 0.17 | 0.24305 | 0.25 | 0.93707 | 1 |
| Student 5 | 0.3 | 0.12142 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.92142 | 2 |
结论:从加权和方法中,可以确定学生4是其中的最佳选择。